|
Jim Challinor
James Pevitt Challinor (2 August 1934 – 18 December 1976) was an English rugby union and professional rugby league footballer who played in the 1950s and 1960s, and coached rugby league in the 1960s and 1970s. A Great Britain international representative three-quarter back, he played club level rugby league (RL) for Warrington (with whom he won the 1954 Challenge Cup), and Barrow (who he also captained). Challinor later coached Great Britain as well as Barrow, Liverpool City and St. Helens. Challinor is a Warrington Wolves Hall of Fame inductee, only two men have played in, and coached Rugby League World Cup winning Great Britain sides, they are; Eric Ashton, and Jim Challinor. Biography Challinor was born in Warrington, Lancashire. Playing career Challinor had been offered a trial at Manchester United, but made his début aged-18 for Warrington against St. Helens in October 1952, he initially played on the , but later moved into the s. Challinor played right- and scored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric Ashton
Eric Ashton MBE (24 January 1935 – 20 March 2008) was an English World Cup winning professional rugby league footballer who played in the 1950s and 1960s, and coached in the 1960s, 1970s and 1980s. He played his whole top flight football career for Wigan along with at times both captaining and coaching them; his position of choice was right-. Over the span of his career he came to be known as one of the best centres in the modern game and formed a devastating partnership with Billy Boston somewhat because of this combination he went on to represent the Great Britain national side making his début in 1957. After his retirement from playing rugby league in 1969, Ashton went on to coach Wigan as well as Leeds, St. Helens, England and Great Britain; he also had a brief stint as chairman of St Helens in 1996. He was a member of the St Helens board for fifteen years. Background Ashton was born and brought up in St Helens, Lancashire, England. He began playing rugby league at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warrington
Warrington () is a town and unparished area in the Borough of Warrington, borough of the same name in the ceremonial county of Cheshire, England, on the banks of the River Mersey. It is east of Liverpool, and west of Manchester. The population in 2019 was estimated at 165,456 for the town's urban area, and just over 210,014 for the entire borough, the latter being more than double that of 1968 when it became a New towns in the United Kingdom, new town. Warrington is the largest town in the ceremonial county of Cheshire. In 2011 the unparished area had a population of 58,871. Warrington was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans at an important crossing place on the River Mersey. A new settlement was established by the Saxons, Saxon Wærings. By the Middle Ages, Warrington had emerged as a market town at the lowest bridging point of the river. A local tradition of textile and tool production dates from this time. The town of Warrington (north of the Mersey) is within the bounda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rugby League World Cup
The Rugby League World Cup is an international rugby league tournament contested by the top national men's representative teams. The tournament is administered by the International Rugby League and was first held in France in 1954, which was the first World Cup held for any form of rugby football. Folkard, 2003: 337 The idea of a rugby league World Cup tournament was first mooted in the 1930s with the French proposal to hold a tournament in 1931, and again in 1951. The tournament's structure, frequency, and size has varied significantly throughout its history. The winners are awarded the Paul Barrière Trophy, named after Paul Barrière, the French Rugby League President of the 1940s and 1950s. Three nations have won the tournament; twelve times, three times, and once. Australia has been in the final of every World Cup, except the first in 1954, when they came third, which was considered to be a complete upset with the bookmakers at the time having Australia as strong fav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1954–55 Northern Rugby Football League Season
The 1954–55 Rugby Football League season was the 60th season of rugby league football. Season summary Warrington won their second Championship when they beat Oldham 7-3 in the play-off final. They also ended the regular season as league leaders. The Challenge Cup winners were Barrow who beat Workington Town 21-12 in the final. Blackpool Borough joined the competition. Warrington won the Lancashire League, and Leeds won the Yorkshire League. Barrow beat Oldham 12–2 to win the Lancashire County Cup, and Halifax beat Hull F.C. 22–14 to win the Yorkshire County Cup. Championship Play-offs Challenge Cup This was also the first time that there was an all-Cumbrian Final. Barrow beat Workington Town 21-12 in the final played at Wembley before a crowd of 66,513. Captained by former Great Britain skipper Willie Horne, this was Barrow’s first Challenge Cup Final win, although have been runners-up on four other occasions. Jack Grundy, Barrow's was awarded the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oldham R
Oldham is a large town in Greater Manchester, England, amid the Pennines and between the rivers Irk and Medlock, southeast of Rochdale and northeast of Manchester. It is the administrative centre of the Metropolitan Borough of Oldham, which had a population of 237,110 in 2019. Within the boundaries of the historic county of Lancashire, and with little early history to speak of, Oldham rose to prominence in the 19th century as an international centre of textile manufacture. It was a boomtown of the Industrial Revolution, and among the first ever industrialised towns, rapidly becoming "one of the most important centres of cotton and textile industries in England." At its zenith, it was the most productive cotton spinning mill town in the world,. producing more cotton than France and Germany combined. Oldham's textile industry fell into decline in the mid-20th century; the town's last mill closed in 1998. The demise of textile processing in Oldham depressed and heavily aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
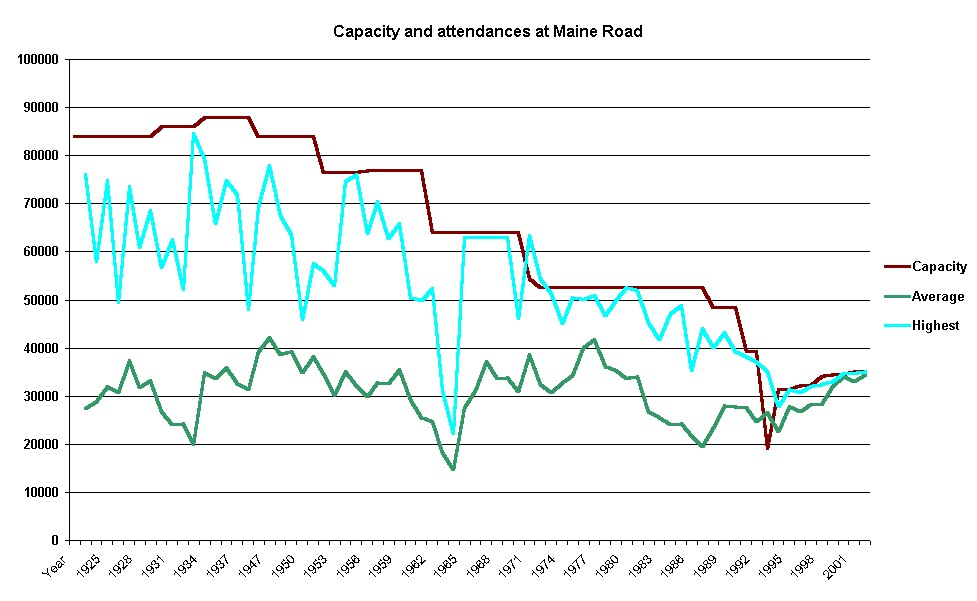
Maine Road
Maine Road was a football stadium in Moss Side, Manchester, England, that was home to Manchester City F.C. from 1923 to 2003. It hosted FA Cup Semi-finals, FA Cup semi-finals, the FA Community Shield, Charity Shield, a 1984 Football League Cup Final, League Cup final and England national football team, England matches. Maine Road's List of record home attendances of English football clubs, highest attendance of 84,569 was set in 1934 at an FA Cup sixth round match between Manchester City and Stoke City F.C., Stoke City, a record for an English club ground. By Manchester City's last season at Maine Road in 2002–03 in English football, 2002–03, it was an all-seater stadium with a capacity of 35,150 and of haphazard design with stands of varying heights due to the ground being renovated several times over its 80-year history. The following season Manchester City moved to the City of Manchester Stadium in east Manchester, a mile from the Manchester city centre, city centre and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rugby Football League Championship
The Rugby Football League Championship First Division was the top division of rugby league in England between 1895 and 1996, when it was replaced by the Super League. History 1895–1904: Foundations The first season of rugby league (1895–96) saw all the breakaway clubs play in a single league competition. The addition of new teams and the problems of travelling led to the league being split in two for the following season; into the Yorkshire League and the Lancashire League. This arrangement lasted until the 1901–02 season, when the top clubs from each league resigned and formed a single new competition. The following season the remaining clubs in the Yorkshire and Lancashire Leagues were re-organised to form a second division. 1905–1970: Restructure In 1905–06 the two divisions were re-combined into a single competition. Clubs played all the teams in their own county on a home-and-away basis, results counting towards the re-formed Yorkshire and Lancashire Lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bradford
Bradford is a city and the administrative centre of the City of Bradford district in West Yorkshire, England. The city is in the Pennines' eastern foothills on the banks of the Bradford Beck. Bradford had a population of 349,561 at the 2011 census; the second-largest population centre in the county after Leeds, which is to the east of the city. It shares a continuous built-up area with the towns of Shipley, Silsden, Bingley and Keighley in the district as well as with the metropolitan county's other districts. Its name is also given to Bradford Beck. It became a West Riding of Yorkshire municipal borough in 1847 and received its city charter in 1897. Since local government reform in 1974, the city is the administrative centre of a wider metropolitan district, city hall is the meeting place of Bradford City Council. The district has civil parishes and unparished areas and had a population of , making it the most populous district in England. In the century lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odsal Stadium
Odsal Stadium in Bradford, West Yorkshire, England, is the home of Bradford Bulls Rugby League team. It has also been used by the Bradford Dukes speedway team, BRISCA F1 and F2 stock cars, the football team Bradford City, following the Valley Parade fire, and for baseball, basketball, kabbadi, show jumping, tennis, live music, international Rugby League and the 1997 Speedway Grand Prix of Great Britain. The stadium's highest attendance was 102,569 in 1954 for the Warrington- Halifax Challenge Cup Final replay, and for a domestic, non-final, Rugby League match, 69,429 at the third round Challenge Cup tie between Bradford Northern and Huddersfield in 1953. The stadium is owned by Bradford City Council, but due to financial problems the Rugby Football League purchased the lease on it in 2012. History 1933–1935: Construction and opening Formed in 1907, the Bradford Northern club had played at a number of venues including the Greenfield Athletic Ground in Dudley Hill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1953–54 Northern Rugby Football League Season
The 1953–54 Rugby Football League season was the 59th season of rugby league football played in England. The championship, which involved thirty teams, started in August, 1953 and culminated in a finals play-off series in April, 1954 which resulted in a championship final between Warrington and Halifax. The season was also punctuated by the 1954 Rugby League World Cup, the first ever, and is also notable for its Challenge Cup final, which was drawn and had to be re-played, attracting a world record crowd for a rugby football match of either code. Season summary The 1953–54 season saw Brian Bevan become the highest try scorer in rugby league history when he passed the 446 tries mark set by Alf Ellaby. *League Champions: Warrington (8-7 v Halifax) *Challenge Cup Winners: Warrington (8-4 v Halifax in replay after 4–4 draw) Warrington won the Lancashire League, and Halifax won the Yorkshire League. St. Helens beat Wigan 16–8 to win the Lancashire County Cup, and Brad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replay (sports)
A replay (also called a rematch) is the repetition of a match in many sports. Association football In association football, replays were often used to decide the winner in a knock-out tournament when the previous match ended in a draw, especially in finals. In 1970, FIFA (the worldwide governing body of the sport) and IFAB (the international rules committee for the sport) allowed penalty shoot-outs to be held if a match ended in a draw after extra time. The penalty shootout made its appearance immediately thereafter. The first instance of a shootout replacing a replay (rather than lots) was the final of the 1976 European championship. The shootout's first use at the World Cup took place in the 1982 semi-finals. Replays are now only used in the early rounds of the English FA Cup tournament, as well as rounds up until the semi-finals in the Scottish Cup. Games going to replays in the FA Cup since 1991 are only replayed once, with extra time and penalty shootouts used to decid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1953–54 Challenge Cup
The 1954 Challenge Cup was the 53rd staging of rugby league's oldest knockout competition, the Challenge Cup. It featured clubs from the 1953–54 Northern Rugby Football League season and is particularly notable for its final, which had to be replayed at Odsal after a drawn match at Wembley, with the replay attracting possibly the largest ever crowd in world rugby league history. First round Second round Quarterfinals Semifinals Final Halifax and Warrington, the teams who had finished first and second respectively on the Championship ladder (separated by only one competition point), reached the Challenge Cup final Saturday 24 April 1954. The game was played at Wembley, and 81,841 spectators saw what turned out to be a comparatively lacklustre match. After a couple of penalties, Halifax held a 4-0 lead at half time. In the second half Warrington drew level, also kicking two penalties. There was no further scoring and the match finished in a draw, at 4 - 4. This match rema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |