|
Jingei-class Submarine Tender
The were a class of submarine tenders of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), and served from the 1920s through World War II. Two vessels of this class were built between 1922 and 1924 under the Eight-eight fleet plan. Background The IJN planned to build over 100 submarines under the Eight-eight fleet plan, and it was recognized that support ships would be needed. The ''Jingei'' class was planned specifically for this purpose. The duties of a submarine tender included serving as a flagship for the Submarine Division Commander and as a depot ship for the nine ''Kaichū''-type submarines in a division.One Submarine Flotilla = 3 × submarines, one Submarine Division = 3 × Submarine Flotillas. Design At first, the ''Jingei'' class was planned as a 14,500 ton submarine tender. However, the specifications were revised to 8,500 tons ( standard), as stipulated by the Washington Naval Treaty. This treaty would turn out to have a great impact on the Japanese shipbuilding industry. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
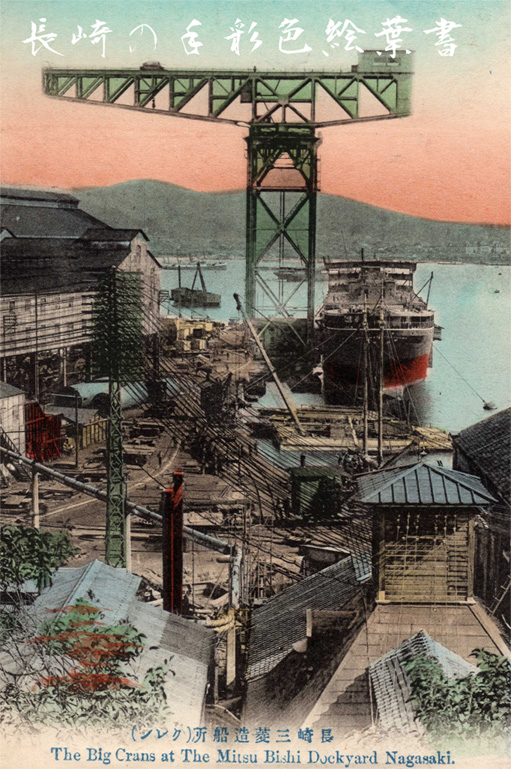
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
is a Japanese multinational engineering, electrical equipment and electronics corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. MHI is one of the core companies of the Mitsubishi Group and its automobile division is the predecessor of Mitsubishi Motors. MHI's products include aerospace and automotive components, air conditioners, elevators, forklift trucks, hydraulic equipment, printing machines, missiles, tanks, power systems, ships, aircraft, railway systems, and space launch vehicles. Through its defense-related activities, it is the world's 23rd-largest defense contractor measured by 2011 defense revenues and the largest based in Japan. History In 1857, at the request of the Tokugawa Shogunate, a group of Dutch engineers were invited, including Dutch naval engineer Hendrik Hardes, and began work on the ''Nagasaki Yotetsusho'' 長崎鎔鉄所 , a modern, Western-style foundry and shipyard near the Dutch settlement of Dejima, at Nagasaki. This was renamed ''Naga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katori-class Cruiser
The were originally ordered by the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) to serve as training ships in the 1937 and 1939 Supplementary Naval budgets. During the Pacific War, they were used as administrative flagships for various fleets, such as submarine command and control, and to command escort squadrons. The ships were upgraded as the war progressed with additional anti-aircraft guns and depth charges. Design Originally ordered by the IJN in the 1937 and 1939 Supplementary Naval budgets, the ''Katori''-class cruisers were purpose-designed to replace the aging armored cruisers in the officer training role, and as such differed from other IJN cruisers in several aspects. Built to commercial standards to minimize cost, the ''Katori'' class had a lower length-to-beam ratio than was usual for cruisers, giving the ships greater initial stability for trainees unfamiliar with lives at sea. Unusually for IJN ships, the ''Katori'' class had mixed steam turbine/diesel propulsion, intended to ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Submarine Tender Jingei
,Nelson. ''Japanese-English Character Dictionary''. pages 872, 984 was the lead vessel of the s operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy, from the 1920s through World War II. She was the first purpose-built submarine tender in the Imperial Japanese Navy.Jentsura, ''Warships of the Imperial Japanese Navy'', p. 237 Background Under the Eight-eight fleet plan, the Imperial Japanese Navy planned to acquire 100 submarines for long-distance scouting operations, which would also be used to conduct attrition warfare against any enemy fleet approaching Japan. ''Jingei'' was intended to serve as a flagship for the Submarine Division Commander and as a depot ship for the nine submarines in a submarine division. Initially, ''Jingei'' was planned as a 14,500-ton vessel; however, her specifications were scaled down to 8,500-tons due to restrictions imposed by the Washington Naval Treaty. Design ''Jingei'' was built by Mitsubishi Yards in Nagasaki, and the contractor was given an unusually free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IJN 6th Fleet
The was a fleet of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) that during World War II, had primary responsibility for the command of submarine operations. History The 6th Fleet was formed on 15 November 1940, and was assigned general control of all IJN submarine operations. Its initial mission was reconnaissance off the west coast of the United States, east coast of Australia, and the sea lanes of the Indian Ocean. Background Japan had prior to the attack on Pearl Harbor a diverse submarine fleet, some of which had unique distinctions: the only submarines in existence of over 5,000 tons submerged displacement, submarines over 400 feet in length (until the advent of nuclear power), the 41 submarines in its retinue (and of the world) that could carry specially designed aircraft, and submarines with the longest ranges and highest speeds of any nation. With the development of the Type 95 submarine-launched variant of the Long Lance oxygen-propelled torpedo, Japan not only had the world's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
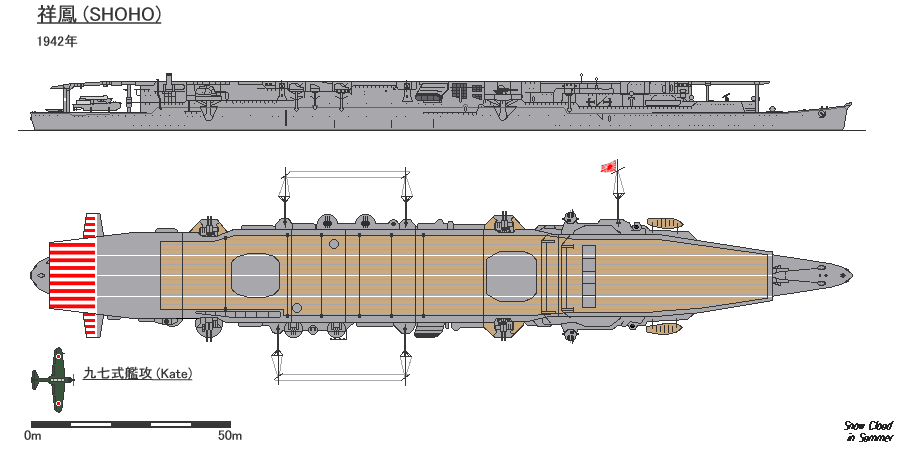
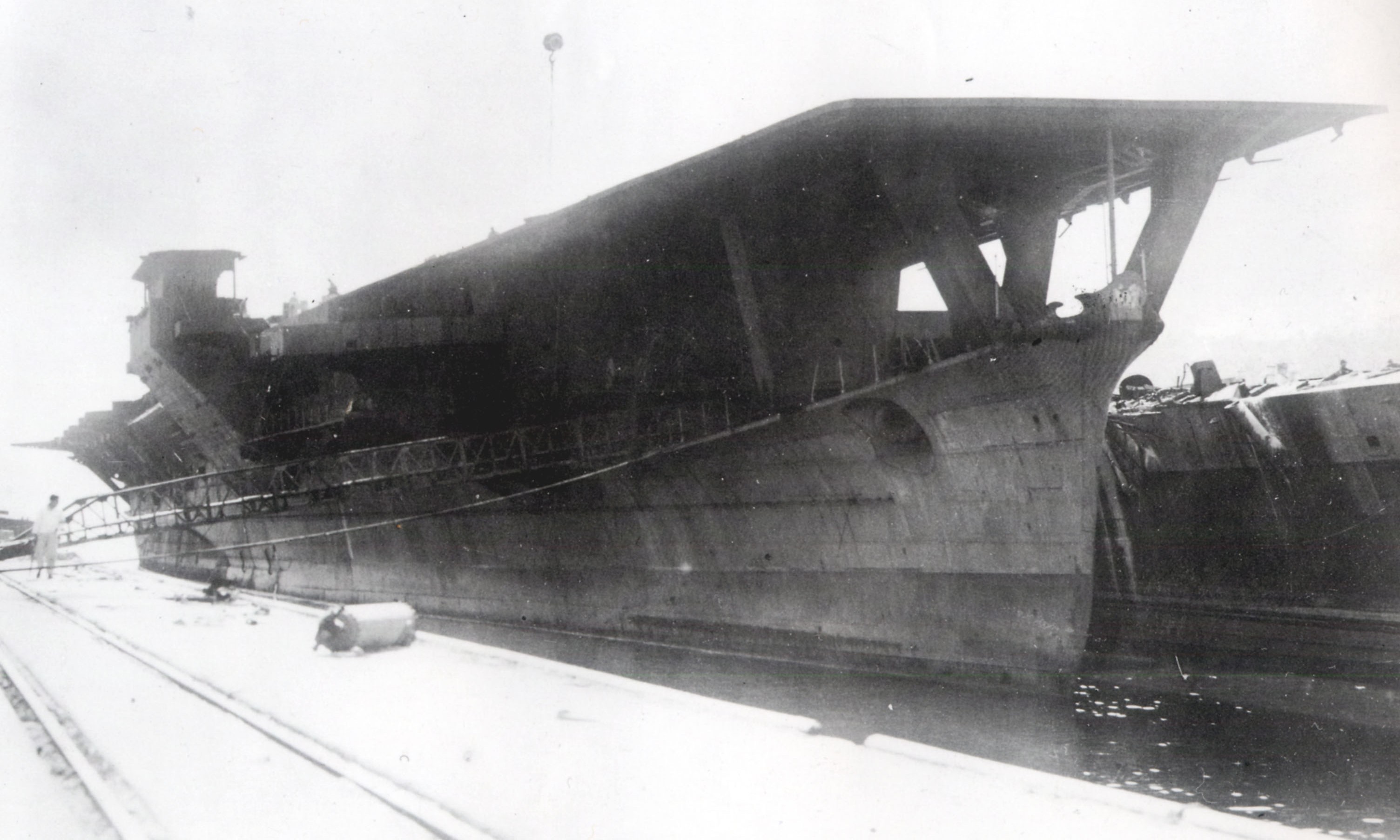
Japanese Aircraft Carrier Shōhō
''Shōhō'' (Japanese: 祥鳳, "Auspicious Phoenix" or "Happy Phoenix") was a light aircraft carrier of the Imperial Japanese Navy. Originally built as the submarine support ship ''Tsurugizaki'' in the late 1930s, she was converted before the Pacific War into an aircraft carrier and renamed. Completed in early 1942, the ship supported the invasion forces in Operation MO, the invasion of Port Moresby, New Guinea, and was sunk by American carrier aircraft on her first combat operation during the Battle of the Coral Sea on 7 May. ''Shōhō'' was the first Japanese aircraft carrier to be sunk during World War II. Design, construction and conversion ''Shōhō'' and her sister were designed to be easily modified as an oil tanker, submarine tender, or aircraft carrier as needed. ''Shōhō'' was laid down by the Yokosuka Naval Arsenal on 3 December 1934 as the submarine tender ''Tsurugizaki''. She was launched on 1 June 1935 and completed on 15 January 1939. Not long after the ship w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Aircraft Carrier Zuihō
was the name ship of her class of two light aircraft carriers built for the Imperial Japanese Navy. Originally laid down as the submarine tender ''Takasaki'', she was renamed and converted while under construction into an aircraft carrier. The ship was completed during the first year of World War II and played a minor role in the Battle of Midway in mid-1942. She participated in the Guadalcanal Campaign during the rest of 1942. Significantly damaged during the Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands in that campaign, after repairs ''Zuihō'' covered the evacuation of Japanese forces from Guadalcanal in early 1943. Her aircraft were disembarked several times in mid- to late-1943 and used from land bases in a series of battles in the Southwest Pacific. ''Zuihō'' participated in the Battles of the Philippine Sea and Leyte Gulf in mid-1944. In this last engagement, she mainly served as a decoy for the main striking forces and was sunk by American aircraft. In between battles, the ship se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kure Naval Arsenal
was one of four principal naval shipyards owned and operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy. History The Kure Naval District was established at Kure, Hiroshima in 1889, as the second of the naval districts responsible for the defense of the Japanese home islands. Along with the establishment of the navy base, a ship repair facility was also constructed, initially by moving the equipment from the Onohama shipyards near Kobe. Construction was supervised by the French engineer Louis-Émile Bertin. The first warship constructed at Kure, '' Miyako'', was launched in 1897. The "Kure Shipyards" were officially renamed the "Kure Naval Arsenal" in 1903. Kure developed into one of the largest shipbuilding facilities in the Empire of Japan, capable of working with the largest vessels. The Arsenal included a major steel works (built with British assistance), and also facilities for producing naval artillery and projectiles. The battleships ''Yamato'' and '' Nagato'' were designed and con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasebo Naval Arsenal
was one of four principal naval shipyards owned and operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy. History The Sasebo Naval District was established at Sasebo, Nagasaki in 1886, as the third of the naval districts responsible for the defense of the Japanese home islands. After the establishment of the navy base, a ship repair facility was established in 1889 with a dry dock. With the addition of equipment and facilities for ship production by 1897, the "Sasebo Shipyards" were officially established, and renamed the "Sasebo Naval Arsenal" in 1903. Construction of the arsenal was supervised by the French engineer Louis-Émile Bertin. In 1913, a 250-ton crane was installed, and the shipbuilding facilities expanded to permit the construction of large warships. With the mothballing of the Maizuru Naval Arsenal due to restrictions by the Washington Naval Treaty, much of the design and prototype work for new classes of destroyers and torpedo boats formerly done at Maizuru was shifted to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomozuru Incident
was one of four s of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). It capsized in a storm on 12 March 1934, shortly after its completion. This incident forced the IJN to review the stability of all recently completed, under construction and planned ships. It was salvaged and put back into service after extensive modifications. During World War II, the ''Tomozuru'' fought in the Battle of the Philippines and in the Dutch East Indies campaign as an escort, and it continued to play that role for the rest of the war. The ''Tomozuru'' Incident In February 1934, ''Tomozuru'' joined the 21st Torpedo Flotilla at Sasebo. *01:00, 12 March 1934, ''Tomozuru'' departed from Sasebo for a night torpedo exercise with the light cruiser and torpedo boat . *03:25, because of stormy weather, ''Tatsuta'' ordered the other two boats to return to base. *03:58, radio contact lost with ''Tomozuru''. Possible loss of power or radio capability. *04:12, ''Tomozuru''s lights disappeared, presumably this is when it c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
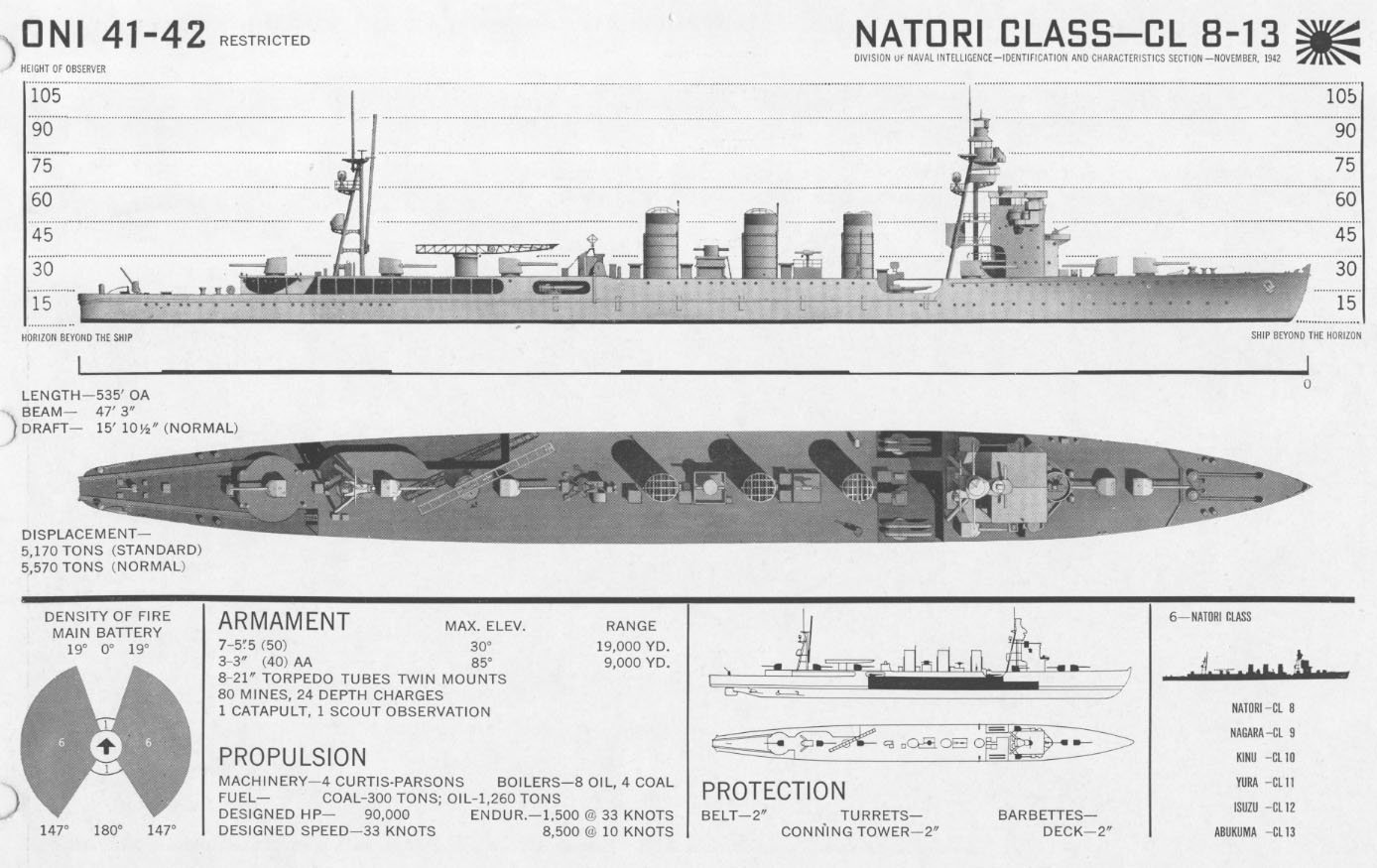
Nagara-class Cruiser
The six were a class of six light cruisers built for and operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy. The ''Nagara''-class cruisers proved useful in combat operations ranging from the Aleutian Islands to the Indian Ocean throughout World War II. Most served as flagships for destroyer or submarine squadrons, and were deployed for transport or local defense missions. Towards the end of the war, the surviving vessels were increasingly obsolete and were retained as second-line units.Stille, ''Imperial Japanese Navy Light Cruisers 1941-45'', page 22 The ''Nagara'' class was followed by the very similar . Background A final three 5,500 ton class light cruisers authorized under the 8-4 Fleet Program were ordered by the Imperial Japanese Navy in 1920. Due to minor changes in design, primarily due to advances in torpedo technology, these three vessels were initially designated as "modified Kuma-class", or "5500-ton class Type II", before being re-designated after the lead vessel, . A secon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuma-class Cruiser
The were a class of five light cruisers built for and operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). The ''Kuma''-class cruisers proved useful in combat operations ranging from the Aleutian Islands to the Indian Ocean throughout World War II. The ''Kuma''-class was followed by the very similar . Background Despite the success of the high speed light cruiser design, the Imperial Japanese Navy realized that they would be outgunned by the larger US Navy and the Dutch Java-class of light cruisers then under development. In addition, the ''Tenryū''-class vessels, with a maximum speed of , were unable to keep up with the newer Japanese destroyers, such as the , which had a design speed of .Stille, '' Imperial Japanese Navy Light Cruisers 1941-45 '', pages 14-18; At the end of 1917, plans for an additional six ''Tenryū''-class vessels, plus three new-design 7200 ton-class scout cruisers were shelved, in place of an intermediate 5,500 ton-class vessel which could be used as both a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |