|
Jewish Religious Movements
Jewish religious movements, sometimes called " denominations", include different groups within Judaism which have developed among Jews from ancient times. Today, the most prominent divisions are between traditionalist Orthodox movements (including Haredi and Religious Zionist () sects); modernist movements such as Conservative, Masorti and Reform Judaism; and secular or Jews. The movements differ in their views on various issues. These issues include the level of observance, the methodology for interpreting and understanding Jewish law, biblical authorship, textual criticism, and the nature or role of the messiah (or messianic age). Across these movements, there are marked differences in liturgy, especially in the language in which services are conducted, with the more traditional movements emphasizing Hebrew. The sharpest theological division occurs between Orthodox and non-Orthodox Jews who adhere to other denominations, such that the non-Orthodox movements are sometimes ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Denomination
A religious denomination is a subgroup within a religion that operates under a common name and tradition among other activities. The term refers to the various Christian denominations (for example, Eastern Orthodox, Catholic, and the many varieties of Protestantism). It is also used to describe the five major branches of Judaism ( Karaite Judaism, Orthodox, Conservative, Reform, and Reconstructionist). Within Islam, it can refer to the branches or sects (such as Sunni, Shia), as well as their various subdivisions such as sub-sects, schools of jurisprudence, schools of theology and religious movements. The world's largest religious denominations are Sunni Islam and Catholic Church. Christianity A Christian denomination is a generic term for a distinct religious body identified by traits such as a common name, structure, leadership and doctrine. Individual bodies, however, may use alternative terms to describe themselves, such as church or fellowship. Divisions b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Services
Jewish prayer ( he, תְּפִלָּה, ; plural ; yi, תּפֿלה, tfile , plural ; Yinglish: davening from Yiddish 'pray') is the prayer recitation that forms part of the observance of Rabbinic Judaism. These prayers, often with instructions and commentary, are found in the '' Siddur'', the traditional Jewish prayer book. Prayer, as a "service of the heart", is in principle a Torah-based commandment. It is not time-dependent and is mandatory for both Jewish men and women. However, the rabbinic requirement to recite a specific prayer text does differentiate between men and women: Jewish men are obligated to recite three prayers each day within specific time ranges ('' zmanim''), while, according to many approaches, women are only required to pray once or twice a day, and may not be required to recite a specific text. Traditionally, three prayer services are recited daily: * Morning prayer: '' Shacharit'' or ''Shaharit'' (, "of the dawn") * Afternoon prayer: '' M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
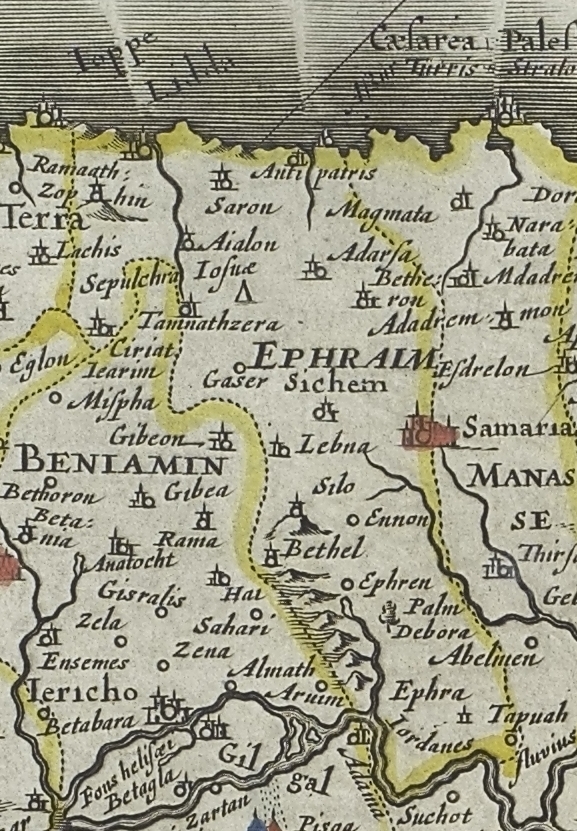
Tribe Of Manasseh
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Manasseh (; Hebrew: ''Ševet Mənašše,'' Tiberian: ''Šēḇeṭ Mănašše'') was one of the Tribes of Israel. It is one of the ten lost tribes. Together with the Tribe of Ephraim, Manasseh also formed the ''House of Joseph''. Biblical Chronicle According to the biblical chronicle, the Tribe of Manasseh was a part of a loose confederation of Israelite tribes from after the conquest of the land by Joshua until the formation of the first Kingdom of Israel in c. 1050 BC. No central government existed, and in times of crisis the people were led by ad hoc leaders known as Judges (see Book of Judges). With the growth of the threat from Philistine incursions, the Israelite tribes decided to form a strong centralised monarchy to meet the challenge, and the Tribe of Manasseh joined the new kingdom with Saul as the first king. After the death of Saul, all the tribes other than Judah remained loyal to the House of Saul, but after the death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe Of Ephraim
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Ephraim ( he, אֶפְרַיִם, ''ʾEp̄rayīm,'' in pausa: אֶפְרָיִם, ''ʾEp̄rāyīm'') was one of the tribes of Israel. The Tribe of Manasseh together with Ephraim formed the ''House of Joseph''. It is one of the ten lost tribes. The etymology of the name is disputed.For the etymology, see Ephraim as portrayed in biblical narrative According to the Bible, the Tribe of Ephraim is descended from a man named Ephraim, who is recorded as the son of Joseph, the son of Jacob, and Asenath, the daughter of Potiphera. The descendants of Joseph formed two of the tribes of Israel, whereas the other sons of Jacob were the founders of one tribe each. The Bible records that the Tribe of Ephraim entered the land of Canaan during its conquest by Joshua, a descendant of Ephraim himself. However, many archeologists have abandoned the idea that Joshua carried out a conquest of Canaan similar to that described in the Book of Joshua, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samaritans
Samaritans (; ; he, שומרונים, translit=Šōmrōnīm, lit=; ar, السامريون, translit=as-Sāmiriyyūn) are an ethnoreligious group who originate from the ancient Israelites. They are native to the Levant and adhere to Samaritanism, an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic and ethnic religion. Samaritan tradition claims the group descends from the northern Twelve Tribes of Israel, Israelite tribes who were not Assyrian captivity, deported by the Neo-Assyrian Empire after the destruction of the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Kingdom of Israel. They consider Samaritanism to be the true Yahwism, religion of the ancient Israelites and regard Judaism as a closely related but altered religion. Samaritans also regard Mount Gerizim (near both Nablus and biblical Shechem), and not the Temple Mount in Jerusalem, to be the holiest place on Earth. They attribute the schism between Samaritanism and Judaism to have been caused by Eli (biblical figure), Eli creating an alternate shrin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Political Movements
Jewish political movements refer to the organized efforts of Jews to build their own political parties or otherwise represent their interest in politics outside the Jewish community. From the time of the siege of Jerusalem by the Romans to the foundation of Israel the Jewish people had no territory, and, until the 19th century they by-and-large were also denied equal rights in the countries in which they lived. Thus, until the 19th century effort for the emancipation of the Jews, almost all Jewish political struggles were internal, and dealt primarily with either religious issues or issues of a particular Jewish community. (See Judaism and politics.) Birth of Jewish political movements Since Jews were excluded as outsiders throughout Europe, they were mostly shut out of politics or any sort of participation in the wider political and social sphere of the nations in which they were involved until the Enlightenment, and its Jewish counterpart, Haskalah, made popular movements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Ethnic Divisions
Jewish ethnic divisions refer to many distinctive communities within the world's ethnically Jewish population. Although considered a self-identifying ethnicity, there are distinct ethnic subdivisions among Jews, most of which are primarily the result of geographic branching from an originating Israelite population, mixing with local communities, and subsequent independent evolutions. As long ago as Biblical times, cultural and linguistic differences between Jewish communities, even within the area of Ancient Israel and Judea, are observed both within the Bible and archeological remains. In more recent human history, an array of Jewish communities were established by Jewish settlers in various places around the Old World, often at great distances from one another, resulting in significant and often long-term isolation from each other. During the millennia of the Jewish diaspora, the communities would develop under the influence of their local environments; political, cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hillel Society
Hillel: The Foundation for Jewish Campus Life, also known as Hillel International or Hillel, is the largest Jewish campus organization in the world, working with thousands of college students globally. Hillel is represented at more than 550 colleges and communities throughout North America and globally, including 30 communities in the former Soviet Union, nine in Israel, and five in South America. The organization is named after Hillel the Elder, a Jewish sage who moved from Babylonia to Judea in the 1st century and is known for his formulation of the Golden Rule. History In 1923, Edward Chauncey Baldwin, Christian professor of Biblical literature at University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign was distressed by his Jewish students' lack of knowledge of the Hebrew Bible, and he discussed his concerns with Rabbi Benjamin Frankel.Spiegel, Irving.Faculty Program Begun by Hillel: 'More Positive Interest' in Judaism Sought by Group: How Hillel Was Founded. ''The New York Times' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Board Of Rabbis
The New York Board of Rabbis is an organization of Orthodox, Reform, Conservative and Reconstructionist rabbis in New York State and the surrounding portions of Connecticut and New Jersey. The roots of the New York Board of Rabbis date to 1881 with the establishment of the New York Board of Jewish Ministers by Rabbis Gustav Gottheil, Adolph Huebsch, Henry S. Jacobs, Kaufmann Kohler, Frederick de Sola Mendes and Abraham Pereira Mendes, who came from differing branches of Judaism, hoping to work together to foster Jewish education and advance Judaism. The New York Board of Rabbis was formally adopted as the organization's name in 1946. Protests were lodged against the 1948 film ''Oliver Twist'' noting that Alec Guinness's portrayal of Fagin was considered anti-Semitic. Guinness wore heavy make-up, including a large prosthetic nose, to make him look like the character as he appeared in George Cruikshank's illustrations in the first edition of the novel. As a result of objections ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halakha
''Halakha'' (; he, הֲלָכָה, ), also transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Jewish religious laws which is derived from the written and Oral Torah. Halakha is based on biblical commandments ('' mitzvot''), subsequent Talmudic and rabbinic laws, and the customs and traditions which were compiled in the many books such as the ''Shulchan Aruch''. ''Halakha'' is often translated as "Jewish law", although a more literal translation of it might be "the way to behave" or "the way of walking". The word is derived from the root which means "to behave" (also "to go" or "to walk"). ''Halakha'' not only guides religious practices and beliefs, it also guides numerous aspects of day-to-day life. Historically, in the Jewish diaspora, ''halakha'' served many Jewish communities as an enforceable avenue of law – both civil and religious, since no differentiation of them exists in classical Judaism. Since the Jewish Enlightenment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Who Is A Jew?
"Who is a Jew?" ( he, מיהו יהודי ) is a basic question about Jewish identity and considerations of Jewish self-identification. The question pertains to ideas about Jewish personhood, which have cultural, ethnic, religious, political, genealogical, and personal dimensions. Orthodox Judaism and Conservative Judaism follow Jewish law (Halakha), deeming people to be Jewish if their mothers are Jewish or if they underwent a halakhic conversion to Judaism#Halakhic considerations, conversion. Reform Judaism and Reconstructionist Judaism accept both matrilineal and patrilineal descent as well as conversion. Karaite Judaism predominantly follows patrilineal descent as well as conversion. Jewish identity is also commonly defined through ethnicity. Opinion polls have suggested that the majority of Jews see being Jewish as predominantly a matter of ancestry and culture, rather than religion. is a Jew? The term "Jew" lends itself to several definitions beyond simply de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)