|
Jognakhera
Jognakhera is an archaeological site belonging to late Harappan phase of Indus Valley civilisation. Jogankhera is located in Kurukshetra District, Haryana, India. Period The find from this site belong to the mature Harappan phase as well as later-era PGW phase (Vedic period). The Painted Grey Ware culture (PGW) probably corresponds to the middle and late Vedic period, i.e., the Kuru- Panchala kingdom, the first large state in South Asia after the decline of the Indus Valley civilization (IVC).Geoffrey Samuel, (2010) ''The Origins of Yoga and Tantra: Indic Religions to the Thirteenth Century'', Cambridge University Press, pp. 45–51Michael Witzel (1989), ''Tracing the Vedic dialects'' in ''Dialectes dans les litteratures Indo-Aryennes'' ed. Caillat, Paris, 97–265. Painted Grey Ware culture (PGW) chiefdoms in the region were succeeded by Northern Black Polished Ware (NBPW) from c. 700-500 BCE, associated with the rise of the great mahajanapada states (mahajanapada states Ku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Indus Valley Civilization Sites
Over 1400 Indus Valley civilisation sites have been discovered, of which 925 sites are in India and 475 sites in Pakistan, while some sites in Afghanistan are believed to be trading colonies. Only 40 sites on the Indus valley were discovered in the pre-Partition era by archaeologists in British India, around 1,100 (80%) sites are located on the plains between the rivers Ganges and Indus. The oldest site of Indus Valley Civilization, Bhirrana and the largest site, Rakhigarhi, are located in the Indian state of Haryana. More than 90% of the inscribed objects and seals that were discovered were found at ancient urban centres along the Indus river in Pakistan, mainly Harappa (Punjab) and Mohenjo-daro (Sindh).Upinder Singh, 2008''A History of Ancient and Early Medieval India From the Stone Age to the 12th Century'' p. 169 More than 50 IVC burial sites have been found, main sites among those are Rakhigarhi (first site with genetic testing), Sanauli, Farmana, Kalibangan, Lothal, D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Painted Grey Ware Culture
The Painted Grey Ware culture (PGW) is an Iron Age Indian culture of the western Gangetic plain and the Ghaggar-Hakra valley in the Indian subcontinent, conventionally dated 1200 to 600–500 BCE, or from 1300 to 500–300 BCE It is a successor of the Cemetery H culture and Black and red ware culture (BRW) within this region, and contemporary with the continuation of the BRW culture in the eastern Gangetic plain and Central India. Characterized by a style of fine, grey pottery painted with geometric patterns in black, the PGW culture is associated with village and town settlements, domesticated horses, ivory-working, and the advent of iron metallurgy. , 1,576 PGW sites have been discovered. Although most PGW sites were small farming villages, "several dozen" PGW sites emerged as relatively large settlements that can be characterized as towns; the largest of these were fortified by ditches or moats and embankments made of piled earth with wooden palisades, albeit smaller and sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kunal, Haryana
Kunal is a Periodisation_of_the_Indus_Valley_Civilisation#Early,_Mature_and_Late_Harappan, pre-Harappan Indus Valley civilisation settlement located in Fatehabad district, Fatehabad district of Haryana state in India. Compared to other IVC sites, such as cities like Rakhigarhi and towns like Kalibangan, Kunal site was a village. Excavation at Kunal show 3 successive phases of Pre-Harappan indigenous culture on the Saraswati river who also traded with Kalibanga and Lothal. Kunal, along with its other contemporary sites Bhirrana and Rakhigarhi on Sarasvati River, Sarasvati-Ghaggar-Hakra River, Ghaggar river system, is recognised as the oldest Pre-Harappan settlement, with Kunal being an older cultural ancestor to Rehman Dheri in Pakistan< which is on the Tentative List for future World Heritage Sites. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries Of The World
