|
Jhulaghat
Jhulaghat ( Kumaoni-Doteli:झुलाघाट) is a small suspension bridge over Kali river on Indo-Nepal border between Uttarakhand and Sudurpashchim. Uttarakhand is a state of India west of the Kali river while Sudurpashchim is a province of Nepal, east of Kali. Jhulaghat is an indo-aryan language word which literally means "Hanging pier". The landmark is known as Jhulaghat after the suspension bridge. The suspension bridge is small in size so only pedestrian, cyclist and biker can cross the border through it. There has been a small town emerged both side of the bridge. The town emerged Indian side of the bridge is a part of Munakot Tehsil in Pithoragarh District of Uttarakhand and Nepalese side is a part of Dasharathchand Municipality. Mahakali-Jhulaghat Custom Office There is a custom station both side of the river in India and Nepal. Pithoragarh-Jhulaghat road connects the Jhulaghat to Pithoragarh which is 38 KM at distance from Jhulaghat. Naini Saini is the nearest ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid-Hills Highway
Pushpalal Highway (H18) ( ne, पुष्पलाल लोकमार्ग (रा.१८), ''Puṣpalāl Lōkamārg (Rā.18)'') is an ongoing road project in Nepal, which is thought to be long. After completion, it will be the longest national highway of Nepal. Nepal has three geographical regions from east to west, plain land or Terai in south, higher mountains or Himalayas in north and hills in middle region. The highway runs through the mid-hills region only. It starts from easternmost hill at Chiyo Bhanjyang of Panchthar District (Province No. 1) and ends at westernmost hill at Jhulaghat of Baitadi District in far west (Sudurpashchim Province). See also * Madan Bhandari Inner Terai Highway *Mahendra Highway Mahendra Highway (), also called East-West Highway () runs across the Terai geographical region of Nepal, from Mechinagar in the east to Bhim Datta in the west, cutting across the entire width of the country. It is the longest highway in Nepal a ... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pithoragarh District
Pithoragarh district is the easternmost district in the state of Uttarakhand. It is located in the Himalayas and has an area of and a population of 483,439 (as of 2011). The city of Pithoragarh, located in Saur Valley, is its headquarters. The district is within the Kumaon division of Uttarakhand state. The Tibet plateau is situated to the north and Nepal is to the east. The Kali River which originates from the Kalagiri Mountain flows south, forming the eastern border with Nepal. The Hindu pilgrimage route for Mount Kailash-Lake Manasarovar passes through this district via Lipulekh Pass in the greater Himalayas. The district is administratively divided into six Tehsils: Munsyari; Dharchula; Didihat; Berinag; Gangolihat; and Pithoragarh. Naini Saini Airport is the nearest civil airport, but it does not have a regular scheduled commercial passenger service. The mineral deposits present in the district are magnesium ore, copper ore, limestone, and slate. There are 11 tehsils. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharda River
The Sharda River, also called Kali River and Mahakali River, originates at Kalapani in the Himalayas at an elevation of in the Pithoragarh district in Uttarakhand, India. It flows along Nepal's western border with India and has a basin area of . It joins Ghaghra River, a tributary of the Ganges. It takes the name Kali River from the union of the two streams at Gunji as it flows through the hills. After Brahmadev Mandi near Tanakpur, it enters the Terai plains, where it is called Sharda River. It offers potential for hydroelectric power generation. The river is also proposed as source for one of the many projects in the Himalayan component of the Indian Rivers Inter-link project. Etymology and naming It is named after Śāradā, which is another name for Saraswati, the goddess of learning. It is called Mahakali River in ne, महाकाली नदी, mahākālī nadī, , in Hindi, and Kali Gad (Kumaoni: काली गाड़, ''kālī gād'') or Kali Ganga in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
