|
Johann Gabriel Doppelmayr
Johann Gabriel Doppelmayr (27 September 1677 – 1 December 1750) was a German mathematician, astronomer, and cartographer. (His surname is also spelled Doppelmayer and Doppelmair.) Professional life and publications He was born in Nuremberg, the son of the merchant Johann Siegmund Doppelmayr. He entered the Aegidien-Gymnasium in Nuremberg in 1689, then the University of Altdorf in 1696. His studies included mathematics, physics, and jurisprudence. Later he continued his studies in HalleRalf Kern. Wissenschaftliche Instrumente in ihrer Zeit. Vol. 3. Cologne, 2010. p. 243. and graduated in 1698 with a dissertation on the Sun. During studying at the University of Halle, he also learned French and Italian. After giving up his legal studies he then spent two years travelling and studying in Germany, Holland, and England, spending time at Utrecht, Leiden, Oxford, and London, during which time he learned to speak French, Italian, and English. He continued to study astronomy and lear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Gabriel Doppelmayr
Johann Gabriel Doppelmayr (27 September 1677 – 1 December 1750) was a German mathematician, astronomer, and cartographer. (His surname is also spelled Doppelmayer and Doppelmair.) Professional life and publications He was born in Nuremberg, the son of the merchant Johann Siegmund Doppelmayr. He entered the Aegidien-Gymnasium in Nuremberg in 1689, then the University of Altdorf in 1696. His studies included mathematics, physics, and jurisprudence. Later he continued his studies in HalleRalf Kern. Wissenschaftliche Instrumente in ihrer Zeit. Vol. 3. Cologne, 2010. p. 243. and graduated in 1698 with a dissertation on the Sun. During studying at the University of Halle, he also learned French and Italian. After giving up his legal studies he then spent two years travelling and studying in Germany, Holland, and England, spending time at Utrecht, Leiden, Oxford, and London, during which time he learned to speak French, Italian, and English. He continued to study astronomy and lear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
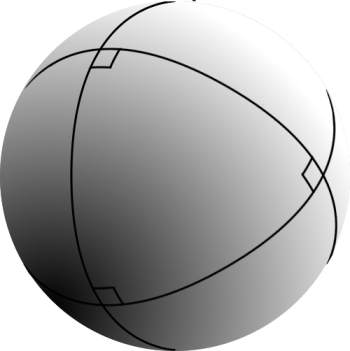
Spherical Trigonometry
Spherical trigonometry is the branch of spherical geometry that deals with the metrical relationships between the sides and angles of spherical triangles, traditionally expressed using trigonometric functions. On the sphere, geodesics are great circles. Spherical trigonometry is of great importance for calculations in astronomy, geodesy, and navigation. The origins of spherical trigonometry in Greek mathematics and the major developments in Islamic mathematics are discussed fully in History of trigonometry and Mathematics in medieval Islam. The subject came to fruition in Early Modern times with important developments by John Napier, Delambre and others, and attained an essentially complete form by the end of the nineteenth century with the publication of Todhunter's textbook ''Spherical trigonometry for the use of colleges and Schools''. Since then, significant developments have been the application of vector methods, quaternion methods, and the use of numerical methods. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1750 Deaths
Year 175 ( CLXXV) was a common year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Piso and Iulianus (or, less frequently, year 928 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 175 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Marcus Aurelius suppresses a revolt of Avidius Cassius, governor of Syria, after the latter proclaims himself emperor. * Avidius Cassius fails in seeking support for his rebellion and is assassinated by Roman officers. They send his head to Aurelius, who persuades the Senate to pardon Cassius's family. * Commodus, son of Marcus Aurelius and his wife Faustina, is named Caesar. * M. Sattonius Iucundus, decurio in Colonia Ulpia Traiana, restores the Thermae of Coriovallum (modern Heerlen) there are sources that state this happen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1677 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – Jean Racine Jean-Baptiste Racine ( , ) (; 22 December 163921 April 1699) was a French dramatist, one of the three great playwrights of 17th-century France, along with Molière and Corneille as well as an important literary figure in the Western traditio ...'s tragedy ''Phèdre'' is first performed, in Paris. * January 21 – The first medical publication in America (a pamphlet on smallpox) is produced in Boston. * February 15 – Four members of the English House of Lords embarrass King Charles II at the opening of the latest session of the "Cavalier Parliament" by proclaiming that the session is not legitimate because it hadn't met in more than a year. The George Villiers, 2nd Duke of Buckingham, Duke of Buckingham, backed by Anthony Ashley Cooper, 1st Earl of Shaftesbury, Lord Shaftesbury, James Cecil, 3rd Earl of Salisbury, Lord Salisbury and Philip Wharton, 4th Baron Wharton, Baron Wharton, makes an unsuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12622 Doppelmayr
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Hieronymus Schröter
Johann Hieronymus Schröter (30 August 1745, Erfurt – 29 August 1816, Lilienthal) was a German astronomer. Life Schröter was born in Erfurt, and studied law at Göttingen University from 1762 until 1767, after which he started a ten-year-long legal practice. In 1777 he was appointed Secretary of the Royal Chamber of George III in Hanover, where he made the acquaintance of two of William Herschel's brothers. In 1779 he acquired a three-foot-long (91 cm, almost one metre) achromatic refractor with lens (50 mm) to observe the Sun, Moon and Venus. Herschel's discovery of Uranus in 1781 inspired Schröter to pursue astronomy more seriously, and he resigned his post and became chief magistrate and district governor of Lilienthal. In 1784 he paid 31 Reichsthaler (about 600 Euros of today) for a Herschel reflector of 122 cm focal length and 12 cm aperture. He quickly gained a good name from his observational reports in journals, but was not satisfied an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each synodic period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doppelmayer (crater)
Doppelmayer is the remains of a lunar impact crater that lies on the southwest edge of Mare Humorum. It was named after the German mathematician and astronomer Johann Gabriel Doppelmayr. To the south-southeast is another flooded crater designated Lee, and to the southeast is Vitello. Just to the east-northeast of Doppelmayer lies the nearly submerged crater Puiseux. The rim of Doppelmayer is nearly round, but is worn and eroded. The most intact section is the southwest half, while in the northeast the rim descends beneath the mare A mare is an adult female horse or other equine. In most cases, a mare is a female horse over the age of three, and a filly is a female horse three and younger. In Thoroughbred horse racing, a mare is defined as a female horse more than four ..., leaving only a slight rise in the surface. The interior has been flooded by lava, leaving a large raised ridge in the center. A small range of hills curves to the west and north from the southern end of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, recognising excellence in science, supporting outstanding science, providing scientific advice for policy, education and public engagement and fostering international and global co-operation. Founded on 28 November 1660, it was granted a royal charter by King Charles II as The Royal Society and is the oldest continuously existing scientific academy in the world. The society is governed by its Council, which is chaired by the Society's President, according to a set of statutes and standing orders. The members of Council and the President are elected from and by its Fellows, the basic members of the society, who are themselves elected by existing Fellows. , there are about 1,700 fellows, allowed to use the postnominal title FRS (Fellow of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecliptic Pole
An orbital pole is either point at the ends of an imaginary line segment that runs through the center of an orbit (of a revolving body like a planet, moon or satellite) and is perpendicular to the orbital plane. Projected onto the celestial sphere, orbital poles are similar in concept to celestial poles, but are based on the body's orbit instead of its equator. The north orbital pole of a revolving body is defined by the right-hand rule. If the fingers of the right hand are curved along the direction of orbital motion, with the thumb extended and oriented to be parallel to the orbital axis, then the direction the thumb points is defined to be the orbital north. The poles of Earth's orbit are referred to as the ecliptic poles. For the remaining planets, the orbital pole in ecliptic coordinates is given by the longitude of the ascending node (☊) and inclination (''i''): ''l'' = ☊ - 90°, ''b'' = 90° - ''i''. In the following table, the planetary orbit poles are given in b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tycho Brahe
Tycho Brahe ( ; born Tyge Ottesen Brahe; generally called Tycho (14 December 154624 October 1601) was a Danish astronomer, known for his comprehensive astronomical observations, generally considered to be the most accurate of his time. He was known during his lifetime as an astronomer, astrologer, and alchemist. He was the last major astronomer before the invention of the telescope. An heir to several noble families, Tycho was well-educated. He took an interest in astronomy and in the creation of more accurate instruments of measurement. He worked to combine what he saw as the geometrical benefits of Copernican heliocentrism with the philosophical benefits of the Ptolemaic system, and devised the Tychonic system, his own version of a model of the universe, with the Sun orbiting the Earth, and the planets as orbiting the Sun. In ''De nova stella'' (1573), he refuted the Aristotelian belief in an unchanging celestial realm. His measurements indicated that "new stars" (''stellae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (; pl, Mikołaj Kopernik; gml, Niklas Koppernigk, german: Nikolaus Kopernikus; 19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon, who formulated a model of the universe that placed the Sun rather than Earth at its center. In all likelihood, Copernicus developed his model independently of Aristarchus of Samos, an ancient Greek astronomer who had formulated such a model some eighteen centuries earlier. The publication of Copernicus's model in his book ' (''On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres''), just before his death in 1543, was a major event in the history of science, triggering the Copernican Revolution and making a pioneering contribution to the Scientific Revolution. Copernicus was born and died in Royal Prussia, a region that had been part of the Kingdom of Poland since 1466. A polyglot and polymath, he obtained a doctorate in canon law and was a mathematician, astro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |