|
Jean Tagault
Jean Tagault or Jean Tagaut (in Latin Joannes Tagaultius) (around 1499 in Vimy or more certainly in Cerisy-Buleux – 25 April 1546 in Paris) was a French physician and anatomist known for his surgical work and for having fought against Michel Servet who defended judicial astrology and divination as sciences. He is often confused with his son Jean Tagaut, a doctor and poet. Biography He studied philosophy and literature at the Collège de Chanac Pompadour before becoming a teacher at the same college. Then he studied medicine at the Faculty of Medicine in Paris, where in 1524 he obtained his medical degree. He married Jeanne Lourdel and had at least one son, his namesake, Jean Tagaut (ca.1515 - 1560), a poet and friend of Pierre de Ronsard, who is often confused with him. The family lived in rue de la Huchette in Paris. Already by this time, Tagault must have chosen the camp of the Evangelical Lutheran Church, and later he was even consulted by Calvin who was ill (1544). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerisy-Buleux
Cerisy-Buleux (; Picard: ''Çrisin-Buleux'') is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France. Geography The commune is situated on the D190 road, some southwest of Abbeville. Population Places of interest * The old railway line:Source:Fcvnet The railway, opened in 1872, was closed on 10 November 1993. Mostly freight trains for the many farming cooperatives, there were also a few passenger trains. Cerisy-Buleux (Somme), France (5).JPG, Townhall. Cerisy-Buleux (Somme), France (7).JPG, Old school. Cerisy-Buleux (Somme), France (6).JPG, Monument. Cerisy-Buleux (Somme), France.JPG, Castle, Arleux street. Cerisy-Buleux (Somme), France (3).JPG, Castle, near the church. Personality * Jean Tagault (circa 1499–1546), anatomist and surgeon. See also * Communes of the Somme department *Réseau des Bains de Mer The Réseau des Bains de Mer (RBM) was a group of five metre gauge railways centred on Noyelles-sur-Mer, with a total route length of so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy De Chauliac
Guy de Chauliac (), also called Guido or Guigo de Cauliaco ( 1300 – 25 July 1368), was a French physician and surgeon who wrote a lengthy and influential treatise on surgery in Latin, titled '' Chirurgia Magna''. It was translated into many other languages (including Middle English) and widely read by physicians in late medieval Europe. Life Guy de Chauliac was born in Chaulhac, Lozère, France, into a family of modest means. He began his study of medicine in Toulouse before going to study in Montpellier, the center for medical knowledge in the 14th century of France. He was in Paris between 1315 and 1320, and around 1325, he became a Master of Medicine and Surgery. After receiving his degree, he went to Bologna to study anatomy under Nicola Bertuccio, from whom he may have learned surgical techniques. It is unknown whether de Chauliac applied his surgical studies and knowledge. Charles H. Talbot writes, "It was seemingly from books that hauliaclearned his surgery.... He may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Somme (department)
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th-century French Physicians
The 16th century begins with the Julian year 1501 ( MDI) and ends with either the Julian or the Gregorian year 1600 ( MDC) (depending on the reckoning used; the Gregorian calendar introduced a lapse of 10 days in October 1582). The 16th century is regarded by historians as the century which saw the rise of Western civilization and the Islamic gunpowder empires. The Renaissance in Italy and Europe saw the emergence of important artists, authors and scientists, and led to the foundation of important subjects which include accounting and political science. Copernicus proposed the heliocentric universe, which was met with strong resistance, and Tycho Brahe refuted the theory of celestial spheres through observational measurement of the 1572 appearance of a Milky Way supernova. These events directly challenged the long-held notion of an immutable universe supported by Ptolemy and Aristotle, and led to major revolutions in astronomy and science. Galileo Galilei became a champion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Surgeons
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to France ** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents ** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with France ** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices Fortnite French places Arts and media * The French (band), a British rock band * "French" (episode), a live-action episode of ''The Super Mario Bros. Super Show!'' * ''Française'' (film), 2008 * French Stewart (born 1964), American actor Other uses * French (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) * French (tunic), a particular type of military jacket or tunic used in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union * French's, an American brand of mustard condiment * French catheter scale, a unit of measurement of diameter * French Defence, a chess opening * French kiss, a type of kiss involving the tongue See also * France (other) * Franch, a surname * French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Canappe
Jean Canappe (sometimes written Jean Canape) (1495- after 1558) was a French physician who was attached to Francis I of France in 1542. He sometimes wrote under the pseudonym Philiatros and was known because he contributed to the transmission of medical and surgical knowledge in French with Pierre Tolet. Biography Jean Canappe was born in 1495. He was principal at the Collège de la Trinité in Lyon from 1528 to 1530 and obtained his medical degree at the University of Montpellier in 1530 in one of the two classes which constituted the "cercle des anticques amys" of Rabelais": Nostradamus, Pierre Tolet, Jacobus Sylvius and Guillaume Rondelet for 1529 and Jean Canappe, Charles des Marais and Antoine Champier for 1530. He worked with Symphorien Champier at the College of Medicine in Lyon and became a friend of Ambroise Paré for whom he translated several books by Galen.. Public reader of the surgeons-barbers in Lyon in 1538 he was the "abbreviator" of Guy de Chauliac himself consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guillaume Rouillé
Guillaume Rouillé ( la, Gulielmus Rovillium; 15181589), also called Roville or Rovillius, was one of the most prominent humanist bookseller-printers in 16th-century Lyon. He invented the pocket book format called the ''sextodecimo'', printed with sixteen leaves to the folio sheet, half the size of the octavo format, and published many works of history and poetry as well as medicine, in addition to his useful compilations and handbooks. Rouillé was born in Tours. Though he was a Frenchman, he served his apprenticeship in the Venetian printing-house of Gabriele Giolito de' Ferrari, and retained his connections with Venice as a source of texts after his arrival in Lyon around 1543. Among his works was the French translation by Barthélemy Aneau of Andrea Alciato's pioneering emblem book, which formed part of a major publishing venture in Lyons by the team of Guillaume Rouillé and his printer Macé Bonhomme, 1549, which extended to translations in Italian and Spanish. Rouillé al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Bauhin
Jean Bauhin (24 August 1511 – 23 January 1582) was a French physician. He was born in Amiens, France and died in Basel, Switzerland, where he had to relocate after converting to Protestantism. He was the physician to Jeanne d'Albret, Queen of Navarre. He had three sons, two of whom were also physicians and notable botanists: Johann Bauhin (also known as Jean Bauhin, 1541–1613) and Gaspard Bauhin (Caspar Bauhin, 1560–1624).''Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie ''Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie'' (ADB, german: Universal German Biography) is one of the most important and comprehensive biographical reference works in the German language. It was published by the Historical Commission of the Bavarian Aca ...'' References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Bauhin, Jean 1511 births 1582 deaths Converts to Protestantism from Roman Catholicism 16th-century French physicians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archiater
An archiater ( grc, ἀρχίατρος) was a chief physician of a monarch, who typically retained several. At the Roman imperial court, their chief held the high rank and specific title of ''Comes archiatrorum''. The term has also been used of chief physicians in communities. The word is formed of the Greek ' , 'chief', and ' , a physician; the Latin equivalents are and . In Finland is the highest honorary title awarded to a physician by the President of Finland, such that there is only one archiater at a time. The most famous archiater in Finland has been Arvo Ylppö, who pioneered pediatrics in the country and is credited for the enormous reduction of infant mortality to the modern, very low levels. In neighbouring Sweden, the title of archiater was bestowed on the great botanist Carl Linnaeus as an honour. In Vatican City, the Pope's personal physician retains the historical title of archiater. See also * City physician City physician (German: ; , , from Latin ) was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
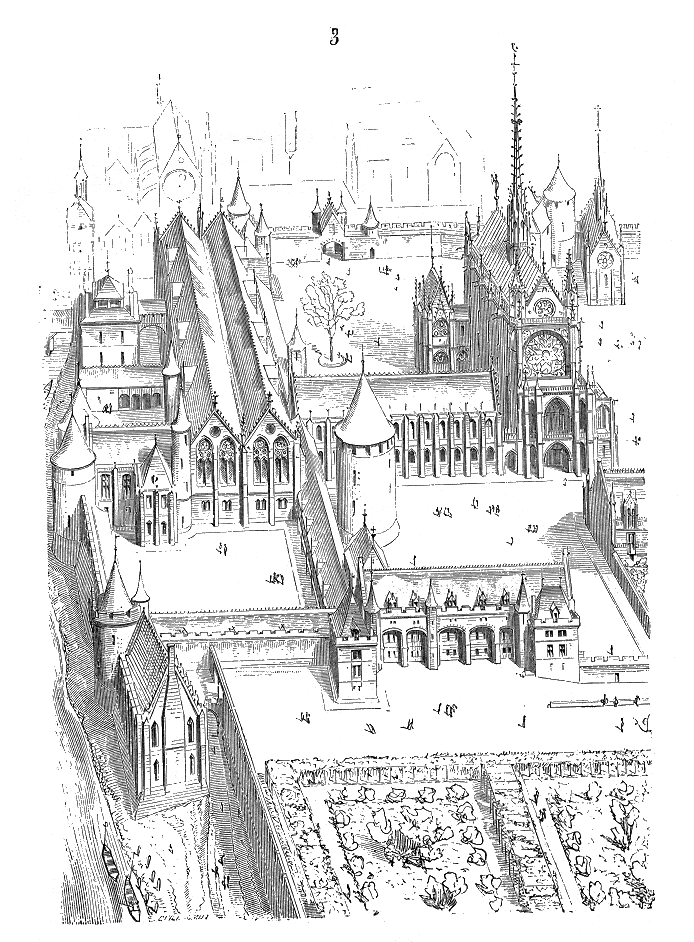
Palais De La Cité
The Palais de la Cité (), located on the Île de la Cité in the Seine River in the centre of Paris, is a major historic building that was the residence of the Kings of France from the sixth century until the 14th century, and has been the center of the French justice system ever since, thus often referred to as the Palais de Justice. From the 14th century until the French Revolution, it was the headquarters of the Parlement of Paris. During the Revolution it served as a courthouse and prison, where Marie Antoinette and other prisoners were held and tried by the Revolutionary Tribunal. Since the early 1800s it has been the seat of the Tribunal de grande instance de Paris, the Court of Appeal of Paris, and the Court of Cassation. The first of these moved to another Parisian location in 2018, while the other two jurisdictions remain located in the Palais de la Cité as of 2022. The palace was built and rebuilt many times over the course of many centuries, including following majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vidus Vidius
Guido Guidi (Latinized name Vidus Vidius) (10 February 1509 – 26 May 1569), was an Italian surgeon, anatomist and translator. Biography His father was a physician and his mother was the daughter of the painter Domenico Ghirlandajo. After practicing at Florence and Rome, he was invited by Francis I of France, Francis I of France to come to Paris to be his personal doctor and teach at the Collège de France. While in Paris, Guido Guidi befriended artist Benvenuto Cellini and published a book on surgery, ''Chirurgia'', in 1544. This book was one of the best illustrated at the time and was based on works of Hippocrates, Galen, and Oribasius. In 1547, Guidi returned to Italy to become the personal physician of Cosimo I de' Medici, Cosimo di Medici and taught at Pisa. He took holy orders and was ennobled. A book on medicine, incomplete at his death in 1569, was finished by his nephew as ''Ars Medicinalis'' between 1596 and 1611. Today, the Vidian nerve in the skull and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis I Of France
Francis I (french: François Ier; frm, Francoys; 12 September 1494 – 31 March 1547) was King of France from 1515 until his death in 1547. He was the son of Charles, Count of Angoulême, and Louise of Savoy. He succeeded his first cousin once removed and father-in-law Louis XII, who died without a son. A prodigious patron of the arts, he promoted the emergent French Renaissance by attracting many Italian artists to work for him, including Leonardo da Vinci, who brought the ''Mona Lisa'' with him, which Francis had acquired. Francis' reign saw important cultural changes with the growth of central power in France, the spread of humanism and Protestantism, and the beginning of French exploration of the New World. Jacques Cartier and others claimed lands in the Americas for France and paved the way for the expansion of the first French colonial empire. For his role in the development and promotion of the French language, he became known as ''le Père et Restaurateur des Lettr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_1938.jpg)

_2.jpg)