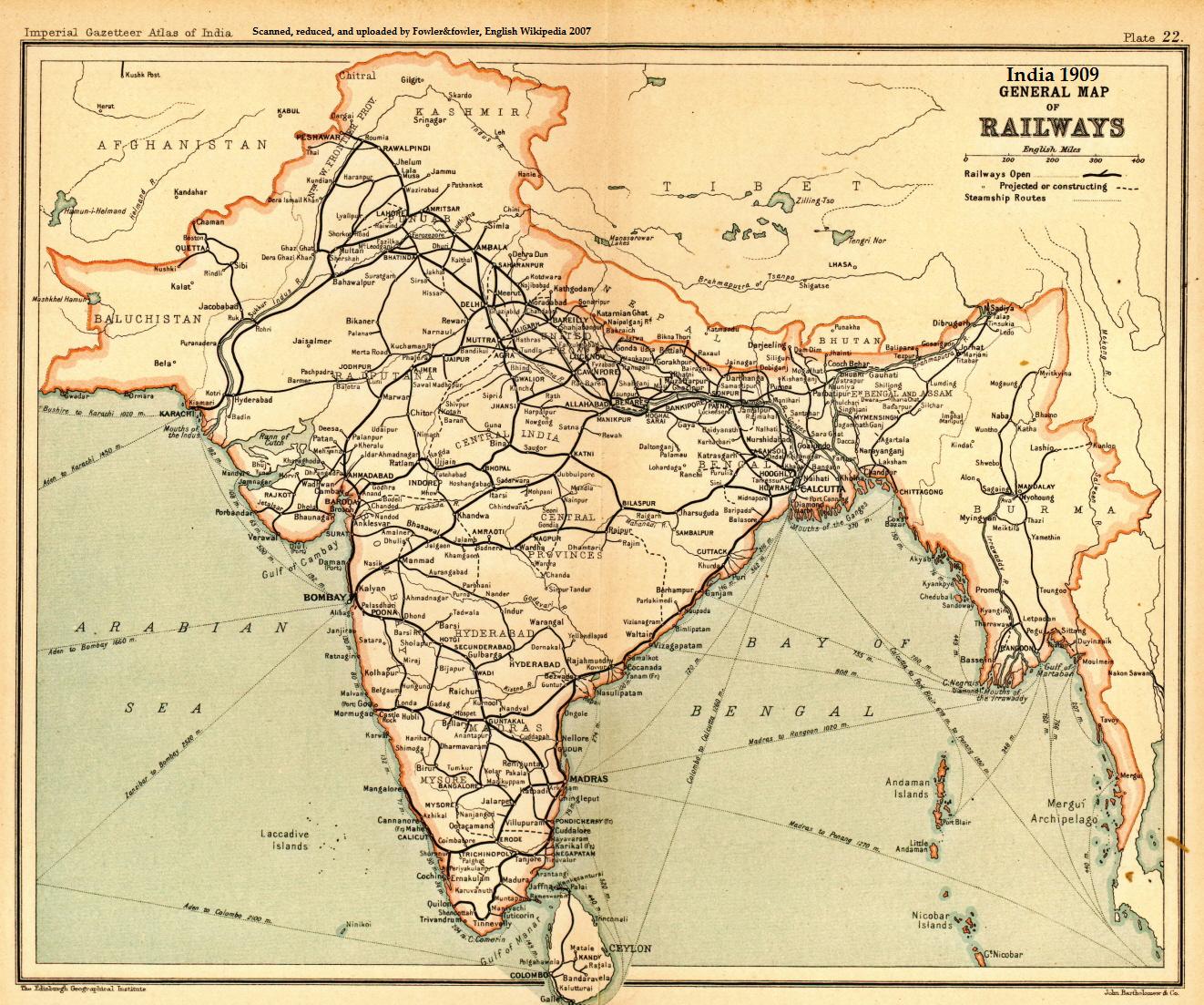
India–Nepal Border
The India–Nepal border is an open international border running between Nepal and the Republic of India. The long border includes the Himalayan territories as well as Indo-Gangetic Plain. The current border was delimited after the Sugauli treaty of 1816 between Nepal and the British Raj. Following Indian independence, the current border was recognised as the border between the Kingdom of Nepal and the Dominion of India. Description The border starts in the west at the western tripoint with China near the Tinkar Pass. It then proceeds to the south-west through the Himalayas, the Sivalik Hills and then the Gangetic plain, initially overland and then utilising the Mahakali river or Sharda River. Just east of Majhola it turns to the south-east and proceeds in that direction overland, occasionally utilising various rivers and hill crests. North-west of Islampur the border turns to the north-east and proceeds overland to the eastern Chinese tripoint. History The border region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kumaoni Language
Kumaoni (; ) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by over two million people of the Kumaon region of the state of Uttarakhand in northern India and parts of Doti region in Western Nepal. As per 1961 survey there were 1,030,254 Kumaoni speakers in India. The number of speakers increased to 2.2 million in 2011. Kumaoni is not endangered but UNESCO's ''Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger'' designates it as a language in the ''unsafe'' category, meaning it requires consistent conservation efforts. Script Kumaoni uses the Devanagari script. Geographic distribution and dialects There are several dialects spoken in the Kumaon region. There is not single accepted method of dividing up the dialects of Kumaoni. Broadly speaking, Kali (or Central) Kumaoni is spoken in Almora and northern Nainital. North-eastern Kumaoni is spoken in Pithoragarh. South-eastern Kumaoni is spoken in South-eastern Nainital. Western Kumaoni is spoken west of Almora and Nainital. More specifically: * Johari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Siliguri Corridor, which borders Bangladesh. Sikkim is the least populous and second smallest among the Indian states. Situated in the Eastern Himalaya, Sikkim is notable for its biodiversity, including alpine and subtropical climates, as well as being a host to Kangchenjunga, the highest peak in India and third highest on Earth. Sikkim's capital and largest city is Gangtok. Almost 35% of the state is covered by Khangchendzonga National Park – a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The Kingdom of Sikkim was founded by the Namgyal dynasty in the 17th century. It was ruled by Buddhist priest-kings known as the Chogyal. It became a princely state of British India in 1890. Following Indian independence, Sikkim continued its protectorate status with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province No
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outside Italy. The term ''province'' has since been adopted by many countries. In some countries with no actual provinces, "the provinces" is a metaphorical term meaning "outside the capital city". While some provinces were produced artificially by colonial powers, others were formed around local groups with their own ethnic identities. Many have their own powers independent of central or federal authority, especially in Canada and Pakistan. In other countries, like China or France, provinces are the creation of central government, with very little autonomy. Etymology The English word ''province'' is attested since about 1330 and derives from the 13th-century Old French , which itself comes from the Latin word , which referred to the sphere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiyo Bhanjyang
Chiyo Bhanjyang ( ne, चियो भञ्ज्याङ) (also known as Chiwa Bhanjyang or Chiya Bhanjyang) is an international mountain pass located at Nepal-Sikkim (India) border. It is located at elevation of above the sea level. The Mid-Hills Highway ( Pushpalal Highway) starts from here and runs across the mid-hills in Nepal. Across the border, in Sikkim "Uttarey-Chiwa Bhanjyang road" starts and connects Gangtok Gangtok is a city, municipality, the capital and the largest populated place of the Indian state of Sikkim. It is also the headquarters of the East Sikkim district, Gangtok District. Gangtok is in the eastern Himalayas, Himalayan range, at an e ... at 170 km of distance. References External linksJoint Press Statement on the Visit of the Prime Minister to Nepal [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahakali Highway
Mahakali Highway ( Nepali: महाकाली राजमार्ग) is a highway in western Nepal. It links Api Municipality in the Lesser Himalayas with the Western Terai region around Dhangadhi spanning around 325 km and links with State Highway 90 in India in the South. Mahakali Highway is proposed to be extended by 90 km to link Tinkar in Darchula District Darchula District ( ne, दार्चुला जिल्ला , a part of Sudurpashchim Province, is one of the nine districts of province and one of seventy-seven districts of Nepal. The district, with Khalanga ( Mahakali Municipality) .... References {{Highways in Nepal Highways in Nepal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kathgodam
Kathgodam is a suburb of Haldwani city in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand state of India. It used to be a part of the twin township of Haldwani-Kathgodam, and is immediately north of Haldwani. It is one of the important collection centres for forest products obtained from Kumaon Himalayas. History Literally meaning ''timber depot'', Kathgodam was a small village in 1901 with a population of 375, though its importance grew rapidly after the railway line was extended here in late 19th century, after it reached Haldwani in 1884. It was previously called 'Chauhan Patta' as it is still recorded in the land records. The advent of the residence of Dan Singh Bist nearby in Beer Bhatti, Jeolikote, and his setting up his major timber depot as the 'Timber King of India' as Chauhan Patta, led to it being called 'Kathgodam'. Similarly, Beer Bhatti is called thus as it was previously an area where the British India Corporation Limited pursued a Beer Brewery until 1924 when Dan Singh Bist p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pithoragarh
Pithoragarh ( Kumaoni: ''Pithor'garh'') is a Himalayan city with a Municipal Board in Pithoragarh district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the fourth largest city of Kumaon and the largest in Kumaon hills. It is an education hub of the hilly region as the town has Laxman Singh Mahar Govt.P.G.College, Seemant Institute of Technology, now known as Nanhi Pari Seemant Engineering Institute and a nursing college. Etymology "The district is named after its headquarters town, Pithoragarh. Tradition has it that during the reign of the Chand Rajas of Kumaon, one Piru, also called Prithvi Gosain, built a fort here and named it Prithvigarh which, in the course of time, got changed to Pithoragarh." History Pithoragarh city and its surrounding areas were part of the Manaskhand region, which extended from the Kailash Mountain in the north to Bhabar & Terai in the south, as mentioned in the Skanda Purana. The Asuras and Nagas appear to be the earliest inhabitants of the reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |