|
Jean Dominique Compans
Count Jean Dominique Compans (26 June 1769, Salies-du-Salat - 10 November 1845, Blagnac) was a French Divisional General from 1811 and a participant of Napoleonic Wars. Biography Upon the outbreak of the French Revolution, Compans enlisted as a volunteer in 1789. At age 23 he was promoted to captain in the 3rd battalion of the volunteers of the Haute-Garonne. In 1793 his commanding general Dugommier promoted him to command a battalion in the brigade of Jean Lannes. Compans distinguished himself in the campaigns in Spain and Italy (1793-1797). In 1798 he was put in command of a corps of 16.000 men with which he took the towns of Fossano and Savigliano. In June 1799 he received a temporary promotion to General de brigade, which was made permanent in October. In 1800 Compans was wounded by a musket ball at San Giacomo. Having recovered, he distinguished himself at Montebello and Marengo. After the Peace of Lunéville Compans was appointed the governor of the province of Coni. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Général Jean Dominique Compans (2)
is the French word for general. There are two main categories of generals: the general officers (), which are the highest-ranking commanding officers in the armed forces, and the specialist officers with flag rank (), which are high-level officers in the other uniformed services. General officers Army History The French army of the monarchy had several ranks of general officer: * ("brigadier of the armies of the King"): a rank in a grey area of seniority, conferred on certain colonels who were in command of a brigade (''cf.'' the grey area of the naval "commodore" rank given to certain captains, the equivalent of army full colonels, who had been in command of a group of ships and over the captains of the group's other ships). These officers wore a colonel's uniform with a star on the shoulder straps. This rank was abolished in 1788. * ("field marshal"(major general)): the first substantive rank of general. The wore a special uniform, blue and red, with a single bar of gold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-de-Dieu Soult
Marshal General Jean-de-Dieu Soult, 1st Duke of Dalmatia, (; 29 March 1769 – 26 November 1851) was a French general and statesman, named Marshal of the Empire in 1804 and often called Marshal Soult. Soult was one of only six officers in French history to receive the distinction of Marshal General of France. The Duke also served three times as President of the Council of Ministers, or Prime Minister of France. Soult played a key role as a corps commander in many of Napoleon's campaigns, most notably at Austerlitz, where his corps delivered the decisive attack that won the battle. Later, Soult's intrigues in the Peninsular War while occupying Portugal earned him the nickname, "King Nicolas", and while he was Napoleon's military governor of Andalusia, Soult looted 1.5 million francs worth of art. One historian called him "a plunderer in the world class." He was defeated in his last offensives in Spain in the Battle of the Pyrenees (Sorauren) and by Freire's Spaniards at San ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peerage Of France