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, 2 United Nations General Assembly observers#Present non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (2 states, both in associated state, free association with New Zealand). Compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surasena
Kingdom of Surasena (or Sourasena) (Sanskrit: ) was an ancient Indian region corresponding to the present-day Braj region in Uttar Pradesh, with Mathura as its capital city. According to the Buddhist text ''Anguttara Nikaya'', Surasena was one of the ''solasa'' (sixteen) Mahajanapadas (powerful realms) in the 6th century BCE. Also, it is mentioned in the Hindu epic poem, the Ramayana. The ancient Greek writers (e.g., Megasthenes) refer to the Sourasenoi and its cities, Methora and Cleisobra. Sourasenoi is one of the Indian tribes and it's a Greek word by megasthenes named as Shoorsaini in modern Era. Etymology The Etymology of the name is uncertain. Location The Śūrasena state was located on the Yamuna, Yamunā river, and its capital was the city of Mathura, Mathurā. History The Mahabharata and the Puranas refer to the rulers of the Mathura region as the Yadus or Yadavas, divided into a number of septs, which include the Vrishnis. The Buddhist texts refer to Avantiputta, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Inventions And Discoveries Of The Indus Valley Civilization
This list of inventions and discoveries of the Indus Valley Civilisation lists the technological and civilisational achievements of the Indus Valley Civilisation, an ancient civilisation which flourished in the Bronze Age around the general region of the Indus River and Ghaggar-Hakra River in what is today Pakistan, and parts of India. Inventions * Button (clothing), Button, ornamental: Buttons—made from seashell—were used in the Indus Valley Civilisation for ornamental purposes by 2000 BCE.Hesse, Rayner W. & Hesse (Jr.), Rayner W. (2007). ''Jewelry making Through History: An Encyclopedia''. Greenwood Publishing Group. 35. . Some buttons were carved into geometric shapes and had holes pierced into them so that they could be attached to clothing by using a thread. Ian McNeil (1990) holds that: "The button, in fact, was originally used more as an ornament than as a fastening, the earliest known being found at Mohenjo-daro in the Indus Valley. It is made of a curved shell a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
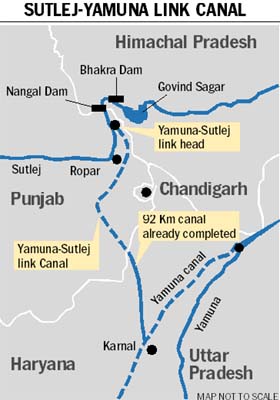
Sutlej Yamuna Link Canal
Satluj Yamuna Link Canal or SYL as it is popularly known, is an under-construction long canal in India to connect the Sutlej and Yamuna rivers. However, the proposal met obstacles and was referred to the Supreme Court of India. It was defined as river water sharing between the states of and . His ...
|
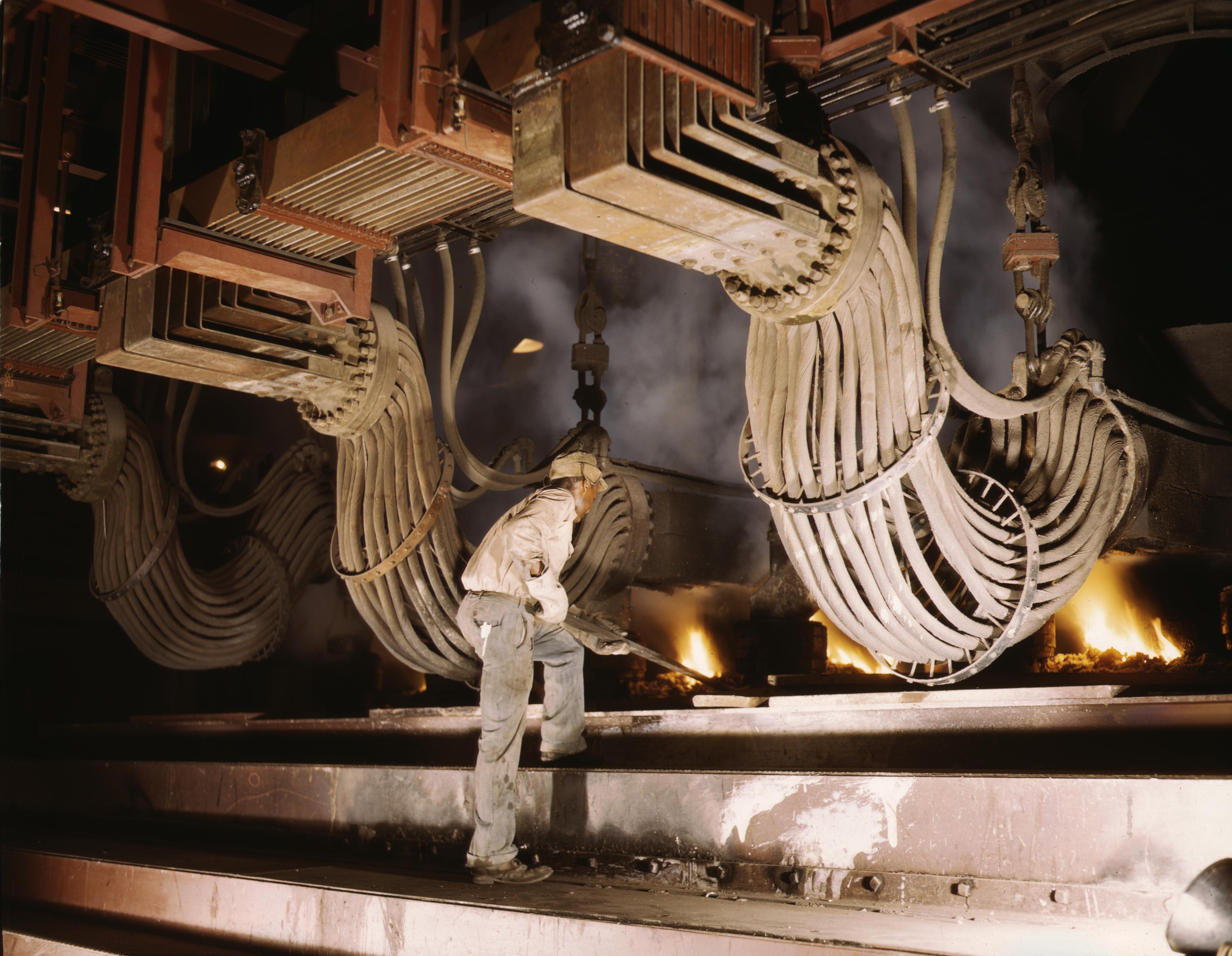
Smelting
