|
Johann Heinrich Ziegler
Johann Heinrich Ziegler (6 December 1857 in Winterthur – 30 January 1936 in Zurich) was a Swiss dye chemist and natural philosopher. Life Johann Heinrich Ziegler was born as the son of the manufacturer Emil Ziegler. He studied chemistry and received his doctorate in 1883 in Erlangen, with his dissertation ''Ueber Derivate des Beta-Naphthylamins'' (''on derivatives of beta-naphthylamine''), under the later Nobel Prize winner Emil Fischer. (retrieved via de Gruyter Online). In 1884, Ziegler developed the yellow azo dye tartrazine in the laboratories of the Bindschedler'sche Fabrik fürchemische Industrie in Basel ( CIBA). This was patented and produced in Germany by BASF in 1885 (DRP 34294). The process was first presented in 1887 in '' Chemische Berichte'', the journal of the German Chemical Society. Although the structure proposed by Ziegler was not confirmed, he was able to develop an alternative synthesis of tartrazine based on the idea that a hydrazone is the tautom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winterthur
, neighboring_municipalities = Brütten, Dinhard, Elsau, Hettlingen, Illnau-Effretikon, Kyburg, Lindau, Neftenbach, Oberembrach, Pfungen, Rickenbach, Schlatt, Seuzach, Wiesendangen, Zell , twintowns = Hall in Tirol (Austria), La Chaux-de-Fonds (Switzerland), Pilsen (Czech Republic), Yverdon-les-Bains (Switzerland) , website = stadt.winterthur.ch Winterthur (; french: Winterthour, lang) is a city in the canton of Zürich in northern Switzerland. With over 110,000 residents it is the country's sixth-largest city by population, and is the ninth-largest agglomeration with about 140,000 inhabitants. Located about northeast of Zürich, Winterthur is a service and high-tech industrial satellite city within Greater Zürich. The official language of Winterthur is German,The official language in any municipality in German-speaking Switzerland is always German. In this context, the term 'German' is used as an umbrella term for any variety of German. So, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lightfast
Lightfastness is a property of a colourant such as dye or pigment that describes its resistance to fading when exposed to light. Dyes and pigments are used for example for dyeing of fabrics, plastics or other materials and manufacturing paints or printing inks. The bleaching of the color is caused by the impact of ultraviolet radiation in the chemical structure of the molecules giving the color of the subject. The part of a molecule responsible for its color is called the chromophore. Light encountering a painted surface can either alter or break the chemical bonds of the pigment, causing the colors to bleach or change in a process known as photodegradation. Materials that resist this effect are said to be lightfast. The electromagnetic spectrum of the sun contains wavelengths from gamma waves to radio waves. The high energy of ultraviolet radiation in particular accelerates the fading of the dye. The photon energy of UVA-radiation which is not absorbed by atmospheric ozone exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1936 Deaths
Events January–February * January 20 – George V of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions and Emperor of India, dies at his Sandringham Estate. The Prince of Wales succeeds to the throne of the United Kingdom as King Edward VIII. * January 28 – Britain's King George V state funeral takes place in London and Windsor. He is buried at St George's Chapel, Windsor Castle * February 4 – Radium E (bismuth-210) becomes the first radioactive element to be made synthetically. * February 6 – The IV Olympic Winter Games open in Garmisch-Partenkirchen, Germany. * February 10– 19 – Second Italo-Ethiopian War: Battle of Amba Aradam – Italian forces gain a decisive tactical victory, effectively neutralizing the army of the Ethiopian Empire. * February 16 – 1936 Spanish general election: The left-wing Popular Front coalition takes a majority. * February 26 – February 26 Incident (二・二六事件, ''Niniroku Jiken''): The I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1857 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – The biggest Estonian newspaper, ''Postimees'', is established by Johann Voldemar Jannsen. * January 7 – The partly French-owned London General Omnibus Company begins operating. * January 9 – The 7.9 Fort Tejon earthquake shakes Central and Southern California, with a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (''Violent''). * January 24 – The University of Calcutta is established in Calcutta, as the first multidisciplinary modern university in South Asia. The University of Bombay is also established in Bombay, British India, this year. * February 3 – The National Deaf Mute College (later renamed Gallaudet University) is established in Washington, D.C., becoming the first school for the advanced education of the deaf. * February 5 – The Federal Constitution of the United Mexican States is promulgated. * March – The Austrian garrison leaves Bucharest. * March 3 ** France and the United Kingdom for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naturforschende Gesellschaft In Zürich
''Naturforschende Gesellschaft in Zürich'' (NGZH; Society of Natural Sciences Zurich) is a Swiss scientific society, founded in 1746 for the purposes of promoting the study of the natural sciences. Prior to that it was known as the ''Physikalische Gesellschaft'', originating in the sixteenth century, when Conrad Gessner and his colleagues first established it in Zürich. As such, it is one of the oldest scientific societies in Switzerland. The society states it mission as "Accessing the 'exact knowledge of nature' through meticulous observations and experiments, and to foster public understanding of the natural sciences, fundamental and applied". To this end it organizes free lectures and excursions and awards an annual prize for high school science projects (''NGZH-Jugendpreis''). As of 2016, there were 350 members, and the president was Fritz Gassmann. Within the Swiss Academy of Natural Sciences, the NGZH is a member organisation of the Natural Sciences Platform. The society ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Ostwald
Friedrich Wilhelm Ostwald (; 4 April 1932) was a Baltic German chemist and German philosophy, philosopher. Ostwald is credited with being one of the founders of the field of physical chemistry, with Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff, Walther Nernst, and Svante Arrhenius. He received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1909 for his scientific contributions to the fields of catalysis, chemical equilibria and Reaction velocity, reaction velocities. Following his 1906 retirement from academic life, Ostwald became much involved in philosophy, art, and politics. He made significant contributions to each of these fields. He has been described as a polymath. Early life and education Ostwald was born ethnically Baltic German in Riga, Russian Empire (now Latvia) to cooper (profession), master-cooper Gottfried Wilhelm Ostwald (1824–1903) and Elisabeth Leuckel (1824–1903). He was the middle child of three, born after Eugen (1851–1932) and before Gottfried (1855–1918). Ostwald developed an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
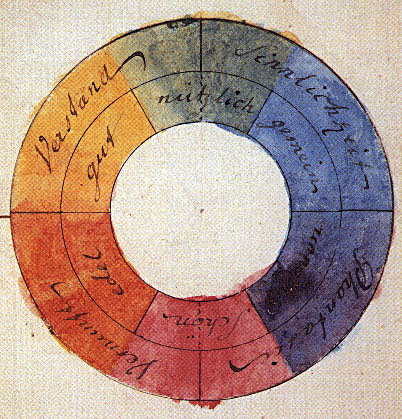
Color Theory
In the visual arts, color theory is the body of practical guidance for color mixing and the visual effects of a specific color combination. Color terminology based on the color wheel and its geometry separates colors into primary color, secondary color, and tertiary color. The understanding of color theory dates to antiquity. Aristotle (d. 322 BCE) and Claudius Ptolemy (d. 168 CE) already discussed which and how colors can be produced by mixing other colors. The influence of light on color was investigated and revealed further by al-Kindi (d. 873) and Ibn al-Haytham (d.1039). Ibn Sina (d. 1037), Nasir al-Din al-Tusi (d. 1274), and Robert Grosseteste (d. 1253) discovered that contrary to the teachings of Aristotle, there are multiple color paths to get from black to white. More modern approaches to color theory principles can be found in the writings of Leone Battista Alberti (c. 1435) and the notebooks of Leonardo da Vinci (c. 1490). A formalization of "color theory" began in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theory Of Relativity
The theory of relativity usually encompasses two interrelated theories by Albert Einstein: special relativity and general relativity, proposed and published in 1905 and 1915, respectively. Special relativity applies to all physical phenomena in the absence of gravity. General relativity explains the law of gravitation and its relation to the forces of nature. It applies to the cosmological and astrophysical realm, including astronomy. The theory transformed theoretical physics and astronomy during the 20th century, superseding a 200-year-old Classical mechanics, theory of mechanics created primarily by Isaac Newton. It introduced concepts including 4-dimensional spacetime as a unified entity of space and time in physics, time, relativity of simultaneity, kinematics, kinematic and gravity, gravitational time dilation, and length contraction. In the field of physics, relativity improved the science of elementary particles and their fundamental interactions, along with ushering in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula , which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius". In 1905, a year sometimes described as his ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plagiarism
Plagiarism is the fraudulent representation of another person's language, thoughts, ideas, or expressions as one's own original work.From the 1995 '' Random House Compact Unabridged Dictionary'': use or close imitation of the language and thoughts of another author and the representation of them as one's own original work qtd. in From the Oxford English Dictionary: The action or practice of taking someone else's work, idea, etc., and passing it off as one's own; literary theft. While precise definitions vary, depending on the institution, such representations are generally considered to violate academic integrity and journalistic ethics as well as social norms of learning, teaching, research, fairness, respect and responsibility in many cultures. It is subject to sanctions such as penalties, suspension, expulsion from school or work, substantial fines and even imprisonment. Plagiarism is typically not in itself a crime, but like counterfeiting, fraud can be punished in a court f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Höngg
Höngg is a quarter in district 10 in Zürich. It was formerly a municipality of its own, having been incorporated into Zürich in 1934. The quarter has a population of 21,186, distributed across an area of 6.98 km². Höngg is renowned for its funfairs, such as the Wümmetfest and the Räbeliechtli Umzug. The Protestant church Alte Kirche Höngg is the main church of Höngg. Sport SV Höngg is the quarter's football team. Werdinsel Werdinsel, also known as Limmatauen Werdhölzli, is an island and protected area in the Limmat The Limmat is a river in Switzerland. The river commences at the outfall of Lake Zurich, in the southern part of the city of Zurich. From Zurich it flows in a northwesterly direction, after 35 km reaching the river Aare. The confluenc ..., to the west of the Europabrücke. Gallery External links A drone flying north over the Reformed church, Meierhofplatz, and looking east down Am Wasser and the Limmat [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Coloring
Food coloring, or color additive, is any dye, pigment, or substance that imparts color when it is added to food or drink. They come in many forms consisting of liquids, powders, gels, and pastes. Food coloring is used in both commercial food production and domestic cooking. Food colorants are also used in a variety of non-food applications, including cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, home craft projects, and medical devices. Purpose of food coloring People associate certain colors with certain flavors, and the color of food can influence the perceived flavor in anything from candy to wine. Sometimes, the aim is to simulate a color that is perceived by the consumer as natural, such as adding red coloring to glacé cherries (which would otherwise be beige), but sometimes it is for effect, like the green ketchup that Heinz launched in 2000. Color additives are used in foods for many reasons including: * To make food more attractive, appealing, appetizing, and informative * Offset c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