The Peerage of France (french: Pairie de France) was a hereditary distinction within the French nobility which appeared in 1180 in the Middle Ages. The prestigious title and position of Peer of France (french: Pair de France, links=no) was held by the greatest, highest-ranking members of the French nobility. French peerage thus differed from British peerage (to whom the term "baronage", also employed as the title of the lowest noble rank, was applied in its generic sense), for the vast majority of French nobles, from baron to duke, were not peers. The title of ''Peer of France'' was an extraordinary honour granted only to a small number of dukes, counts, and princes of the Roman Catholic Church. It was analogous to the rank of ''Grandee of Spain'' in this respect. The distinction was abolished in 1789 during the French Revolution, but it reappeared in 1814 at the time of the Bourbon Restoration, which followed the fall of the First French Empire, when the Chamber of Peers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred Days
The Hundred Days (french: les Cent-Jours ), also known as the War of the Seventh Coalition, marked the period between Napoleon's return from eleven months of exile on the island of Elba to Paris on20 March 1815 and the second restoration of King Louis XVIII on 8 July 1815 (a period of 110 days). This period saw the War of the Seventh Coalition, and includes the Waterloo Campaign, the Neapolitan War as well as several other minor campaigns. The phrase ''les Cent Jours'' (the hundred days) was first used by the prefect of Paris, Gaspard, comte de Chabrol, in his speech welcoming the king back to Paris on 8 July. Napoleon returned while the Congress of Vienna was sitting. On 13March, seven days before Napoleon reached Paris, the powers at the Congress of Vienna declared him an outlaw, and on 25March Austria, Prussia, Russia and the United Kingdom, the four Great Powers and key members of the Seventh Coalition, bound themselves to put 150,000 men each into the field to end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis XVIII Of France
Louis XVIII (Louis Stanislas Xavier; 17 November 1755 – 16 September 1824), known as the Desired (), was King of France from 1814 to 1824, except for a brief interruption during the Hundred Days in 1815. He spent twenty-three years in exile: during the French Revolution and the First French Empire (1804–1814), and during the Hundred Days. Until his accession to the throne of France, he held the title of Count of Provence as brother of King Louis XVI. On 21 September 1792, the National Convention abolished the monarchy and deposed Louis XVI, who was later executed by guillotine. When his young nephew Louis XVII died in prison in June 1795, the Count of Provence proclaimed himself (titular) king under the name Louis XVIII. Following the French Revolution and during the Napoleonic era, Louis XVIII lived in exile in Prussia, England, and Russia. When the Sixth Coalition finally defeated Napoleon in 1814, Louis XVIII was placed in what he, and the French royalists, con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of La Fère-Champenoise
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Leipzig