Smelting is a process of applying heat to ore, to extract a base metal. It is a form of extractive metallurgy. It is used to extract many metals from their ores, including silver, iron, copper, and other base metals. Smelting uses heat and a chemical reducing agent to decompose the ore, driving off other elements as gases or slag and leaving the metal base behind. The reducing agent is commonly a fossil fuel source of carbon, such as coke—or, in earlier times, charcoal. The oxygen in the ore binds to carbon at high temperatures due to the lower potential energy of the bonds in carbon dioxide (). Smelting most prominently takes place in a blast furnace to produce pig iron, which is converted into steel. The carbon source acts as a chemical reactant to remove oxygen from the ore, yielding the purified metal element as a product. The carbon source is oxidized in two stages. First, the carbon (C) combusts with oxygen (O2) in the air to produce carbon monoxide (CO). Second, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Times Of India
''The Times of India'', also known by its abbreviation ''TOI'', is an Indian English-language daily newspaper and digital news media owned and managed by The Times Group. It is the third-largest newspaper in India by circulation and largest selling English-language daily in the world. It is the oldest English-language newspaper in India, and the second-oldest Indian newspaper still in circulation, with its first edition published in 1838. It is nicknamed as "The Old Lady of Bori Bunder", and is an Indian " newspaper of record". Near the beginning of the 20th century, Lord Curzon, the Viceroy of India, called ''TOI'' "the leading paper in Asia". In 1991, the BBC ranked ''TOI'' among the world's six best newspapers. It is owned and published by Bennett, Coleman & Co. Ltd. (B.C.C.L.), which is owned by the Sahu Jain family. In the Brand Trust Report India study 2019, ''TOI'' was rated as the most trusted English newspaper in India. Reuters rated ''TOI'' as India's most trus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suraj Bhan
Suraj Bhan (1 October 1928 – 6 August 2006) was a former Governor, Member of Parliament and an Indian politician from Bharatiya Janata Party. Personal life Suraj Bhan Banswal was born on 1 October 1928 at Mehlanwali, Yamuna Nagar district of Haryana into Chamar community and studied MA and LLB at Panjab University and Kurukshetra University. He started his public life as a volunteer of the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh. His son Arun Kumar is also associated with BJP and been in-charge in various municipal corp. elections in Hayana. Political career *He started his political career with Bharatiya Jana Sangh which eventually became the Bharatiya Janata Party and dropped his last name "Banswal" after joining active politics. *He represented the Ambala parliamentary constituency of Haryana in the 4th (1967–1970), 6th (1977–1979), 7th (1979–1984) and the 11th Lok Sabhas (1996–1997). *In 1987, he was elected to Haryana Legislative Assembly and served as Revenue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doab
''Doab'' () is a term used in South Asia Quote: "Originally and chiefly in South Asia: (the name of) a strip or narrow tract of land between two rivers; spec. (with) the area between the rivers Ganges and Jumna in northern India." for the tract Quote: "confluence, land between two rivers, used in India of the tongue of land between the Ganges and Jumna, and of similar tracts in the Punjab, etc., lit. ‘two waters’ " of land lying between two confluent rivers. It is similar to an interfluve. Quote: " a tract of land between two rivers : interfluve" In the ''Oxford Hindi-English Dictionary'', R. S. McGregor defines it as from Persian ''do-āb'' (, literally "two odiesof water") "a region lying between and reaching to the confluence of two rivers. The Doab ''The Doab'' designates the flat alluvial tract between the Ganges and Yamuna rivers extending from the Sivalik Hills to the two rivers' confluence at Prayagraj. It is also called as ''Ganges-Yamuna Doab'' or ''Ganga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)