|
Jingxi (prince)
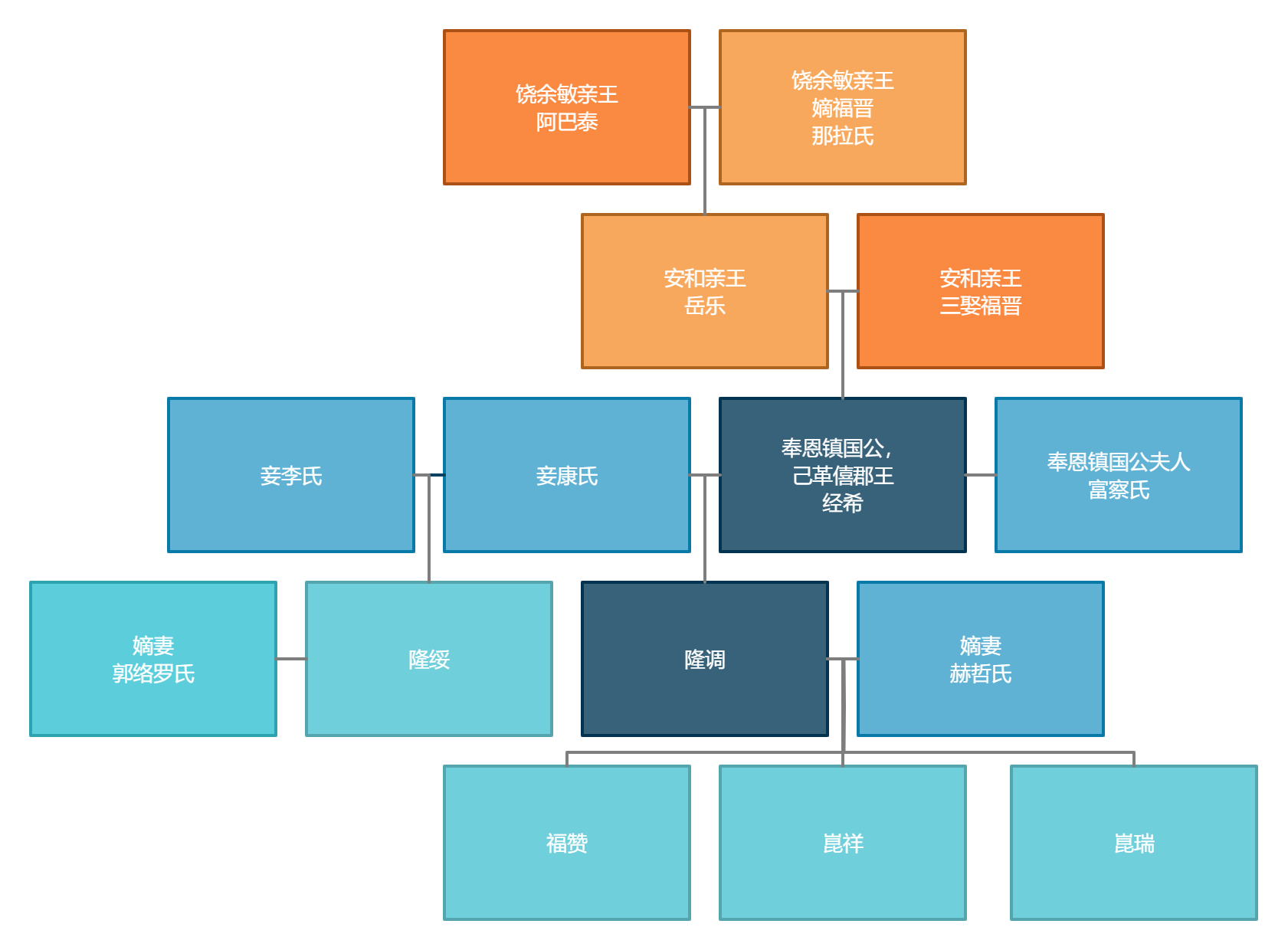
Aisin Gioro Jingxi (; 1663–1717) was Qing dynasty imperial prince as 17th son of Yolo, Abatai's son and Nurhaci's grandson. Initially Jingxi became Prince Xi of the Second Rank, but was convicted of crime and demoted to grace defender duke. The peerage was not granted iron-cap status, which meant that each successive bearer of the title would hold diminished ranks vis-a-vis his predecessor. Prince Xi of the Second Rank peerage was passed to Longdiao, Jingxi's son. As Longdiao's sons died prematurely, the peerage became extinct. Life of Jingxi Jingxi was born in 1663 to lady Hešeri, Yolo's third primary consort and aunt of Empress Xiaochengren, Kangxi Emperor's first empress. In 1683, Jingxi was made the first Prince Xi of the Second Rank (僖郡王, meaning "guardful", "precautious"). In 1690, after Nuoni (member of Prince Keqin peerage ) discovered that Yolo had sown discord among the regents and princes and, moreover, had framed Nuoni for unwilling to demonstrate filial piety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria (modern-day Northeast China and Outer Manchuria). It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince An
Prince An of the First Rank, or simply Prince An, was the title of a princely peerage used in China during the Manchu-led Qing dynasty (1644–1912). As the Prince A peerage was not awarded "iron-cap" status, this meant that each successive bearer of the title would normally start off with a title downgraded by one rank ''vis-à-vis'' that held by his predecessor. However, the title would generally not be downgraded to any lower than a ''feng'en fuguo gong'' except under special circumstances. The first bearer of the title was Abatai (1589–1646), the seventh son of Nurhaci, the founder of the Qing dynasty. In 1644, he was awarded the status of a ''junwang'' (prince of the second rank) by his nephew, the Shunzhi Emperor, under the title "Prince Raoyu of the Second Rank" ( mnc, ''doroi bayan giyūn wang'') or simply "Prince Raoyu". The title was renamed to "Prince An of the Second Rank" in 1651 when it was passed down to Abatai's fourth son, Yolo (1625–1689). In 1723, the Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Xi
Prince Xi of the Second Rank (僖郡王) was a Qing dynasty princely peerage. The peerage was created in 1682 for Jingxi, Nurhaci Nurhaci (14 May 1559 – 30 September 1626), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Qing (), was a Jurchen chieftain who rose to prominence in the late 16th century in Manchuria. A member of the House of Aisin-Gioro, he reigned ...i's great-grandson and 17th son of Prince An of the Second Rank Yolo. As the peerage was not granted perpetual inheritability, each successive bearer held diminished ranks vis-a-vis his predecessor. Prince Xi of the Second Rank * 1682-1717:Grace defender duke Jingxi. Jingxi was granted a title of prince of the second rank with the honorific name "Xi" and demoted to grace defender duke in 1690. References Prince Xi Extinct Qing dynasty princely peerages {{China-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria (modern-day Northeast China and Outer Manchuria). It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Li (理)
Prince Li of the First Rank, or simply Prince Li, was the title of a princely peerage used in China during the Manchu-led Qing dynasty (1644–1912). As the Prince Li peerage was not awarded "iron-cap" status, this meant that each successive bearer of the title would normally start off with a title downgraded by one rank ''vis-à-vis'' that held by his predecessor. However, the title would generally not be downgraded to any lower than a ''feng'en fuguo gong'' except under special circumstances. The first bearer of the title was Yunreng (1674–1725), the Kangxi Emperor's second son and former heir apparent for two terms between 1675 and 1712. After Yunreng died, he was posthumously honoured with the title "Prince Li of the First Rank" by his fourth brother, the Yongzheng Emperor, who succeeded their father. The title was passed down over eight generations and held by ten persons. Members of the Prince Li peerage * Yunreng (1674–1725), the Kangxi Emperor's second son, posthum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shunzhi Emperor
The Shunzhi Emperor (15 March 1638 – 5 February 1661) was the second Emperor of China, emperor of the Qing dynasty of China, and the first Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1644 to 1661. A Deliberative Council of Princes and Ministers, committee of Manchu princes chose him to succeed his father, Hong Taiji (1592–1643), in September 1643, when he was five years old. The princes also appointed two co-regents: Dorgon (1612–1650), the 14th son of the Qing dynasty's founder Nurhaci (1559–1626), and Jirgalang (1599–1655), one of Nurhaci's nephews, both of whom were members of the Aisin Gioro, Qing imperial clan. From 1643 to 1650, political power lay mostly in the hands of Dorgon. Under his leadership, the Qing Empire conquered most of the territory of the fallen Ming dynasty (1368–1644), chased Southern Ming, Ming loyalist regimes deep into the southwestern provinces, and established the basis of Qing rule over China proper despite highly unpopular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabula (general)
Gabula (; died 1681) of the Manchu Hešeri clan was a duke and military general during the Qing Dynasty. He was Empress Xiaochengren's father, maternal grandfather of the crown prince Yinreng, and son of Sonin (duke of the First Rank, one of the Four Regents of the Kangxi Emperor The Four Regents of the Kangxi Emperor were nominated by the Shunzhi Emperor to oversee the government of the Qing dynasty during the early reign of the Kangxi Emperor before he came of age. The four were Sonin, Ebilun, Suksaha, and Oboi. Backgrou ...). Qing dynasty politicians Manchu politicians Manchu Plain Yellow Bannermen Hešeri clan {{China-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Yu (裕)
Prince Yu of the First Rank, or simply Prince Yu, was the title of a princely peerage used in China during the Manchu-led Qing dynasty (1644–1912). As the Prince Yu peerage was not awarded "iron-cap" status, this meant that each successive bearer of the title would normally start off with a title downgraded by one rank ''vis-à-vis'' that held by his predecessor. However, the title would generally not be downgraded to any lower than a ''feng'en fuguo gong'' except under special circumstances. The first bearer of the title was Fuquan (1653–1703), the Shunzhi Emperor's second son. In 1667, Fuquan was granted the title "Prince Yu of the First Rank" by his third brother, the Kangxi Emperor. The peerage was passed down over ten generations and held by 12 persons. Members of the Prince Yu peerage * Fuquan (1653 – 1703) (1st), the Shunzhi Emperor's second son, held the title Prince Yu of the First Rank from 1667 to 1703, posthumously honoured as Prince Yu Xian of the First Ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dodo, Prince Yu
Dodo ( mnc, ᡩᠣᡩᠣ, z=Dodo; 2 April 1614 – 29 April 1649), formally known as Prince Yu, was a Manchu prince and military general of the early Qing dynasty. Family background Dodo was born in the Manchu Aisin Gioro clan as the 15th son of Nurhaci, the founder of the Qing dynasty. His mother was Nurhaci's primary spouse Lady Abahai, who also bore Dodo's full brothers Ajige and Dorgon. Career Hong Taiji's reign In 1620, Dodo was conferred the title of an ''ejen''. He became a ''beile'' at the age of 13 and was put in charge of the Plain White Banner, and started administrating affairs in the Ministry of Rites and Ministry of War. In 1628, Dodo followed Hong Taiji on the conquest of Chahar, Mongolia, and was granted the title of ''eerkechuhuer'' (額爾克楚虎爾) for his achievements. The following year, he followed Hong Taiji again on the conquest of the Ming dynasty, crossing the Great Wall and closing in on the Ming capital Beijing. In 1631, Dodo was involve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hong Taiji
Hong Taiji (28 November 1592 – 21 September 1643), also rendered as Huang Taiji and sometimes referred to as Abahai in Western literature, also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizong of Qing, was the second khan of the Later Jin dynasty (reigned from 1626 to 1636) and the founding emperor of the Qing dynasty (reigned from 1636 to 1643). He was responsible for consolidating the empire that his father Nurhaci had founded and laid the groundwork for the conquest of the Ming dynasty, although he died before this was accomplished. He was also responsible for changing the name of the Jurchen ethnicity to "Manchu" in 1635, and changing the name of his dynasty from "Great Jin" to "Great Qing" in 1636. The Qing dynasty lasted until 1912. Names and titles It is unclear whether "Hong Taiji" was a title or a personal name. Written ''Hong taiji'' in Manchu, it was borrowed from the Mongolian title ''Khong Tayiji''. That Mongolian term was itself derived from the Chinese ''h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonin (regent)
Soni (1601–1667), also known as Sonin, and rarely Sony ( mnc, ; ), was a Manchu noble of the Hešeri clan who served as one of the Four Regents of the Kangxi Emperor (r. 1661–1722) during the Qing dynasty (1644–1912). His clan belonged to the Plain Yellow Banner. Early life Soni's father Šose (Chinese: Shuose 硕色) and uncle Hife (Xifu 希福), who were both fluent in Mandarin, Mongolian and Manchu, served as high officials under Manchu patriarch Nurhaci (1559–1626). Like them, Soni was valued for his linguistic abilities. In 1628, under Nurhaci's successor Hong Taiji (1592–1643), Soni led a successful diplomatic mission to convince the recently surrendered Khorchin Mongols to honor their pledge to help the Manchus militarily. In 1629 he was named to the newly created "Literary Office" (Chinese: ''wenguan'' 文館), an institution that kept a detailed record of Manchu history and translated Chinese books about statecraft and Chinese and Korean state documents into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |