|
Jerry Potts
Jeremiah “Jerry” Potts (1840 – July 14, 1896), (also known as Ky-yo-kosi, meaning "Bear Child"), was an American - Canadian plainsman, buffalo hunter, horse trader, interpreter, and scout of Kainai (Blood) and Scots heritage. Early life Potts was born in or before 1840 near Fort McKenzie, Montana. He was the only child of his Kainai-Cree mother, ''Namo-pisi'' (Crooked Back), and Andrew R. Potts, a Scottish fur trader. Upon the death of his father in 1840, Jerry was given to American Fur Company trader Alexander Harvey by Namo-pisi prior to rejoining her tribe. A violent, vindictive man, Harvey neglected and mistreated Potts before deserting him in 1845. American Fur Company trader Andrew Dawson of Fort Benton, Montana, a gentle man who was called "the last king of the Missouri," adopted young Potts. He taught the boy to read and write and allowed him to mix with the Native Americans who visited the trading post to learn their customs and languages. In his late teens P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Canadian Mounted Police
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP; french: Gendarmerie royale du Canada; french: GRC, label=none), commonly known in English as the Mounties (and colloquially in French as ) is the federal police, federal and national police service of Canada. As police services are the constitutional responsibility of provinces and territories of Canada, the RCMP's primary responsibility is the enforcement of federal criminal law, and sworn members of the RCMP have jurisdiction as a Law enforcement officer, peace officer in all provinces and territories of Canada.Royal Canadian Mounted Police Act', RSC 1985, c R-10, s 11.1. However, the service also provides police services under contract to eight of Canada's Provinces and territories of Canada#Provinces, provinces (all except Ontario and Quebec), all three of Canada's Provinces and territories of Canada#Territories, territories, more than 150 municipalities, and 600 Indigenous peoples in Canada, Indigenous communities. In addition to en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
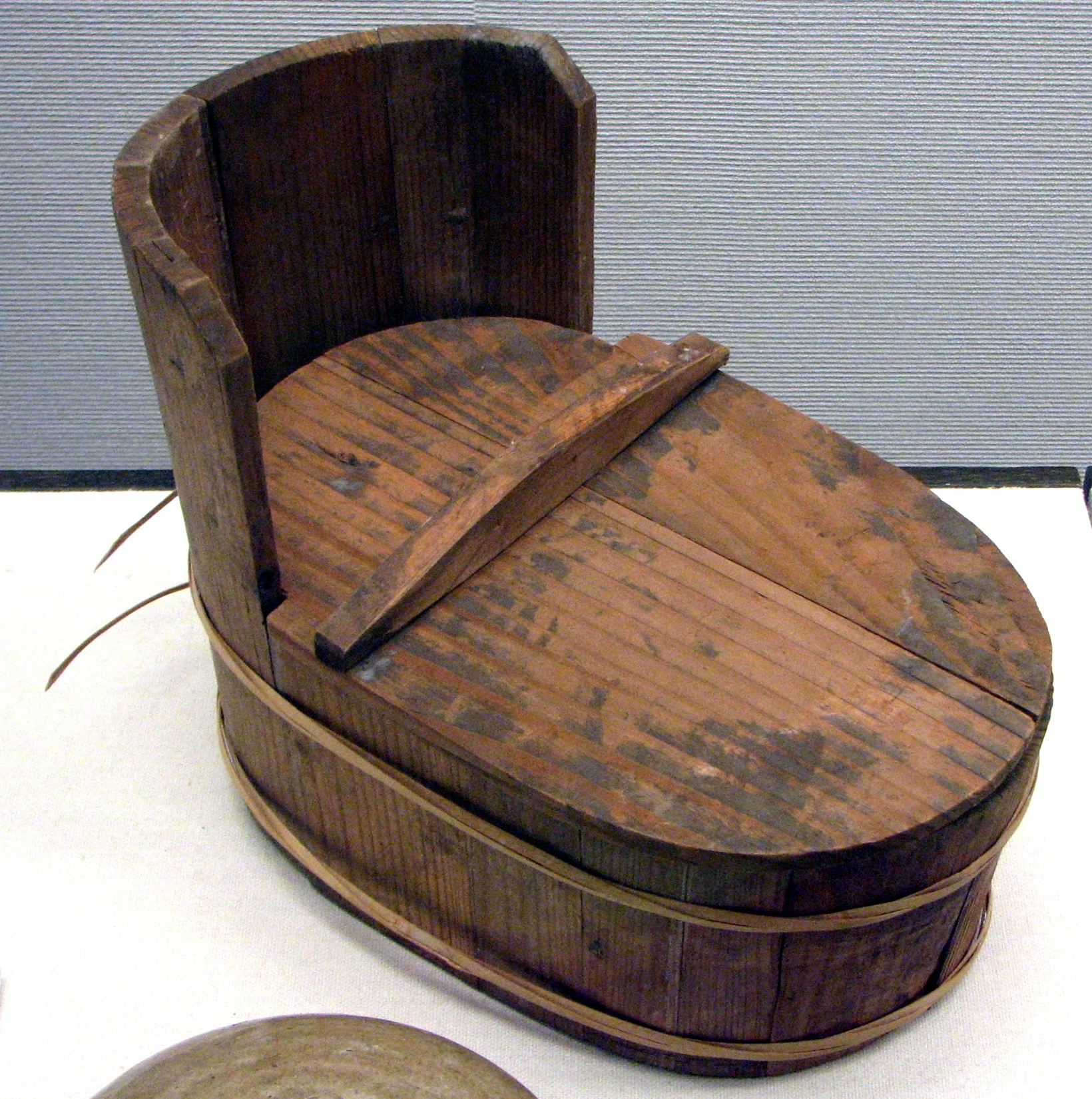
Chamber Pot
A chamber pot is a portable toilet, meant for nocturnal use in the bedroom. It was common in many cultures before the advent of indoor plumbing and flushing toilets. Names and etymology "Chamber" is an older term for bedroom. The chamber pot is also known as a , a jerry, a guzunder, a po (possibly from french: pot de chambre), a potty pot, a potty, a thunder pot or a thunder mug. It was also known as a chamber utensil or bedroom ware. History Chamber pots were used in ancient Greece at least since the 6th century BC and were known under different names: (''amis''), (''ouranē'') and (''ourētris'', from - ''ouron'', "urine"), / (''skōramis''), (''chernibion''). The introduction of indoor flush toilets started to displace chamber pots in the 19th century, but they remained common until the mid-20th century. The alternative to using the chamber pot was a trip to the outhouse. In China, the chamber pot (便壶 (biàn hú) was common. A wealthy salt merchant in the city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
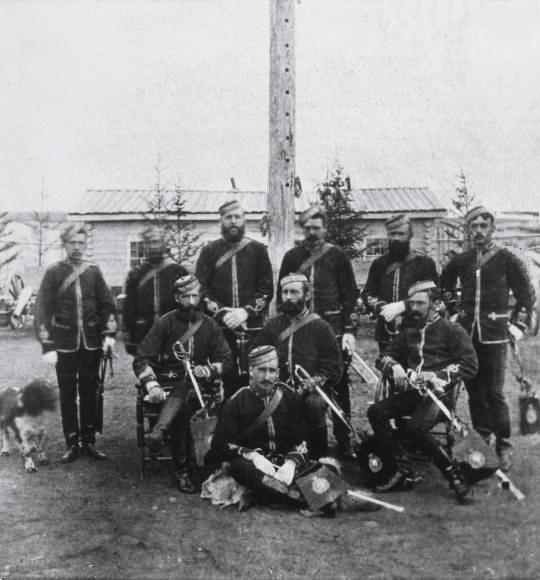
North-West Mounted Police
The North-West Mounted Police (NWMP) was a Canadian para-military police force, established in 1873, to maintain order in the new Canadian North-West Territories (NWT) following the 1870 transfer of Rupert’s Land and North-Western Territory to Canada from the Hudson’s Bay Company, the Red River Rebellion and in response to lawlessness, demonstrated by the subsequent Cypress Hills Massacre and fears of United States military intervention. The NWMP combined military, police and judicial functions along similar lines to the Royal Irish Constabulary. A small, mobile police force was chosen to reduce potential for tensions with the United States and First Nations in Canada, First Nations. The NWMP uniforms included red coats deliberately reminiscent of British and Canadian military uniforms. The NWMP was established by the Canadian government during the ministry of Prime Minister of Canada, Prime Minister Sir John A. Macdonald, John Macdonald who defined its purpose as "the pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algonquian Languages
The Algonquian languages ( or ; also Algonkian) are a subfamily of Indigenous languages of the Americas, indigenous American languages that include most languages in the Algic languages, Algic language family. The name of the Algonquian language family is distinguished from the orthographically similar Algonquin language, Algonquin dialect of the Indigenous Ojibwe language (Chippewa), which is a senior member of the Algonquian language family. The term ''Algonquin'' has been suggested to derive from the Maliseet word (), "they are our relatives/allies". A number of Algonquian languages are considered extinct languages by the modern linguistic definition. Algonquian peoples, Speakers of Algonquian languages stretch from the east coast of North America to the Rocky Mountains. The proto-language from which all of the languages of the family descend, Proto-Algonquian language, Proto-Algonquian, was spoken around 2,500 to 3,000 years ago. There is no scholarly consensus about wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assiniboine Language
The Assiniboine language (also known as Assiniboin, Hohe, or Nakota, Nakoda, Nakon or Nakona, or Stoney) is a Nakotan Siouan language of the Northern Plains. The name Assiniboine comes from the term ''Asiniibwaan'', from Ojibwe, meaning "Stone Siouans". The reason they were called this was that Assiniboine people used heated stone to boil their food. In Canada, Assiniboine people are known as Stoney Indians, while they called themselves Nakota or Nakoda, meaning "allies"''.'' Classification The Dakotan group of the Siouan family has five main divisions: Dakota (Santee-Sisseton), Dakota (Yankton-Yanktonai), Lakota (Teton), Nakoda (Assiniboine) and Nakoda (Stoney).Miller, D., Smith, D., McGeshick, J. R., Shanley, J., & Shields, C. (2008). ''The History of the Assiniboine and Sioux Tribes of the Fort Peck Indian Reservation, Montana'', 1800-2000. Montana: Montana Historical Society Press. Along with the closely related Stoney, Assiniboine is an n variety of the Dakotan languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakota Language
Lakota ( ), also referred to as Lakhota, Teton or Teton Sioux, is a Siouan language spoken by the Lakota people of the Sioux tribes. Lakota is mutually intelligible with the two dialects of the Dakota language, especially Western Dakota, and is one of the three major varieties of the Sioux language. Speakers of the Lakota language make up one of the largest Native American language speech communities in the United States, with approximately 2,000 speakers, who live mostly in the northern plains states of North Dakota and South Dakota. Many communities have immersion programs for both children and adults. The language was first put into written form by European-American missionaries around 1840. The orthography has since evolved to reflect contemporary needs and usage. History and origin The Lakota people's creation stories say that language originated from the creation of the tribe. Other creation stories say language was invented by Iktomi. Phonology Vowels Lakota has fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plains Cree Language
Plains Cree (endonym: ) is a dialect of the Algonquian language, Cree, which is the most populous Canadian indigenous language. Plains Cree is considered a dialect of the Cree-Montagnais language or a dialect of the Cree language that is distinct from the Montagnais language. Plains Cree is one of five main dialects of Cree in this second sense, along with Woods Cree, Swampy Cree, Moose Cree, and Atikamekw. Although no single dialect of Cree is favored over another, Plains Cree is the one that is the most widely used. Out of the 116,500 speakers of the Cree language, the Plains Cree dialect is spoken by about 34,000 people primarily in Saskatchewan and Alberta but also in Manitoba and Montana. The number of people who can speak an Aboriginal language, such as Plains Cree, has increased. For example, in the 2016 census, 263,840 people could speak an Aboriginal language well enough to conduct a conversation. From 1996 to 2016, the total number of people who were able to speak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crow Language
Crow ( native name: ''Apsáalooke'' ) is a Missouri Valley Siouan language spoken primarily by the Crow Nation in present-day southeastern Montana. The word, ''Apsáalooke,'' translates to "children of the raven." It is one of the larger populations of American Indian languages with 2,480 speakers according to the 1990 US Census.Ethnologue Dialects Crow is closely related to Hidatsa spoken by the Hidatsa tribe of the Dakotas; the two languages are the only members of the Missouri Valley Siouan family.Silver and Miller 1997: 367.Graczyk, 2007: 2 Despite their similarities, Crow and Hidatsa are not mutually intelligible. Status According to Ethnologue with figures from 1998, 77% of Crow people over 66 years old speak the language; "some" parents and older adults, "few" high school students and "no pre-schoolers" speak Crow. 80% of the Crow Nation prefers to speak in English. The language was defined as "definitely endangered" by UNESCO as of 2012. However, R. Graczyk claims in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackfoot Language
The Blackfoot language, also called Siksiká (its denomination in ISO 639-3, ; Siksiká ik͡siká syllabics ), often anglicised as ', is an Algonquian language spoken by the Blackfoot or ''Niitsitapi'' people, who currently live in the northwestern plains of North America. There are four dialects, three of which are spoken in Alberta, Canada, and one of which is spoken in the United States: ''Siksiká'' (Blackfoot), to the southeast of Calgary, Alberta; ''Kainai'' (Blood, Many Chiefs), spoken in Alberta between Cardston and Lethbridge; ''Aapátohsipikani'' (Northern Piegan), to the west of Fort MacLeod which is Brocket (Piikani) and ''Aamsskáápipikani'' (Southern Piegan), in northwestern Montana. The name Blackfoot probably comes from the blackened soles of the leather shoes that the people wore.Gibson 2003 There is a distinct difference between Old Blackfoot (also called High Blackfoot), the dialect spoken by many older speakers, and New Blackfoot (also called Modern Blac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the Languages of the United States, most widely spoken language in the United States and in most circumstances is the de facto common language used in government, education and commerce. Since the 20th century, American English has become the most influential form of English worldwide. American English varieties include many patterns of pronunciation, vocabulary, grammar and particularly spelling that are unified nationwide but distinct from other English dialects around the world. Any North American English, American or Canadian accent (sociolinguistics), accent perceived as lacking noticeably local, ethnic or cultural markedness, markers is popularly called General American, "General" or "Standard" American, a fairly uniform dialect continuum, accent continuum native to certain regions of the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apache
The Apache () are a group of culturally related Native American tribes in the Southwestern United States, which include the Chiricahua, Jicarilla, Lipan, Mescalero, Mimbreño, Ndendahe (Bedonkohe or Mogollon and Nednhi or Carrizaleño and Janero), Salinero, Plains (Kataka or Semat or "Kiowa-Apache") and Western Apache ( Aravaipa, Pinaleño, Coyotero, Tonto). Distant cousins of the Apache are the Navajo, with whom they share the Southern Athabaskan languages. There are Apache communities in Oklahoma and Texas, and reservations in Arizona and New Mexico. Apache people have moved throughout the United States and elsewhere, including urban centers. The Apache Nations are politically autonomous, speak several different languages, and have distinct cultures. Historically, the Apache homelands have consisted of high mountains, sheltered and watered valleys, deep canyons, deserts, and the southern Great Plains, including areas in what is now Eastern Arizona, Northern Mexico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |