|
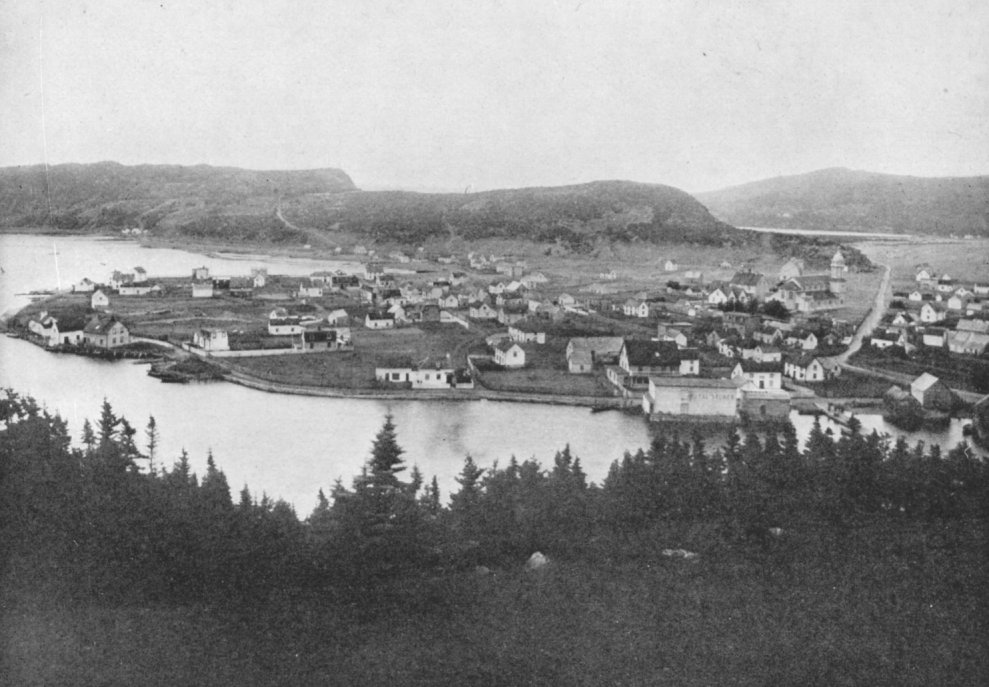
Jerseyside
Placentia is a town located in the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It consists of the Argentia Industrial Park and amalgamated communities of Townside, Freshwater, Dunville, Southeast, Point Verde and Jerseyside. History There is considerable evidence that Placentia Bay was intermittently occupied by Little Passage people.I. Marshall, ''A History and Ethnography of the Beothuk'' (Montréal: McGill-Queens University Press, 2014): 273. Their descendants, the Beothuk, continued to settle there until the 17th century. Remnants of Beothuk occupation from the surrounding area has been carbon dated back to as far as 1500 CE. Whether the Beothuk had come to permanently settle or just to fish has proved difficult to ascertain. By the late 17th century, the English and French settlers and fishermen had claimed the bays of Placentia.Newfoundland and Labrador Heritage Web Site, accessed March 5, 2019Disappearance of the Beothuk/ref> This effectively cut the natives off f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunville, Newfoundland And Labrador
Dunville is a neighborhood located in the Town of Placentia, in Canada. it was earlier called Northeast or North East Placentia. The name was formed from "Dunphy's Village" a part of Northeast Placentia. It is a community that makes up the north-eastern section of the Town of Placentia. It stretches approximately 8 km along the northern shore of the North-East Arm of Placentia Bay. The Post Office was established in 1895 and the first Post Master was Joachim Connors. Dunville was incorporated as a town on June 11, 1963. By 1966, it had a population of 1,606. Along with Freshwater, Argentia, and Jerseyside, it became part of Placentia in 1991. It was flooded quite badly by Tropical Storm Chantel on August 1, 2007, when approximately 200 mm of rain fell within 6 hours. This washed away several roads and caused a large amount of other damage. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentia
Argentia ( ) is a Canadian commercial seaport and industrial park located in the Town of Placentia, Newfoundland and Labrador. It is situated on the southwest coast of the Avalon Peninsula and defined by a triangular shaped headland which reaches northward out into Placentia Bay creating a natural harbour in length. Originally settled by the French in the 1630s that fishing settlement was called Petit Plaisance, meaning "Pleasant Little Place". The name was retained in English (Little Placentia) when the French lost control of the area following the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713. The census of 1706 records 149 individuals in 14 habitations. The community adopted its present name (unofficially in 1895 and officially in 1901) for the presence of silver ore near Broad Cove Point on the east side of the harbour. The name "Argentia" is Latin, meaning "Land of Silver" and was chosen by Father John St. John, the parish priest at Holy Rosary Parish from September 18, 1895, to Februa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces And Territories Of Canada
Within the geographical areas of Canada, the ten provinces and three territories are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada (which upon Confederation was divided into Ontario and Quebec)—united to form a federation, becoming a fully independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the world's second-largest country by area. The major difference between a Canadian province and a territory is that provinces receive their power and authority from the ''Constitution Act, 1867'' (formerly called the ''British North America Act, 1867''), whereas territorial governments are creatures of statute with powers delegated to them by the Parliament of Canada. The powers flowing from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
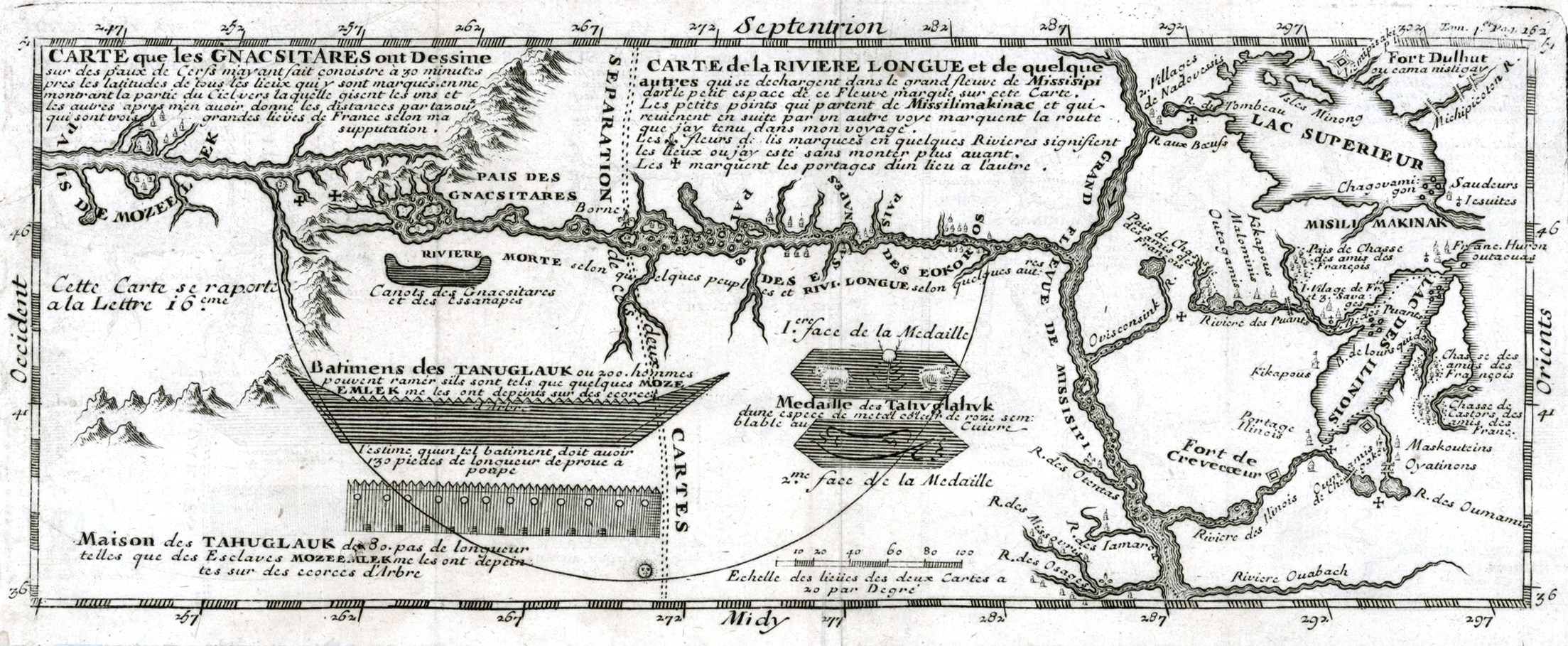
Louis-Armand De Lom D'Arce De Lahontan, Baron De Lahontan
Louis Armand, Baron de Lahontan (9 June 1666 – prior to 1716) served in the French military in Canada where he traveled extensively in the Wisconsin and Minnesota region and the upper Mississippi Valley. Upon his return to Europe he wrote an enormously popular travelogue. In it he recounted his voyage up the "Long River," now thought to be the Missouri. He wrote at length and in very positive terms about Native American culture, portraying Indian people as free, rational, and generally admirable. Early life He was born into the aristocracy and inherited the title Baron Lahontan upon his father's death in 1674. De Lahontan joined the troupes de la marine and was sent to New France in 1683 at age 17 along with two other officers and three companies of troops.Lanctôt, Gustave. The Oakes Collection. Ottawa: J.O. Patenaude, 1940. 11. After arriving at Quebec in November and settling in Beaupré, he would lead his company in 1684 on an unsuccessful offense against the Iroquois from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recollects
The Recollects (french: Récollets) were a French reform branch of the Order of Friars Minor, Friars Minor, a Franciscan order. Denoted by their gray habits and pointed hoods, the Recollects took vows of poverty and devoted their lives to prayer, penance, and spiritual reflection. Today, they are best known for their presence as missionaries in various parts of the world, most notably in early Canada. The order had its origins in the 16th century. Officially named the "Order of Friars Minor Recollect", they used the post-nominal initials ''O.F.M. Rec.'' ( la, Ordo fratrum minorum recollectorum)"Order of Friars Minor Recollect (O.F.M. Rec.) - Récollets" ''GCatholic.org''. Gabriel Chow. Retrieved February 29, 2016 or ''O.M.R.'' (). In 1897, Pope Leo XIII officially dissolved the Recolle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Philip of Anjou and Charles of Austria, and their respective supporters, among them Spain, Austria, France, the Dutch Republic, Savoy and Great Britain. Related conflicts include the 1700–1721 Great Northern War, Rákóczi's War of Independence in Hungary, the Camisards revolt in southern France, Queen Anne's War in North America and minor trade wars in India and South America. Although weakened by over a century of continuous conflict, Spain remained a global power whose territories included the Spanish Netherlands, large parts of Italy, the Philippines, and much of the Americas, which meant its acquisition by either France or Austria potentially threatened the European balance of power. Attempts by Louis XIV of France and William III o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by the Habsburg monarchy), the Dutch Republic, England, Spain, Savoy, Sweden and Portugal. Although not the first European war to spill over to Europe's overseas colonies, the events of the war spread to such far away places as the Americas, India, and West Africa. It is for this reason that it is sometimes considered the first world war. The conflict encompassed the Glorious Revolution in England, where William of Orange deposed the unpopular James VII and II and subsequently struggled against him for control of Scotland and Ireland, and a campaign in colonial North America between French and English settlers and their respective Native American allies. Louis XIV of France had emerged from the Franco-Dutch War in 1678 as the most powerful monarch in Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Saint Louis (Newfoundland)
Fort Saint Louis was a French fort built in the 17th century on Newfoundland at the time of the New France. The construction began in 1690 for a new French fort on Newfoundland. In 1662, the French had established a strategic trading post in a well protected cove overlooking Placentia Bay that separates Avalon to the rest of Newfoundland and near the Grand Banks. To protect this place, several forts were built around the cove, Fort Plaisance from 1662, the Fort Royal in 1687 and Saint Louis 1690. Fort Saint Louis was built inside the harbor in order to protect the small port city of Plaisance from an enemy attack. It was to reinforce the old fort built of wood in Placentia. Fort Saint Louis was built in stone. Its enclosure was nearly 250 meters long, encircling two bastions, the headquarters of the governor and the buildings of the garrison. The walls stood four meters high and the walls measured two meters thick. Almost thirty guns were operational on this fort. The fort was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Royal (Newfoundland)
Fort Royal is a French fort built in 1687 on the island of Newfoundland during the time of New France. In 1662, the French established a commercial counter on a well protected hill overlooking Placentia Bay which separates the Avalon Peninsula form the rest of Newfoundland island and situated near Grand Banks where fish are abundant. In order to protect the bay, several forts were erected around the hill, Fort Plaisance (1662), Fort Royal (1687) and Fort Saint Louis (1690). Fort Royal was constructed on the top of the hill which dominated the bay and the port village of Plaisance. Fort Royal served as bastion and home for the governor. In 1713, the Treaty of Utrecht forced the French to abandon their establishments in Newfoundland. Fort Royal and Fort Saint Louis were renamed "'' Castle Hill''" by the English, and "Plaisance" became "Placentia". The French inhabitants were displaced to Isle Royale (Cape Breton), where they began the construction of Louisbourg.Canada- Québec, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Plaisance
Fort Plaisance was a French fort built in the 17th century on the island of Newfoundland at the time of the New France. In 1662, the French established a strategic trading post in a well protected cove overlooking Placentia Bay that separates Avalon from the rest of the island of Newfoundland, located close to Grand Banks. To protect this place, several forts were built around the cove, Fort Plaisance in 1662, Fort Royal in 1687, and Fort Saint Louis in 1690. Fort Plaisance was built inside the harbor in order to protect the small port city of Plaisance from an attack enemy. During its construction, the Fort Plaisance had earthen ramparts reinforced by wooden stakes. In the beginning it had four guns. Its armament was gradually increased and in 1667, the fort had 32 guns. In 1713, the Treaty of Utrecht forced the French to abandon their settlements in Newfoundland. 'Plaisance' become 'Placentia'. The French inhabitants were moved to Île Royale which began the construction of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Canada
Atlantic Canada, also called the Atlantic provinces (french: provinces de l'Atlantique), is the region of Eastern Canada comprising the provinces located on the Atlantic coast, excluding Quebec. The four provinces are New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. As of 2021, the landmass of the four Atlantic provinces was approximately 488,000 km2, and had a population of over 2.4 million people. The provinces combined had an approximate GDP of $121.888 billion in 2011. The term ''Atlantic Canada'' was popularized following the admission of Newfoundland as a Canadian province in 1949. History The first premier of Newfoundland, Joey Smallwood, coined the term "Atlantic Canada" when Newfoundland joined Canada in 1949. He believed that it would have been presumptuous for Newfoundland to assume that it could include itself within the existing term "Maritime provinces," used to describe the cultural similarities shared by New Brunswick, Prince ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.png)