The Battle of Leipzig (french: Bataille de Leipsick; german: Völkerschlacht bei Leipzig, ); sv, Slaget vid Leipzig), also known as the Battle of the Nations (french: Bataille des Nations; russian: Битва народов, translit=Bitva narodov), was fought from 16 to 19 October 1813 at Leipzig, Saxony. The Coalition armies of Austria, Prussia, Sweden, and Russia, led by Tsar Alexander I and Karl von Schwarzenberg, decisively defeated the '' Grande Armée'' of French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. Napoleon's army also contained Polish and Italian troops, as well as Germans from the Confederation of the Rhine (mainly Saxony and Württemberg). The battle was the culmination of the German Campaign of 1813 and involved 560,000 soldiers, 2,200 artillery pieces, the expenditure of 400,000 rounds of artillery ammunition, and 133,000 casualties, making it the largest battle in Europe prior to World War I. Decisively defeated again, Napoleon was compelled to return to France while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
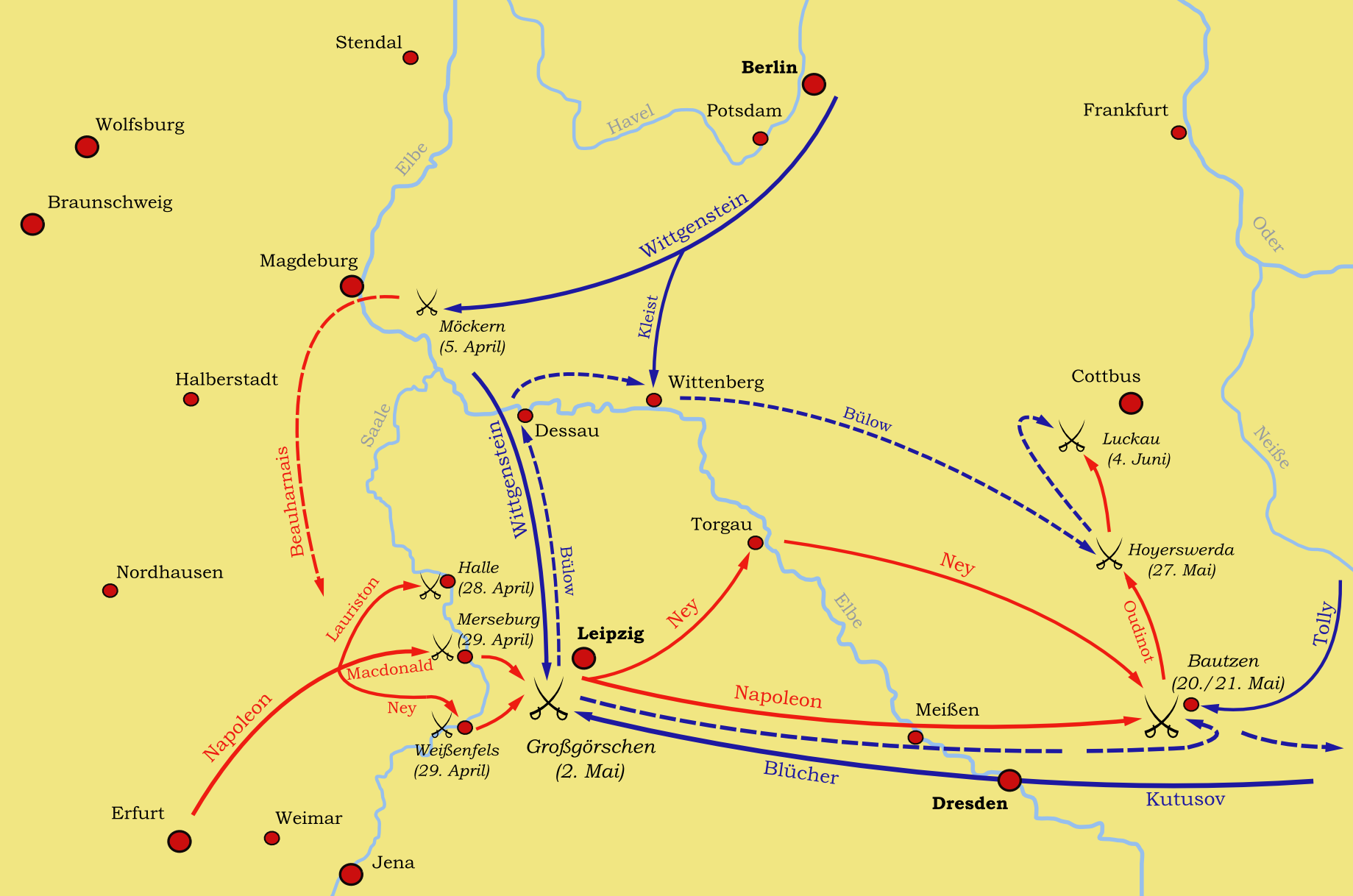
Battle Of Bautzen (1813)
In the Battle of Bautzen (20–21 May 1813), a combined Prusso–Russian army, that was massively outnumbered, was pushed back by Napoleon but escaped destruction, with some sources claiming that Marshal Michel Ney failed to block their retreat. The Prussians under General Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher and Russians under General Peter Wittgenstein, retreating after their defeat at Lützen were attacked by French forces under Napoleon. Prelude The Prusso-Russian army was in a full retreat following their defeat at the Battle of Lützen. Finally, generals Wittgenstein and Blücher were ordered to stop at Bautzen by Tsar Alexander I and King Frederick William III. The Russo-Prussian army was nearly 96,000 strong, but Napoleon had 144,000. Wittgenstein formed two strong defensive lines east of the River Spree, with the first holding strongpoints in villages and along hills and the second holding the bridges behind a river bend. Their left flank was anchored by the town of Baut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
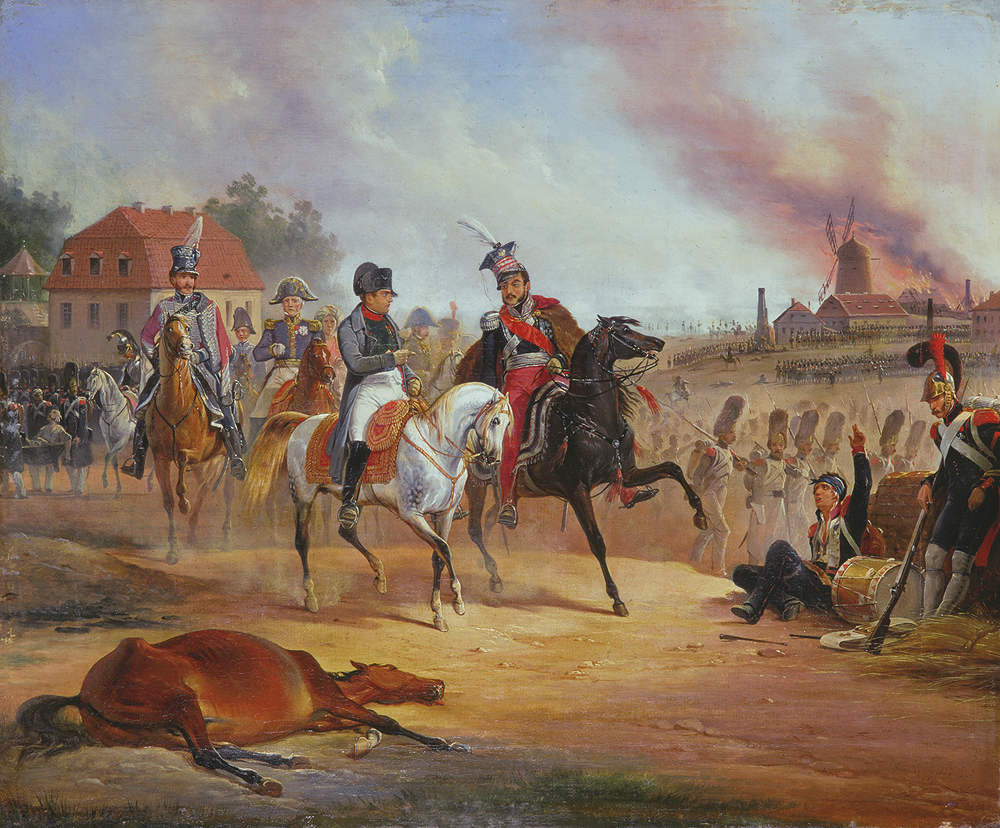
Battle Of Lützen (1813)
In the Battle of Lützen (German: ''Schlacht von Großgörschen'', 2 May 1813), Napoleon I of France defeated an allied army of the Sixth Coalition. The Russian commander, Prince Peter Wittgenstein, attempting to forestall Napoleon's capture of Leipzig, attacked the French right wing near Lützen, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany, surprising Napoleon. Quickly recovering, he ordered a double envelopment of the allies. After a day of heavy fighting, the imminent encirclement of his army prompted Wittgenstein to retreat. Due to a shortage of cavalry, the French did not pursue. The next battle would be fought at Bautzen three weeks later. Prelude Following the disaster of French invasion of Russia in 1812, a new Coalition consisting of Britain, Sweden, Prussia and Russia formed against France. In response to this, Napoleon hastily assembled an army of just over 200,000 which included inexperienced recruits, troops from Spain and garrison battalions but was severely short of horses (a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Maloyaroslavets
The Battle of Maloyaroslavets took place on 24 October 1812 as part of the French invasion of Russia. It was Kutuzov's decisive battle to force Napoleon to retreat northwest over Mozhaisk to Smolensk on the devastated route of his advance with a higher probability of starvation. Kutuzov's next attack against the remnants of the Grande Armee, the Battle of Krasnoi, began on 15 November 1812, 3 weeks later. Prelude The last major battle had been the Battle of Tarutino on 18 October 1812, that was won by the Russian army. A great part of the large mob of non-combatants, invalids from the hospitals, women, fugitive inhabitants of Moscow, whose number can only be guessed at, was directed upon Vereia and the straight road to Smolensk and only the fighting force was to march towards Kaluga. On 19 October 1812, Napoleon had retreated from Moscow and marched south-west to Kaluga, Eugene de Beauharnais leading the advance The French army leaving Moscow was estimated by Wilson: 90,000 eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Borodino
The Battle of Borodino (). took place near the village of Borodino on during Napoleon's invasion of Russia. The ' won the battle against the Imperial Russian Army but failed to gain a decisive victory and suffered tremendous losses. Napoleon fought against General Mikhail Kutuzov, whom the Emperor Alexander I of Russia had appointed to replace Barclay de Tolly on after the Battle of Smolensk. After the Battle of Borodino, Napoleon remained on the battlefield with his army; the Imperial Russian forces retreated in an orderly fashion southwards. Because the Imperial Russian army had severely weakened the ', they allowed the French occupation of Moscow since they used the city as bait to trap Napoleon and his men. The failure of the ' to completely destroy the Imperial Russian army, in particular Napoleon's reluctance to deploy his guard, has been widely criticised by historians as a huge blunder, as it allowed the Imperial Russian army to continue its retreat into territory in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Smolensk (1812)
The Battle of Smolensk was the first major battle of the French invasion of Russia. It took place on 16–18 August 1812 and involved about 45,000 men of the Grande Armée under Emperor Napoleon I against about 30,000 Russian troops under General Barclay de Tolly. Napoleon occupied Smolensk by driving out Prince Pyotr Bagration's Second Army. The French artillery bombardment burned the city to the ground. Of 2,250 buildings, 84% were destroyed with only 350 surviving intact. Of the city's 15,000 inhabitants, about 1,000 were left at the end of the battle inside the smoking ruins. With over 15,000 casualties, it was one of the bloodiest battles of the invasion. Prelude Vitebsk operation The Russian First Western Army under General Michael Andreas Barclay de Tolly slipped away from Vitebsk on 27 July after an inconclusive fight against Emperor Napoleon, avoiding a general engagement. Napoleon was frustrated by his inability to bring the Russian army to battle and lingered at Vite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |