|
Jindřich Jindřich
Jindřich is a given name. It is the Czech version of the English name Henry. People with the name include: *Jindřich Bačkovský (1912–2000), Czech physicist *Jindřich Balcar (born 1950), Czechoslovak ski jumper who competed from 1974 to 1976 *Jindřich Chmela (1924–2010), Czech Olympic fencer *Jindřich Feld (1925–2007), Czech composer of classical music *Jindřich Kabát (1953–2020), Czech psychologist, professor and politician *Jindřich Krepindl (born 1948), Czechoslovak handball player *Jindřich Svoboda (aviator) (1917–1942), Czech aviator * Jindřich Svoboda (footballer) (born 1952), Czech football player *Josef Jindřich Šechtl (1877–1954), Czech photographer, specialized in photojournalism and portrait photography *Jindřich Šimon Baar (1869–1925), Czech Catholic priest and writer, realist and author *Jindřich Štyrský (1899–1942), Czech Surrealist painter, poet, editor, photographer, and graphic artist *Jindřich Matyáš Thurn (1567–1640), Bohemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry (given Name)
Henry is a masculine given name derived from Old French ''Henri'' / ''Henry'', itself derived from the Old Frankish name ''Heimeric'', from Common Germanic ''*Haimarīks'' (from '' *haima-'' "home" and ''*rīk-'' "ruler"). In Old High German, the name was conflated with the name ''Haginrich'' (from ''hagin'' "enclosure" and ''rich'' "ruler") to form Heinrich. The Old High German name is recorded from the 8th century, in the variants ''Haimirich, Haimerich, Heimerich, Hemirih''. Harry, its English short form, was considered the "spoken form" of Henry in medieval England. Most English kings named ''Henry'' were called ''Harry''. The name became so popular in England that the phrase "Tom, Dick, and Harry" began to be used to refer to men in general. The common English feminine forms of the name are Harriet and Henrietta. It has been a consistently popular name in English-speaking countries for centuries. It was among the top 100 most popular names used for men born in the Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jindřich Štyrský
Jindřich Štyrský (11 August 1899, Čermná u Kyšperka – 21 March 1942, Prague) was a Czech Surrealist painter, poet, editor, photographer, and graphic artist. His outstanding and varied oeuvre included numerous book covers and illustrations. He also wrote studies of both Arthur Rimbaud and Marquis de Sade. Along with his artistic partner Toyen (Marie Čermínová), he became a member of '' Devětsil'' in 1923, participating in their group exhibitions. He and Toyen also exhibited in Paris in the late 1920s, where they founded their own movement, Artificialism. Between 1928 and 1929 he was designer for the group's drama wing, the ''Osvobozené divadlo'', where he collaborated with Vítězslav Nezval and others. Štyrský was also an active editor. In addition to his ''Edition 69'' series, he edited the ''Erotická revue'', which he launched in 1930, and ''Odeon'', where many of his shorter texts appeared. He was a founding member of The Surrealist Group of Czechoslovakia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jindřich Wybraniec
Jindřich Wybraniec (born July 2, 1948) is a Czechoslovak sprint canoer who competed in the mid-1970s. He was eliminated in the semifinals of the K-4 1000 m event at the 1976 Summer Olympics in Montreal Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- .... ReferencesSports-Reference.com profile 1948 births Canoeists at the 1976 Summer Olympics Czechoslovak male canoeists Living people Olympic canoeists of Czechoslovakia {{Slovakia-canoe-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jindřich Wankel
Jindřich Wankel ( German: Heinrich Wankel; July 15, 1821, Prague – April 5, 1897, Olomouc) was a Bohemian palaeontologist and archaeologist. Wankel was born to Damian Wankel, a clerk, and his wife Magdalena, née Schwarz, in a bilingual environment. He attended German schools in Prague and later studied Medicine at the University of Prague as a student of Josef Hyrtl. He came to work in the area of the Moravský kras The Moravian Karst ( cs, Moravský kras) is a karst landscape and protected landscape area to the north of Brno in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. It encompasses a number of notable geological features, including roughly 1100 c ... (''Moravian Karst'', today's Czech Republic) in 1847, and from 1849 lived in Blansko as a medical doctor. He started geological exploration of the area and later carried out palaeontological, archaeological, and anthropological research. In 1850, in Blansko, he set up the first ever laboratory to research fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jindřich Waldes
Jindřich Waldes (also Heinrich Waldes or Henry Waldes; 2 July 1876, Nemyšl – 1 July 1941, Havana) was a leading industrialist, founder of the Waldes Koh-i-noor Company, Czech patriot of Jewish origin and art collector. Life Karel Waldes, father of Jindřich, had an inn and a small haberdashery shop in the village of Nemyšl near the town of Tábor in southern Bohemia. He wanted his son to continue his business but Jindřich found a position of a clerk at the firm of Eduard Lokesch and Son in Prague. This company made buttons and cufflinks. As Waldes had a good knowledge of languages he became Lokesch's business agent and travelled the world on behalf of the firm. In 1902 together with an engineer Hynek Puc (1856–1938) Waldes left Lokesch and founded his own company Waldes a spol. A year later Puc invented a special machine that inserted a small spring into concealed dress fasteners, the main product of the new firm. The new machine supplemented labour of ten skilled wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Václav Jindřich Veit
Václav Jindřich Veit known in German as Wenzel Heinrich Veit (19 January 1806 in the village of Řepnice, now part of Libochovany, near Litoměřice – 16 February 1864, Litoměřice) Czech composer, copyist, pianist and lawyer. To pay tuition at a law school in Prague, Veit gave music lessons. After earning his law degree and getting a position as a legal clerk, Veit continued to teach music and even started writing music. He wrote mostly chamber music, and later on in his life wrote more and more songs with texts in Czech, such as "Pozdravení pěvcovo". He also wrote some church music, including a setting of the Te Deum and a couple of masses. Although he wrote some orchestral music, such as a violin concertino and a parody of Berlioz's Symphonie fantastique, Veit only wrote one symphony, in E minor, which is however considered "a notable milestone in the development of the Czech symphonic style."Adrienne Simpson Adrienne Marie Chilton (; 26 November 1943 – 4 December 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
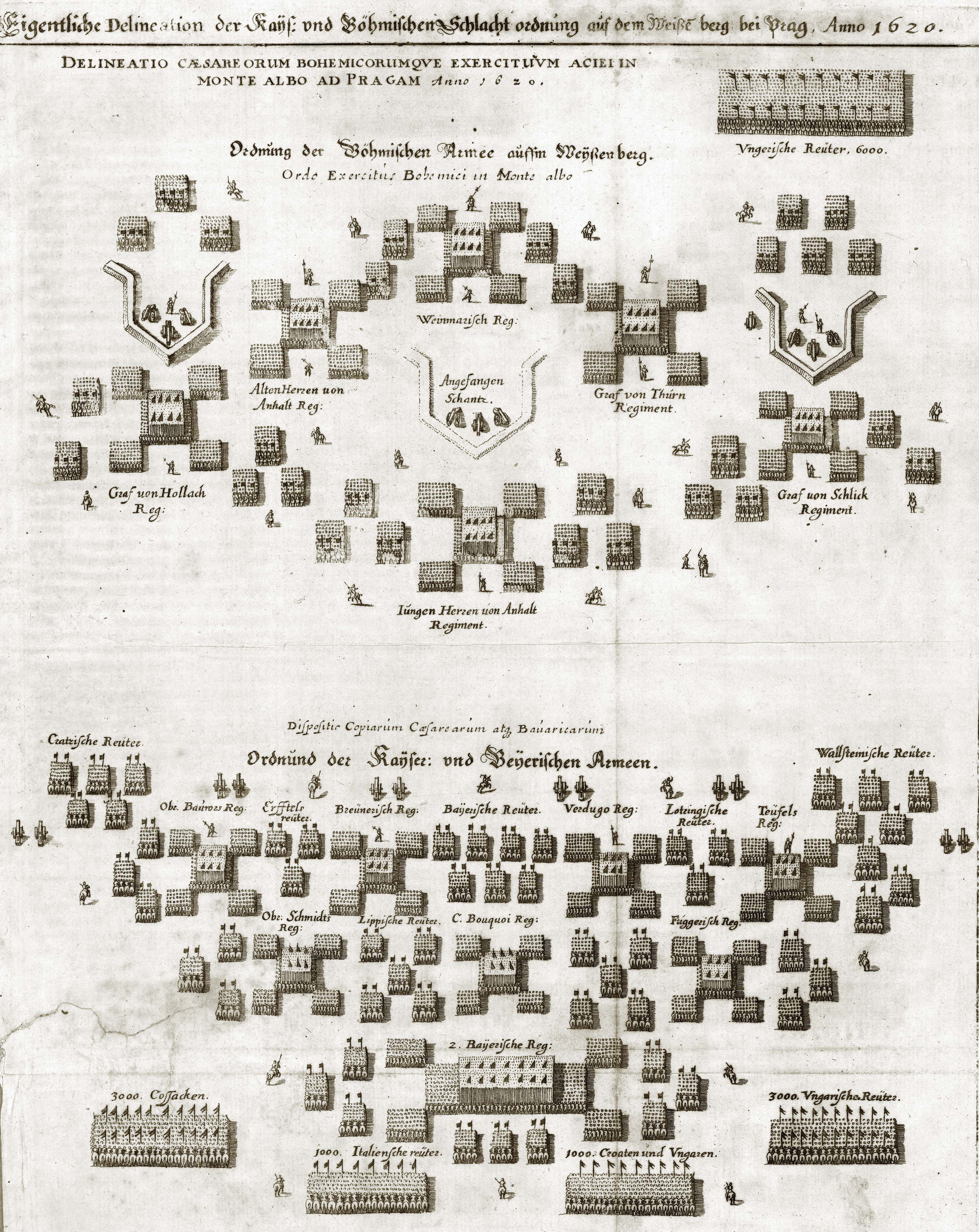
Battle Of White Mountain
), near Prague, Bohemian Confederation(present-day Czech Republic) , coordinates = , territory = , result = Imperial-Spanish victory , status = , combatants_header = , combatant1 = Catholic League , combatant2 = Bohemian Confederation Electoral Palatinate , commander1 = , commander2 = , strength1 = 23,00012 guns , strength2 = 21,00010 guns , casualties1 = 650 killed and wounded , casualties2 = 2,800 killed and wounded , map_type = Czech Republic Prague#Czech Republic , map_mark = Battle icon (crossed swords).svg , map_relief = , map_size = 300px , map_marksize = 30 , map_caption = , map_label = White Mountain The Battle of White Mountain ( cz, Bitva na Bílé hoře; german: Schlacht am Weißen Berg) was an important battle in the early stages of the Thirty Years' War. It led to the defeat of the Bohemian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohemian Revolt
The Bohemian Revolt (german: Böhmischer Aufstand; cs, České stavovské povstání; 1618–1620) was an uprising of the Bohemian estates against the rule of the Habsburg dynasty that began the Thirty Years' War. It was caused by both religious and power disputes. The estates were almost entirely Protestant, mostly Utraquist Hussite but there was also a substantial German population that endorsed Lutheranism. The dispute culminated after several battles in the final Battle of White Mountain, where the estates suffered a decisive defeat. This started re-Catholisation of the Czech lands, but also expanded the scope of the Thirty Years' War by drawing Denmark and Sweden into it. The conflict spread to the rest of Europe and devastated vast areas of Central Europe, including the Czech lands, which were particularly stricken by its violent atrocities. Rebellion Without heirs, Emperor Matthias sought to assure an orderly transition during his lifetime by having his d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Years War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle, famine, and disease, while some areas of what is now modern Germany experienced population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War, and the Portuguese Restoration War. Until the 20th century, historians generally viewed it as a continuation of the religious struggle initiated by the 16th-century Reformation within the Holy Roman Empire. The 1555 Peace of Augsburg attempted to resolve this by dividing the Empire into Lutheran and Catholic states, but over the next 50 years the expansion of Protestantism beyond these boundaries destabilised the settlement. While most modern commentators accept differences over religion and Imperial authority were im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jindřich Matyáš Thurn
Count Jindřich Matyáš of Thurn-Valsassina (german: Heinrich Matthias Graf von Thurn und Valsassina; it, Enrico Matteo Conte della Torre di Valsassina) (24 February 1567 – 26 January 1640), was one of the leaders of the Protestant Bohemian Revolt against Emperor Ferdinand II. He took part in events that led to the Thirty Years' War, and after the war he became a military leader and diplomat in Swedish service, who eventually resided in Swedish Estonia. Life He was the son of a member of the '' geheimrat'' of Ferdinand II, Archduke of Austria, Franz Napus von Thurn und Valsassina (František Thurn), count of Linz (1508–1586) and his second wife, Countess Barbora Gräfin von Schlick (1547–1581), daughter of Count Hieronymus Schlick of Bassano and Weißkirchen and countess Katharina von Gleichen-Tonna. Both of his parents were Protestants. Count Jindřich Matyáš was born on in Lipnice nad Sázavou castle in the Crown of Bohemia. After the death of his father ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jindřich Šimon Baar
Jindřich Šimon Baar (7 February 1869, Klenčí pod Čerchovem – 24 October 1925, Klenčí pod Čerchovem) was a Czech Catholic priest and writer, realist, author of the so-called ''country prose''. He joined the Czech ''Catholic modern style'', but later severed the ties with that movement. As writer, he emphasized traditional moral values of the countryside. Born into a peasant family, he did religious studies and was ordained as a Catholic priest in 1892. As a priest, he strived, unsuccessfully, for reforms in the church. Works Among his novels are: * ''Cestou křížovou'' (1900) – the first fruit, autobiographic description of the uneasy life as a reform priest * ''Pro kravičku'' (1905) * ''Farská panička'' (1906) * ''Farské historky'' (1908) * ''Jan Cimbura'' (1908) – highly idealized depiction of peasant life * historical trilogy: ''Paní komisarka'' (1923), ''Osmačtyřicátníci'' (1924) and ''Lůsy'' (1925) He also published several short stories and co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jindřich Bačkovský
Jindřich Bačkovský (; May 4, 1912 – 2000) was an eminent Czechoslovak physicist whose work focused on X-ray spectroscopy, the structure of crystals, vacuum techniques, radiometry Radiometry is a set of techniques for measurement, measuring electromagnetic radiation, including visible light. Radiometric techniques in optics characterize the distribution of the radiation's power (physics), power in space, as opposed to phot ... and the physics of high pressures. Many of his findings are used in industry, especially in the manufacture of semiconductor parts and synthetic diamonds. External linksCzech archives (Czech) {{DEFAULTSORT:Backovsky, Jindrich < ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |