|
Joe Travis
Joe Travis (c. 1815 – Unknown) was an enslaved man who was one of the only survivors of the Battle of the Alamo. Joe was sold four times in his life, with his most well known owner being William B. Travis, a 19th century lawyer and soldier, who would later be the lieutenant colonel for The Battle of the Alamo. Early life Joe Travis was born in Lexington, Kentucky in 1815, to his mother Elizabeth. He had five siblings, all whom had different fathers. One of his siblings was abolitionist and novelist, William Wells Brown. Brown escaped enslavement in 1833 and is considered the first African American to publish a novel, titled Clotel, in 1853. Travis’ grandfather was also said to be Daniel Boone, famous pioneer and folk hero of the United States, who was father to his mother Elizabeth. Joe grew up working in the fields with his family and often spent his free time fishing and hunting, or working extra jobs to save money to help his family. The owner of the farm, and Joe, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1854 Alamo
Events January–March * January 4 – The McDonald Islands are discovered by Captain William McDonald aboard the ''Samarang''. * January 6 – The fictional detective Sherlock Holmes is perhaps born. * January 9 – The Teutonia Maennerchor Hall, Teutonia Männerchor in Pittsburgh, U.S.A. is founded to promote German culture. * January 20 – The North Carolina General Assembly in the United States charters the Atlantic and North Carolina Railroad, to run from Goldsboro, North Carolina, Goldsboro through New Bern, North Carolina, New Bern, to the newly created seaport of Morehead City, North Carolina, Morehead City, near Beaufort, North Carolina, Beaufort. * January 21 – The iron clipper runs aground off the east coast of Ireland, on her maiden voyage out of Liverpool, bound for Australia, with the loss of at least 300 out of 650 on board. * February 11 – Major streets are lit by coal gas for the first time by the Pacific Gas and Electric Compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
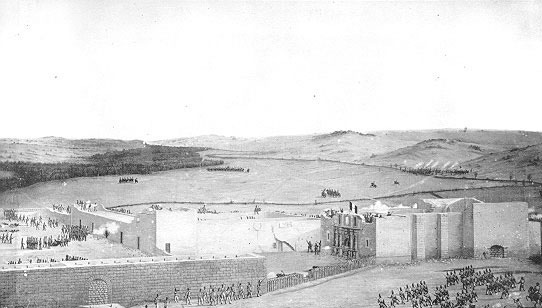
Alamo Mission In San Antonio
The Battle of the Alamo (February 23 – March 6, 1836) was a pivotal event in the Texas Revolution. Following a 13-day siege, Mexican troops under President General Antonio López de Santa Anna reclaimed the Alamo Mission near San Antonio de Béxar (modern-day San Antonio, Texas, United States), killing most of the occupants inside. Santa Anna's refusal to take prisoners during the battle inspired many Texians and Tejanos to join the Texian Army. Motivated by a desire for revenge, as well as their written desire to preserve a border open to immigration and the importation and practice of slavery, the Texians defeated the Mexican Army at the Battle of San Jacinto, on April 21, 1836, ending the rebellion in favor of the newly formed Republic of Texas. Several months previously, Texians, who were primarily recent immigrants from USA, had killed or driven all Mexican troops out of Mexican Texas. About 100 Texians were then garrisoned at the Alamo. The Texian force grew s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
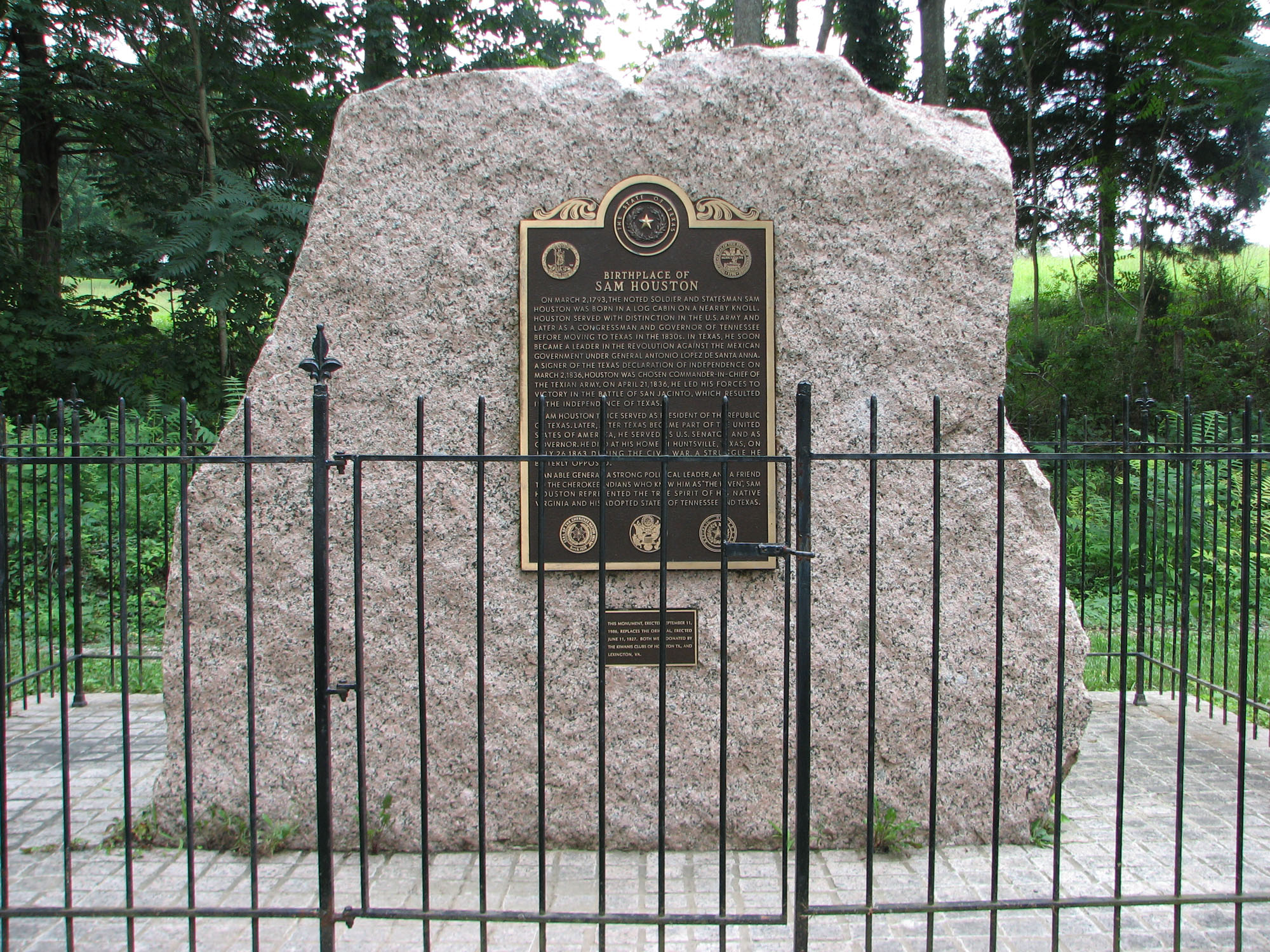
Sam Houston
Samuel Houston (, ; March 2, 1793 – July 26, 1863) was an American general and statesman who played an important role in the Texas Revolution. He served as the first and third president of the Republic of Texas and was one of the first two individuals to represent Texas in the United States Senate. He also served as the sixth governor of Tennessee and the seventh governor of Texas, the only individual to be elected governor of two different states in the United States. Born in Rockbridge County, Virginia, Houston and his family migrated to Maryville, Tennessee, when Houston was a teenager. Houston later ran away from home and spent about three years living with the Cherokee, becoming known as Raven. He served under General Andrew Jackson in the War of 1812, and after the war, he presided over the removal of many Cherokee from Tennessee. With the support of Jackson and others, Houston won election to the United States House of Representatives in 1823. He strongly supported ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonzales, Texas
Gonzales is a city in Gonzales County, Texas, United States. It is the county seat. The population was 7,165 at the 2020 census. The "Come and Take It" flag in the War for Texas Independence from Mexico originated in Gonzales. Its economy is enhanced through lodging oil field workers from the nearby Eagle Ford Shale. It was the site of the first battle of the Texas Revolution. History Gonzales is one of the earliest Anglo-American settlements in Texas, the first west of the Colorado River. It was established by Empresario Green DeWitt as the capital of his colony in August 1825. DeWitt named the community for Rafael Gonzáles, governor of Coahuila y Tejas. Informally, the community was known as the DeWitt Colony. The original settlement (located where Highway 90-A crosses Kerr Creek) was abandoned in 1826 after two Indian attacks. It was rebuilt nearby in 1827. The town remains today as it was originally surveyed. Gonzales is referred to as the " Lexington of Texas" because i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susanna Dickinson
Susanna Wilkerson Dickinson (1813 – October 7, 1883) and her infant daughter, Angelina, were among the few American survivors of 1836 Battle of the Alamo during the Texas Revolution. Her husband, Almaron Dickinson, and 185 other Texian defenders were killed by the Mexican Army. Early life In Tennessee's Williamson County, Susanna was born in 1814, yet she never learned to read or write. She married Almaron Dickinson on May 24, 1829, when she was only 15 years old. After acquiring land along the San Marcos River, they became DeWitt Colonists two years later. They then constructed a blacksmith shop there and made investments in fellow colonist George Kimbell's Gonzales hat business. Texas Revolution As the Mexican government increasingly abandoned its federalist structure in favor of a more centralized government, Almaron Dickinson became one of the early proponents of war. He would later join with other volunteers during the Battle of Gonzales, becoming one of the "Old G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miguel Barragán
Miguel Francisco Barragán Andrade (8 March 1789 – 1 March 1836) was a Mexican soldier and politician who served as interim president of Mexico in 1836. He had previously served as Governor of Veracruz, and gained national fame for the capture of the Fortress of San Juan de Ulúa in 1824, through which Spanish military presence was finally expelled from Mexico. He initially was a supporter of the federalist Constitution of 1824, but became a partisan of the conservative Escoses Party, who strongly critiqued the Constitution, and would eventually transform the First Mexican Republic into the Centralist Republic of Mexico, a transition in which Barragán played a military role. During the Centralist Republic, he was nominated by Antonio López de Santa Anna to hold presidential office while Santa Anna went off to fight insurrections against the new constitution, including the Texas Revolution, but Barragán's poor health led him to die in office. He was succeeded by his Minister ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Degüello
The Degüello (Spanish: ''El toque a degüello'') is a bugle call, notable in the United States for its use as a march by Mexican Army buglers during the 1836 Siege and Battle of the Alamo to signal that the defenders of the garrison would receive no quarter by the attacking Mexican Army under General Antonio López de Santa Anna. The Degüello was introduced to the Americas by the Spanish armies and was later adopted by the patriot armies fighting against them during the Spanish American wars of independence. It was also widely used by Simon Bolivar's armies, notably during the Battle of Junin and the Battle of Ayacucho. "Degüello" is a Spanish noun from the verb " degollar", to describe the action of throat-cutting. More figuratively, it means "give no quarter." It "signifies the act of beheading or throat-cutting and in Spanish history became associated with the battle music, which, in different versions, meant complete destruction of the enemy without mercy." It is similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Bowie
James Bowie ( ) ( – March 6, 1836) was a 19th-century American pioneer, slave smuggler and trader, and soldier who played a prominent role in the Texas Revolution. He was among the Americans who died at the Battle of the Alamo. Stories of him as a fighter and frontiersman, both real and fictitious, have made him a legendary figure in Texas history and a folk hero of American culture. Bowie was born in Kentucky. He spent most of his life in Louisiana, where he was raised and where he later worked as a land speculator. His rise to fame began in 1827 on reports of the Sandbar Fight near present-day Vidalia, Louisiana. What began as a duel between two other men deteriorated into a mêlée in which Bowie, having been shot and stabbed, killed the sheriff of Rapides Parish with a large knife. This, and other stories of Bowie's prowess with a knife, led to the widespread popularity of the Bowie knife. Bowie enlarged his reputation during the Texas Revolution. After moving to Tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Davy Crockett
David Crockett (August 17, 1786 – March 6, 1836) was an American folk hero, frontiersman, soldier, and politician. He is often referred to in popular culture as the "King of the Wild Frontier". He represented Tennessee in the U.S. House of Representatives and served in the Texas Revolution. Crockett grew up in East Tennessee, where he gained a reputation for hunting and storytelling. He was made a colonel in the militia of Lawrence County, Tennessee and was elected to the Tennessee state legislature in 1821. In 1827, he was elected to the U.S. Congress where he vehemently opposed many of the policies of President Andrew Jackson, especially the Indian Removal Act. Crockett's opposition to Jackson's policies led to his defeat in the 1831 elections. He was re-elected in 1833, then narrowly lost in 1835, prompting his angry departure to Texas (then the Mexican state of Tejas) shortly thereafter. In early 1836, he took part in the Texas Revolution and died at the Battle of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martín Perfecto De Cos
Martín Perfecto de Cos (1800–1 October 1854) was a Mexican Army general and politician during the mid-19th century. Born in Veracruz, the son of an attorney, he became an army cadet at the age of 20, a lieutenant in 1821, and a brigadier general in 1833. Cos is perhaps best known as a commander of Mexican forces during the Texas Revolution in the 1830s. In September 1835, he was sent by President-General Antonio López de Santa Anna to investigate the refusal of Texians to pay duties during the Anahuac Disturbances. General Cos dispersed the legislature of Coahuila y Tejas, then in session at Monclova, landed 300 men at Matagorda Bay, established a headquarters in San Antonio, and declared his intention of ending Anglo-American resistance in Texas. He attempted to arrest several Texian critics of Santa Anna, but his demands were resisted; a force of Texians under Stephen F. Austin and Edward Burleson held the Mexican troops for two months in the siege of Béxar until Cos surr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonio López De Santa Anna
Antonio de Padua María Severino López de Santa Anna y Pérez de Lebrón (; 21 February 1794 – 21 June 1876),Callcott, Wilfred H., "Santa Anna, Antonio Lopez De,''Handbook of Texas Online'' Retrieved 18 April 2017. usually known as Santa Anna or López de Santa Anna, was a Mexican politician and general. His influence on post-independence Mexican politics and government in the first half of the nineteenth century is such that historians of Mexico often refer to it as the "Age of Santa Anna". He has been called "the Man of Destiny", "a quintessential ''caudillo'' trongman. Although initially in the post-independence period he identified as a federalist and participated in a coup that ousted the conservatives in 1833, he became increasingly conservative. Elected President in 1833, López de Santa Anna declined to serve and retired to his home state and power base of Veracruz, a pattern that was to repeat itself until his ouster in 1855. López de Santa Anna's military and poli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |