|
Jie-zhong Zou
Jie-zhong Zou (born October 15, 1947) is a mathematician known for his research on mathematical probability theory and its applications, in particular in topics such as homogeneous Markov chains, queuing theory and mathematical finance. He entered Changsha Railway Institute (Central South University now) in 1980 and received his Ph.D. at the Changsha Railway Institute in 1987 under advisor Zhen-ting Hou. Since 1987 Jie-zhong Zou has been on the faculty at Changsha Railway Institute (Central South University now). He was awarded the Rollo Davidson Prize in 1987, and was elected a Fellow of the Chinese Mathematical Society The Chinese Mathematical Society (CMS, ) is an academic organization for Chinese mathematicians, with the official websitwww.cms.org.cn It is a member of China Association of Science and Technology. History The Chinese Mathematical Society (CMS) w .... He attended the International Congress of Mathematician in Beijing in 2002. Papers * Jie-zhong Zou, "The os ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central South University
Central South University (CSU; ) is a national public university in Changsha, Hunan, China. The university is sponsored by the Ministry of Education of the People's Republic of China, China Ministry of Education. It is a Chinese state Double First Class University Plan, Double First Class University. Hunan Medical University, Changsha Railway College, and Central South University of Technology merged to establish Central South University in April 2000. History CSU was established by approval of the State Council of the People's Republic of China, State Council on April 29, 2000 by merging three separate universities: Hunan Medical University (HMU), Changsha Railway University (CRU) and Central South University of Technology (CSUT). HMU, formerly under the administration of the Ministry of Health, dates back to 1914 when Xiangya Medical College was founded through the joint efforts of Hunan Yuqun Society and the Yale-China Association. CRU, one of the universities under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems. Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, structure, space, models, and change. History One of the earliest known mathematicians were Thales of Miletus (c. 624–c.546 BC); he has been hailed as the first true mathematician and the first known individual to whom a mathematical discovery has been attributed. He is credited with the first use of deductive reasoning applied to geometry, by deriving four corollaries to Thales' Theorem. The number of known mathematicians grew when Pythagoras of Samos (c. 582–c. 507 BC) established the Pythagorean School, whose doctrine it was that mathematics ruled the universe and whose motto was "All is number". It was the Pythagoreans who coined the term "mathematics", and with whom the study of mathematics for its own sake begins. The first woman mathematician recorded by history was Hypati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with probability. Although there are several different probability interpretations, probability theory treats the concept in a rigorous mathematical manner by expressing it through a set of axioms. Typically these axioms formalise probability in terms of a probability space, which assigns a measure taking values between 0 and 1, termed the probability measure, to a set of outcomes called the sample space. Any specified subset of the sample space is called an event. Central subjects in probability theory include discrete and continuous random variables, probability distributions, and stochastic processes (which provide mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic or uncertain processes or measured quantities that may either be single occurrences or evolve over time in a random fashion). Although it is not possible to perfectly predict random events, much can be said about their behavior. Two major results in probability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homogeneous Markov Chain
A Markov chain or Markov process is a stochastic model describing a sequence of possible events in which the probability of each event depends only on the state attained in the previous event. Informally, this may be thought of as, "What happens next depends only on the state of affairs ''now''." A countably infinite sequence, in which the chain moves state at discrete time steps, gives a discrete-time Markov chain (DTMC). A continuous-time process is called a continuous-time Markov chain (CTMC). It is named after the Russian mathematician Andrey Markov. Markov chains have many applications as statistical models of real-world processes, such as studying cruise control systems in motor vehicles, queues or lines of customers arriving at an airport, currency exchange rates and animal population dynamics. Markov processes are the basis for general stochastic simulation methods known as Markov chain Monte Carlo, which are used for simulating sampling from complex probability distri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
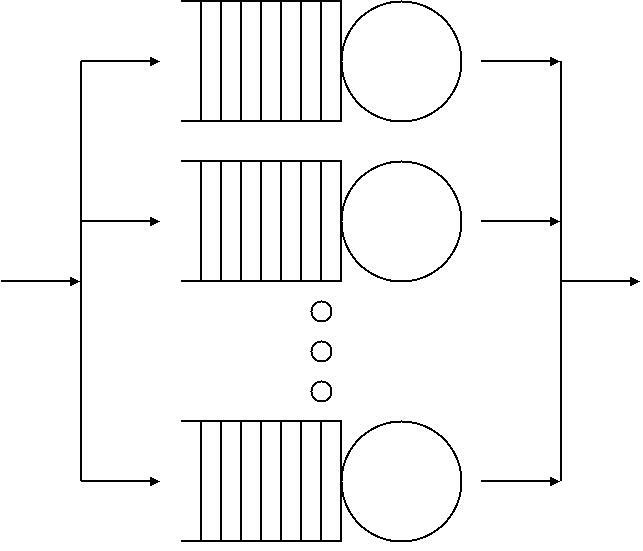
Queuing Theory
Queueing theory is the mathematical study of waiting lines, or queues. A queueing model is constructed so that queue lengths and waiting time can be predicted. Queueing theory is generally considered a branch of operations research because the results are often used when making business decisions about the resources needed to provide a service. Queueing theory has its origins in research by Agner Krarup Erlang when he created models to describe the system of Copenhagen Telephone Exchange company, a Danish company. The ideas have since seen applications including telecommunication, traffic engineering, computing and, particularly in industrial engineering, in the design of factories, shops, offices and hospitals, as well as in project management. Spelling The spelling "queueing" over "queuing" is typically encountered in the academic research field. In fact, one of the flagship journals of the field is ''Queueing Systems''. Single queueing nodes A queue, or queueing node ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Finance
Mathematical finance, also known as quantitative finance and financial mathematics, is a field of applied mathematics, concerned with mathematical modeling of financial markets. In general, there exist two separate branches of finance that require advanced quantitative techniques: derivatives pricing on the one hand, and risk and portfolio management on the other. Mathematical finance overlaps heavily with the fields of computational finance and financial engineering. The latter focuses on applications and modeling, often by help of stochastic asset models, while the former focuses, in addition to analysis, on building tools of implementation for the models. Also related is quantitative investing, which relies on statistical and numerical models (and lately machine learning) as opposed to traditional fundamental analysis when managing portfolios. French mathematician Louis Bachelier's doctoral thesis, defended in 1900, is considered the first scholarly work on mathematical fina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rollo Davidson Prize
The Rollo Davidson Prize is a prize awarded annually to early-career probabilists by the Rollo Davidson trustees. It is named after English mathematician Rollo Davidson (1944–1970). Rollo Davidson Trust In 1970, Rollo Davidson, a Fellow-elect of Churchill College, Cambridge died on Piz Bernina, a mountain in Switzerland. In 1975, a trust fund was established at Churchill College in his memory, endowed initially through the publication in his honour of two volumes of papers, edited by E. F. Harding and D. G. Kendall. The Rollo Davidson Trust has awarded an annual prize to young probabilists since 1976, and has organized occasional lectures in honour of Davidson. Since 2012 the Trust has also awarded an annual Thomas Bond Sprague Prize.http://www.admin.cam.ac.uk/reporter/2011-12/weekly/6273/section12.shtml#heading2-35 Cambridge University Reporter CLXII no 38 List of recipients of the Rollo Davidson Prize * 1976 – Brian D. Ripley * 1977 – Olav Kallenberg * 1978 – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Mathematical Society
The Chinese Mathematical Society (CMS, ) is an academic organization for Chinese mathematicians, with the official websitwww.cms.org.cn It is a member of China Association of Science and Technology. History The Chinese Mathematical Society (CMS) was founded in July 1935 in Shanghai. The inaugural conference was held in the library of Shanghai Jiao Tong University on July 25, and 33 people attended the meeting. Its founding members included Hu Dunfu, Feng Zuxun, Zhou Meiquan, Jiang Lifu, Xiong Qinglai, Chen Jiangong, Gu Deng, Su Buqing, Jiang Zehan, Qian Baozong, and Fu Zhongsun. Hu Dunfu served as its first president. The society published ''Journal of Chinese Mathematical Society'', and a math promoting magazine, ''Mathematics Magazine''. In 1952 and 1953, these two journals was renamed ''Acta Mathematica Sinica'', and '' Mathematics Letters''. The CMS was originally located at the China Science Society at 533 Albert Road (now South Shaanxi Road) in Shanghai. After establishm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematicians From Hunan
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems. Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, structure, space, models, and change. History One of the earliest known mathematicians were Thales of Miletus (c. 624–c.546 BC); he has been hailed as the first true mathematician and the first known individual to whom a mathematical discovery has been attributed. He is credited with the first use of deductive reasoning applied to geometry, by deriving four corollaries to Thales' Theorem. The number of known mathematicians grew when Pythagoras of Samos (c. 582–c. 507 BC) established the Pythagorean School, whose doctrine it was that mathematics ruled the universe and whose motto was "All is number". It was the Pythagoreans who coined the term "mathematics", and with whom the study of mathematics for its own sake begins. The first woman mathematician recorded by history was Hypatia o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Theorists
Probability is the branch of mathematics concerning numerical descriptions of how likely an event is to occur, or how likely it is that a proposition is true. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1, where, roughly speaking, 0 indicates impossibility of the event and 1 indicates certainty."Kendall's Advanced Theory of Statistics, Volume 1: Distribution Theory", Alan Stuart and Keith Ord, 6th Ed, (2009), .William Feller, ''An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications'', (Vol 1), 3rd Ed, (1968), Wiley, . The higher the probability of an event, the more likely it is that the event will occur. A simple example is the tossing of a fair (unbiased) coin. Since the coin is fair, the two outcomes ("heads" and "tails") are both equally probable; the probability of "heads" equals the probability of "tails"; and since no other outcomes are possible, the probability of either "heads" or "tails" is 1/2 (which could also be written as 0.5 or 50%). These conce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |