|
Jobless Recovery
A jobless recovery or jobless growth is an economic phenomenon in which a macroeconomy experiences growth while maintaining or decreasing its level of employment. The term was coined by the economist Nick Perna in the early 1990s. Causes Economists are still divided about the causes and cures of a jobless recovery: some argue that increased productivity through automation has allowed economic growth without reducing unemployment. Other economists state that blaming automation is an example of the luddite fallacy and that jobless recoveries stem from structural changes in the labor market, leading to unemployment as workers change jobs or industries. Industrial consolidation Some have argued that the recent lack of job creation in the United States is due to increased industrial consolidation and growth of monopoly or oligopoly power. The argument is twofold: firstly, small businesses create most American jobs, and secondly, small businesses have more difficulty starting and gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macroeconomy
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that deals with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole. This includes regional, national, and global economies. Macroeconomists study topics such as output (economics), output/Gross domestic product, GDP (gross domestic product) and national income, unemployment (including Unemployment#Measurement, unemployment rates), price index, price indices and inflation, Consumption (economics), consumption, saving, investment (macroeconomics), investment, Energy economics, energy, international trade, and international finance. Macroeconomics and microeconomics are the two most general fields in economics. The focus of macroeconomics is often on a country (or larger entities like the whole world) and how its markets interact to produce large-scale phenomena that economists refer to as aggregate variables. In microeconomics the focus of analysis is often a single market, such as whether changes in supply or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underemployment Equilibrium
In Keynesian economics, underemployment equilibrium is a situation with a persistent shortfall relative to full employment and potential output so that unemployment is higher than at the NAIRU or the "natural" rate of unemployment. Theoretical framework Origin The concept of underemployment equilibrium originates from analyzing underemployment in the context of General Equilibrium Theory, a branch of microeconomics. It describes a steady economic state when consumptions and production outputs are both suboptimal – many economic agents in the economy are producing less than what they could produce in some other equilibrium states. Economic theory dictates that underemployment equilibrium possesses certain stability features under standard assumptions – the “invisible hand” (market force) can not, by itself, alter the equilibrium outcome to a more socially desirable equilibrium. Exogenous forces such as fiscal policy have to be implemented in order to drive the economy to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Of Automation
Impact may refer to: * Impact (mechanics), a large force or mechanical shock over a short period of time * Impact, Texas, a town in Taylor County, Texas, US Science and technology * Impact crater, a meteor crater caused by an impact event * Impact event, the collision of a meteoroid, asteroid or comet with Earth * Impact factor, a measure of the citations to a science or social science journal * Impact wrench, a socket wrench power tool capable of high torque Books and magazines * ''Impact'' (novel), a 2010 novel by Douglas Preston *'' Impact Press'', a former Orlando, Florida-based magazine * Impact Magazines, a former UK magazine publisher * ''Impact'' (conservative magazine), a British political magazine * ''Impact'' (British magazine), a British action film magazine * ''Impact'', a French action film magazine spun off from ''Mad Movies'' * ''Impact'' (UNESCO magazine), a former UNESCO quarterly titled ''IMPACT of science on society'' * ''Impact'' (student magazine), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Unemployment
Structural unemployment is a form of involuntary unemployment caused by a mismatch between the skills that workers in the economy can offer, and the skills demanded of workers by employers (also known as the skills gap). Structural unemployment is often brought about by technological changes that make the job skills of many workers obsolete. Structural unemployment is one of three categories of unemployment distinguished by economists, the others being frictional unemployment and cyclical unemployment. Because it requires either migration or re-training, structural unemployment can be long-term and slow to fix. Causes and examples From an individual perspective, structural unemployment can be due to: * Inability to afford or decision not to pursue further education or job training. * Choice of a field of study which did not produce marketable job skills. * Inability to afford relocation. * Inability to relocate due to inability to sell a house (for example due to the colla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Offshoring
Offshoring is the relocation of a business process from one country to another—typically an operational process, such as manufacturing, or supporting processes, such as accounting. Usually this refers to a company business, although state governments may also employ offshoring. More recently, technical and administrative services have been offshored. Offshoring neither implies nor precludes involving a different company to be responsible for a business process. Therefore, offshoring should not be confused with outsourcing which does imply one company relying on another. In practice, the concepts can be intertwined, i.e offshore outsourcing, and can be individually or jointly, partially or completely reversed, as described by terms such as reshoring, inshoring, and insourcing. In-house offshoring is when the offshored work is done by means of an internal (captive) delivery model. Imported services from subsidiaries or other closely related suppliers are included, whereas in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lost Decades
The Lost Decades are a lengthy period of economic stagnation in Japan precipitated by the asset price bubble's collapse beginning in 1990. The singular term originally referred to the 1990s, but the 2000s (Lost 20 Years, ) and the 2010s (Lost 30 Years, ) have been included by commentators as the phenomenon continued. From 1991 to 2003, the Japanese economy, as measured by GDP, grew only 1.14% annually, while the average real growth rate between 2000 and 2010 was about 1%, both well below other industrialized nations. Debt levels continued to rise due to the 2008 financial crisis and the Great Recession, the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, the Fukushima nuclear disaster, and the COVID-19 pandemic and COVID-19 recession. Broadly impacting the entire Japanese economy, over the period of 1995 to 2023, the country's nominal GDP fell from $5.33 trillion to $4.21 trillion, real wages fell around 11%, while the country experienced a stagnant or decreasing price l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Involuntary Unemployment
Involuntary unemployment occurs when a person is unemployed despite being willing to work at the prevailing wage. It is distinguished from voluntary unemployment, where a person chooses not to work because their reservation wage is higher than the prevailing wage. In an economy with involuntary unemployment, there is a surplus of labor at the current real wage. This occurs when there is some force that prevents the real wage rate from decreasing to the real wage rate that would equilibrate supply and demand (such as a minimum wage above the market-clearing wage). Structural unemployment is also involuntary. Economists have several theories explaining the possibility of involuntary unemployment including implicit contract theory, Disequilibrium macroeconomics, disequilibrium theory, staggered wage setting, and efficiency wages. The officially measured unemployment rate is the ratio of involuntary unemployment to the sum of involuntary unemployment and employment (the denominator of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Labor Arbitrage
Global labor arbitrage is an economic phenomenon where, as a result of the removal of or disintegration of barriers to international trade, jobs move to nations where labor and the cost of doing business (such as environmental regulations) are inexpensive and/or impoverished labor moves to nations with higher paying jobs.The "global labor arbitrage" phenomenon has been described by economist Stephen S. Roach. See Mike Whitney"Labor arbitrage,"''Entrepreneur'', June 2006. Two common barriers to international trade are tariffs (politically imposed) and the costs of transporting goods across oceans. With the advent of the Internet, the decrease of the costs of telecommunications, and the possibility of near-instantaneous document transfer, the barriers to the trade of intellectual work product, which is, essentially, any kind of work that can be performed on a computer (such as computer programming) or that makes use of college education, have been greatly reduced. Often, a prospe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Employment-to-population Ratio
Employment-to-population ratio, also called the employment rate, is a statistical ratio that measures the proportion of a country's working age population (statistics are often given for ages 15 to 64) that is employed. This includes people that have stopped looking for work.Employment/Population Ratios for the 50 Largest Metropolitan Statistical Areas: 2008, 2009, and 2010. (2011, September). Retrieved December 10, 2012, from United States Census Bureau website: https://www.census.gov/prod/2011pubs/ acsbr10-09.pdf The International Labour Organization states that a person is considered employed if they have worked at least 1 hour in "gainful" employment in the most recent week. The employment-to-population ratio is usually calculated and reported periodically for the economy by the national agency of statistics. It is usually calculated by using a survey data collection and the answers of certain people to the questions of the national agency for the economy an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deindustrialization
Deindustrialization is a process of social and economic change caused by the removal or reduction of industrial capacity or activity in a country or region, especially of heavy industry or manufacturing industry. There are different interpretations of what deindustrialization is. Many associate American deindustrialization with the mass closing of automaker plants in the now so-called Rust Belt between 1980 and 1990. The US Federal Reserve raised interest and exchange rates beginning in 1979, and continuing until 1984, which automatically caused import prices to fall. Japan was rapidly expanding productivity during this time, and this decimated the US machine tool sector. A second wave of deindustrialization occurred between 2001 and 2009, culminating in the automaker bailout of GM and Chrysler. Research has pointed to investment in patents rather than in new capital equipment as a contributing factor.Kerwin Kofi Charles et al. (201The Transformation of Manufacturing an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civilian Noninstitutional Population
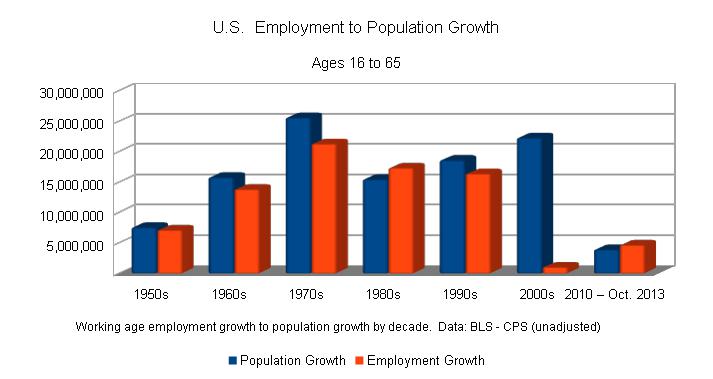
In the United States, the civilian noninstitutional population refers to people 16 years of age and older residing in the 50 States and the District of Columbia who are not inmates of institutions (penal system, penal, mental facilities, homes for the aged), and who are not on active duty in the Armed Forces. Data The data series can be obtained from the Federal Reserve Economic Database (FRED). As of October 2024, there were 269,300,000 persons in the civilian noninstitutional population out of a U.S. population of 337,446,000 approximately. It has steadily grown along with the U.S. population, roughly 1% per year for 2005-2013 period. Usage The measure is used to help gauge the percentage of the population that is employed or in the workforce, as the denominator in the "civilian employment to population ratio", also called the EM ratio, and the "civilian labor force participation rate." Trends in these figures are shown in the first graphic; the computation of these figures is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Population Survey
The Current Population Survey (CPS) is a monthly survey of about 60,000 U.S. households conducted by the United States Census Bureau for the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). The BLS uses the data to publish reports early each month called the Employment Situation. This report provides estimates of the unemployment rate and the numbers of employed and unemployed people in the United States based on the CPS. A readable Employment Situation Summary is provided monthly. Annual estimates include employment and unemployment in large metropolitan areas. Researchers can use some CPS microdata to investigate these or other topics. The survey asks about the employment status of each member of the household 15 years of age or older as of a particular calendar week. Based on responses to questions on work and job search activities, each person 16 years and over in a sample household is classified as employed, unemployed, or not in the labor force. The CPS began in 1940, and responsibilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |