|
Jina Language
Jina (Zina) is an Afroasiatic language of Cameroon. The Muxule variety may be a distinct language. Jina is spoken in Zina commune, located just to the south of Logone-Birni commune. Muxule is spoken in a few villages to the north of Logone-Birni (department of Logone-et-Chari Logone-et-Chari is a department of Extreme-Nord Province in Cameroon. The department covers an area of 12,133 km and at the 2005 Census had a total population of 486,997. The capital of the department is at Kousséri. Most inhabitants of ..., Far North Region) by 1,500 speakers. The people of Zina claim to understand Lagwan and Munjuk better than Muxule. References Biu-Mandara languages Languages of Cameroon {{Cameroon-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cameroon
Cameroon (; french: Cameroun, ff, Kamerun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (french: République du Cameroun, links=no), is a country in west-central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west and north; Chad to the northeast; the Central African Republic to the east; and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Its coastline lies on the Bight of Biafra, part of the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean. Due to its strategic position at the crossroads between West Africa and Central Africa, it has been categorized as being in both camps. Its nearly 27 million people speak 250 native languages. Early inhabitants of the territory included the Sao civilisation around Lake Chad, and the Baka hunter-gatherers in the southeastern rainforest. Portuguese explorers reached the coast in the 15th century and named the area ''Rio dos Camarões'' (''Shrimp River''), which became ''Cameroon'' in English. Fulani soldiers founded the Adamawa Emirate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chadic Languages
The Chadic languages form a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken in parts of the Sahel. They include 150 languages spoken across northern Nigeria, southern Niger, southern Chad, the Central African Republic, and northern Cameroon. The most widely spoken Chadic language is Hausa, a ''lingua franca'' of much of inland Eastern West Africa. Composition Paul Newman (1977) classified the languages into the four groups which have been accepted in all subsequent literature. Further subbranching, however, has not been as robust; Roger Blench(2006), for example, only accepts the A/B bifurcation of East Chadic. Kujargé has been added from Blench (2008), who suggests Kujargé may have split off before the breakup of Proto-Chadic and then subsequently became influenced by East Chadic. Subsequent work by Joseph Lovestrand argues strongly that Kujarge is a valid member of East Chadic. The placing of Luri as a primary split of West Chadic is erroneous. Bernard Caron (200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
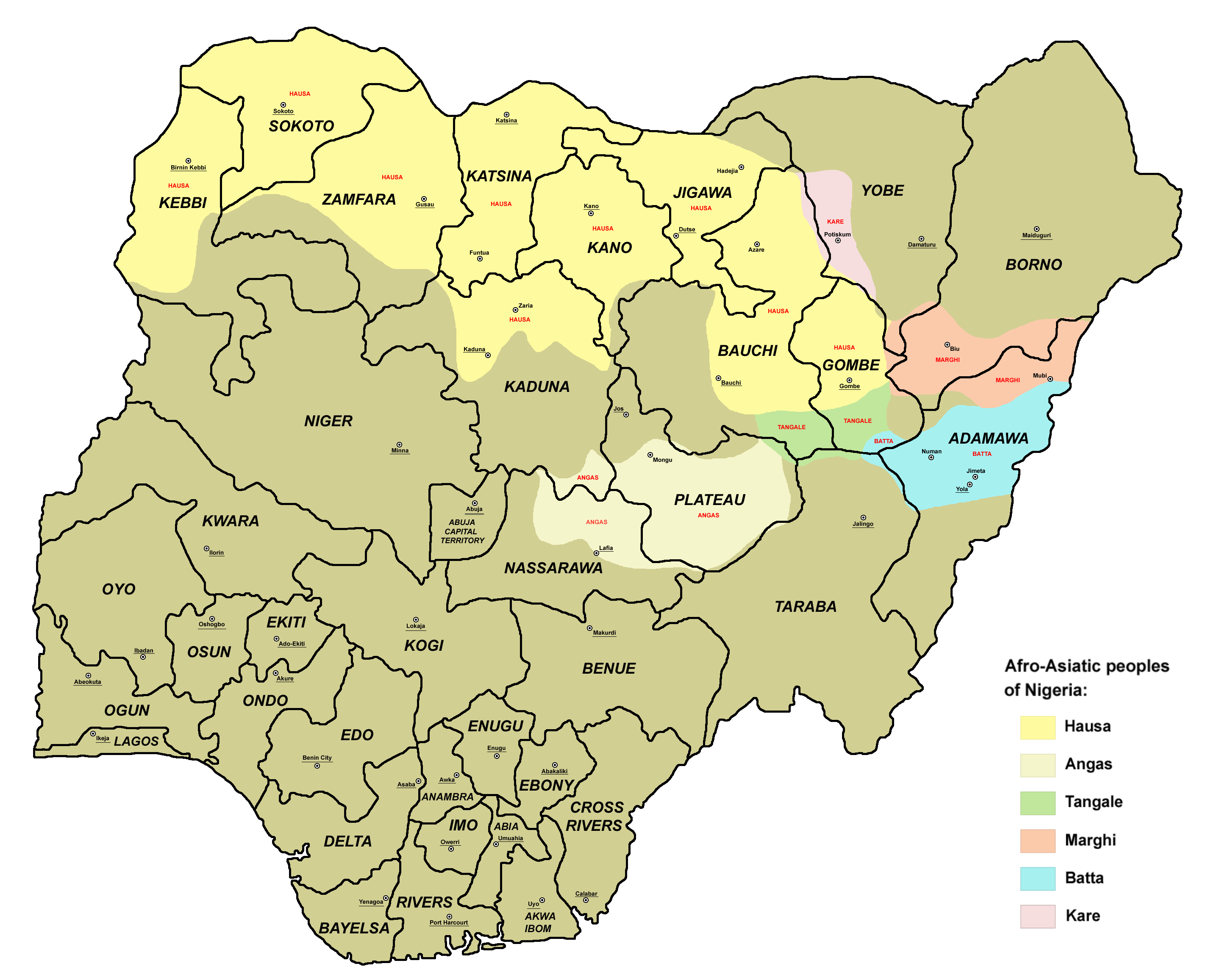
Biu–Mandara Languages
The Biu–Mandara or Central Chadic languages of the Afro-Asiatic family are spoken in Nigeria, Chad and Cameroon. A reconstruction of Proto-Central Chadic has been proposed by Gravina (2014). Languages Gravina (2014) Gravina (2014) classifies Central Chadic as follows, as part of a reconstruction of the proto-language. Letters and numbers in parentheses correspond to branches in previous classifications. The greatest changes are breaking up and reassigning the languages of the old Mafa branch (A.5) and Mandage (Kotoko) branch (B.1). *South **South ***Bata (A.8) ****Bata Proper: Bacama, Bata, Fali, Gude, Gudu, Holma (†), Jimi, Ngwaba (from A.1 Tera), Nzanyi, Sharwa ****Tsuvan: Tsuvan, Zizilivakan ***Daba (A.7) ****Daba Proper: Daba, Mazagway Hidi ****Mina: Mina, Mbudum ****Buwal: Buwal, Gavar ***Mafa (= South A.5 Mafa (d)): Mafa, Mefele, Cuvok ***Tera (A.1): ****East Tera: Boga, Ga'anda, Hwana ****(West Tera): Jara, Tera *** Sukur (A.6) *Hurza **Hurza (fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afroasiatic Languages
The Afroasiatic languages (or Afro-Asiatic), also known as Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic, and sometimes also as Afrasian, Erythraean or Lisramic, are a language family of about 300 languages that are spoken predominantly in the geographic subregions of Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and parts of the Sahara/Sahel. With the exception of its Semitic branch, all branches of the Afroasiatic family are exclusively native to the African continent. Afroasiatic languages have over 500 million native speakers, which is the fourth-largest number of native speakers of any language family (after Indo-European, Sino-Tibetan, and Niger–Congo). The phylum has six branches: Berber, Chadic, Cushitic, Egyptian, Semitic, and Omotic. The most widely spoken modern Afroasiatic language or dialect continuum by far is Arabic, a ''de facto'' group of distinct language varieties within the Semitic branch. The languages that evolved from Proto-Arabic have around 313 million na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zina
''Zināʾ'' () or ''zinā'' ( or ) is an Islamic legal term referring to unlawful sexual intercourse. According to traditional jurisprudence, ''zina'' can include adultery, fornication, prostitution, rape, sodomy, incest, and bestiality. ''Zina'' must be proved by testimony of four Muslim eyewitnesses to the actual act of penetration, or a confession repeated four times and not retracted later. The offenders must have acted of their own free will. Rapists could be prosecuted under different legal categories which used normal evidentiary rules.A. Quraishi (1999), Her honour: an Islamic critique of the rape provisions in Pakistan's ordinance on ''zina'', ''Islamic studies'', Vol. 38, No. 3, pp. 403–431 Making an accusation of ''zina'' without presenting the required eyewitnesses is called ''qadhf'' (), which is itself a ''hudud'' offense. There are very few recorded examples of the stoning penalty for ''zinā'' being implemented legally. Prior to legal reforms introduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logone-Birni
Logone-Birni is a town and commune in Cameroon. The town lies on the left (west) bank of the Logone River which at this point forms the state boundary between Cameroon and Chad. It is the capital of the Kotoko people, whose two other principal cities are Kousséri and Goulfey. History Logone-Birne means Fort Logone and was founded around 1700 by Prince Bruha. Dixon Denham visited Logone on 23 January 1824. He reported: :''"I rode down the river, which here flows with great beauty and majesty past the high walls of this capital Loggun; it comes direct from the south-west, with a rapid current. We enetred the town by the western gate, which leads to the principle street: it is as wide as Pall Mall and has large dwellings on each side, built with great uniformity, each having a courtyard in front, surrounded by a wall, and a handsome entrance. with a strong door hasped with iron: a number of the inhabitants were seated at their doors for the purpose of seeing us enter, with their s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logone-et-Chari
Logone-et-Chari is a department of Extreme-Nord Province in Cameroon. The department covers an area of 12,133 km and at the 2005 Census had a total population of 486,997. The capital of the department is at Kousséri. Most inhabitants of this department speak Chadian Arabic. Subdivisions The department is divided administratively into 10 communes and in turn into villages. Communes * Blangoua * Darak * Fotokol * Goulfey * Hile-Alifa * Kousséri * Logone-Birni * Makary * Waza * Zina Languages Languages spoken include: * Afade * Chadian Arabic * Jina * Kuo * Lagwan * Majera Majera (Mazera) is a minor Afro-Asiatic language of Chad and Cameroon. Majéra is spoken in and around Majéra in the arrondissement of Zina (Logone-et-Chari Logone-et-Chari is a department of Extreme-Nord Province in Cameroon. The departm ... * Malgbe * Maslam * Masana * Nzakambay References Departments of Cameroon Far North Region (Cameroon) {{Cameroon-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagwan Language
Lagwan (Logone) is a Chadic language spoken in northern Cameroon and southwestern Chad. Dialects include Logone-Birni and Logone-Gana. Lagwan is spoken in the northern part of Logone-Birni, from the banks of the Logone River to the Nigerian border (Logone-et-Chari Logone-et-Chari is a department of Extreme-Nord Province in Cameroon. The department covers an area of 12,133 km and at the 2005 Census had a total population of 486,997. The capital of the department is at Kousséri. Most inhabitants of ... Department, Far North Region). It is also spoken in Chad and Nigeria. It has 38,500 speakers in Cameroon. Phonology As is common in Chadic languages, the principal vowel is the low central vowel /a/; where there is no underlying V-slot, an epenthetic ‘zero vowel’ is inserted. Despite the limited distribution of the other vowels, /i, u, e, o/ have emerging phonological status. However, as has been observed in other Chadic languages, certain contrasts are productiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |