|
Jean-François Joly De Fleury
Jean-François Joly de Fleury (1718-1802) was a minor figure serving in the French government as finance minister within a decade of the French Revolution. He was a member of the influential Joly de Fleury family. Family He was the son of , of the Parlement of Paris and of Marie Francoise Le Maistre. His brothers were Guillaume-François-Louis Joly de Fleury (1710-1787) who succeeded their father in his post as Procurator General, and Joseph Omer Joly de Fleury who may best be known for his unjust prosecution of Thomas Arthur, comte de Lally, Lally Tollendal on charges of treason. Finance Minister Joly de Fleury's predecessor was Jacques Necker, the Swiss wunderkind who was brought into the French ministry at a time of great debt in 1777. By the time Necker left in 1781, two things had occurred that exacerbated the crisis growing in the coffers of King Louis XVI of France. First, Necker had published the Compte rendu au roi, a "full" accounting of the King's finances—which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Necker
Jacques Necker (; 30 September 1732 – 9 April 1804) was a Genevan banker and statesman who served as finance minister for Louis XVI. He was a reformer, but his innovations sometimes caused great discontent. Necker was a constitutional monarchist, a political economist, and a moralist, who wrote a severe critique of the new principle of equality before the law. Necker held the finance post between July 1777 and 1781, being "remembered today for taking the unprecedented step in 1781 of making public the country's budget, a novelty in an absolute monarchy where the state of finances had always been kept a secret." Necker was dismissed within a few months. By 1788, the inexorable compounding of interest on the national debt brought France to a fiscal crisis. Necker was recalled to royal service. His dismissal on 11 July 1789 was a factor in causing the Storming of the Bastille. Within two days, Necker was recalled by the king and the assembly. Necker entered France in triumph and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Alexandre De Calonne
Charles Alexandre de Calonne (20 January 173430 October 1802), titled Count of Hannonville in 1759, was a French statesman, best known for his involvement in the French Revolution. Realizing that the Parlement de Paris would never agree to reform, Calonne handpicked an Assembly of Notables in 1787 to approve new taxes. When they refused, Calonne's reputation plummeted and he was forced to leave the country. Origins and rise to prominence Born in Douai of an upper-class family, he entered the legal profession and became a lawyer to the general council of Artois, procureur to the ''parlement'' of Douai, ''Master of Requests (France)'', intendant of Metz (1768) and of Lille (1774). He seems to have been a man with notable business abilities and an entrepreneurial spirit, while generally unscrupulous in his political actions. In the terrible crisis preceding the French Revolution, when successive ministers tried in vain to replenish the exhausted royal treasury, Calonne was summoned a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis XVI Of France
Louis XVI (''Louis-Auguste''; ; 23 August 175421 January 1793) was the last King of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. He was referred to as ''Citizen Louis Capet'' during the four months just before he was executed by guillotine. He was the son of Louis, Dauphin of France, son and heir-apparent of King Louis XV, and Maria Josepha of Saxony. When his father died in 1765, he became the new Dauphin. Upon his grandfather's death on 10 May 1774, he became King of France and Navarre, reigning as such until 4 September 1791, when he received the title of King of the French, continuing to reign as such until the monarchy was abolished on 21 September 1792. The first part of his reign was marked by attempts to reform the French government in accordance with Enlightenment ideas. These included efforts to abolish serfdom, remove the ''taille'' (land tax) and the ''corvée'' (labour tax), and increase tolerance toward non-Catholics as well as abolis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parlement Of Paris
The Parliament of Paris (french: Parlement de Paris) was the oldest ''parlement'' in the Kingdom of France, formed in the 14th century. It was fixed in Paris by Philip IV of France in 1302. The Parliament of Paris would hold sessions inside the medieval royal palace on the Île de la Cité, nowadays still the site of the Paris Hall of Justice. History In 1589, Paris was effectively in the hands of the Catholic League. To escape, Henry IV of France summoned the parliament of Paris to meet at Tours, but only a small faction of its parliamentarians accepted the summons. (Henry also held a parliament at Châlons, a town remaining faithful to the king, known as the Parliament of Châlons.) Following the assassination of Henry III of France by the Dominican lay brother Jacques Clément, the "Parliament of Tours" continued to sit during the first years of Henry IV of France's reign. The royalist members of the other provincial parliaments also split off—the royalist members of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marie Francoise Le Maistre
Marie may refer to: People Name * Marie (given name) * Marie (Japanese given name) * Marie (murder victim), girl who was killed in Florida after being pushed in front of a moving vehicle in 1973 * Marie (died 1759), an enslaved Cree person in Trois-Rivières, New France * ''Marie'', Biblical reference to Holy Mary, mother of Jesus * Marie Curie, scientist Surname * Jean Gabriel Marie (other) * Peter Marié (1826–1903), American socialite from New York City, philanthropist, and collector of rare books and miniatures * Rose Marie (1923–2017), American actress and singer * Teena Marie (1956–2010), American singer, songwriter, and producer Places * Marie, Alpes-Maritimes, commune of the Alpes-Maritimes department, France * Lake Marie, Umpqua Lighthouse State Park, Winchester Bay, Oregon, U.S. * Marie, Arkansas, U.S. * Marie, West Virginia, U.S. Art, entertainment, and media Music * "Marie" (Cat Mother and the All Night Newsboys song), 1969 * "Marie" (Johnny Hallyda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Omer Joly De Fleury
Joseph Omer Joly de Fleury (1715-1810) was a member of the distinguished Joly de Fleury family, originally from Burgundy, from which came a number of leading French magistrates and officials under the Ancien Régime, ancien regime. He is notable for four principal things: his strong opposition to the philosophes and the publication of the ''Encyclopedie'' in 1759; his role in the expulsion of the Suppression of the Society of Jesus, Jesuits; his involvement in the Thomas Arthur, comte de Lally, Lally Tollendal Affair; and his ban on inoculation against smallpox in June 1763. In a pun on his name, Voltaire described him as ‘ni Homère, ni joli, ni fleuri' ( = neither Homer, nor pretty, nor flowery, a sarcastic comment on his apparently dreary oratory). In one of his private letters, Voltaire described him as a ‘little black balloon puffed up with stinking vapours’ Family He was the son of , of the Parlement of Paris and of Marie Francoise Le Maistre. His brothers were Guilla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
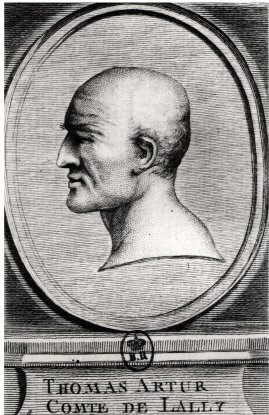
Thomas Arthur, Comte De Lally
Thomas Arthur, comte de Lally, baron de Tollendal (13 January 17029 May 1766) was a French general of Irish Jacobite ancestry. Lally commanded French forces, including two battalions of his own red-coated Regiment of Lally of the Irish Brigade, in India during the Seven Years' War. After a failed attempt to capture Madras he lost the Battle of Wandiwash to British forces under Eyre Coote and then was forced to surrender the remaining French post at Pondicherry. After time spent as a prisoner of war in Britain, Lally voluntarily returned to France to face charges where he was beheaded for his alleged failures in India. Ultimately the jealousies and disloyalties of other officers, together with insufficient resources and limited naval support prevented Lally from securing India for France. In 1778, he was publicly exonerated by Louis XVI from his alleged crime. Life He was born at Romans-sur-Isère, Dauphiné, the son of Sir Gerald Lally, an Irish Jacobite from Tuam, Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Louis XVI Of France
Louis XVI (''Louis-Auguste''; ; 23 August 175421 January 1793) was the last King of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. He was referred to as ''Citizen Louis Capet'' during the four months just before he was executed by guillotine. He was the son of Louis, Dauphin of France, son and heir-apparent of King Louis XV, and Maria Josepha of Saxony. When his father died in 1765, he became the new Dauphin. Upon his grandfather's death on 10 May 1774, he became King of France and Navarre, reigning as such until 4 September 1791, when he received the title of King of the French, continuing to reign as such until the monarchy was abolished on 21 September 1792. The first part of his reign was marked by attempts to reform the French government in accordance with Enlightenment ideas. These included efforts to abolish serfdom, remove the ''taille'' (land tax) and the ''corvée'' (labour tax), and increase tolerance toward non-Catholics as well as aboli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compte Rendu Au Roi
The ''Compte rendu'' (full name ''Compte rendu au roi'', translated as "''report to the king''") was a document published in February 1781 by Jacques Necker, finance minister to the King, in which he presented the state of France's finances. Content of the report The report stated that ordinary revenues in France were exceeding expenditure by over 10 million livres. The health of the accounts as reported in the Compte rendu boosted confidence among lenders and ordinary people, who saw Necker as a strong financial manager due to his prior experience as a banker; the report bolstered his reputation further. As a consequence, the French government was able to raise new loans to pay for the costs of continued involvement in the American War of Independence. However, Necker's reporting of the accounts obscured the financial problems which the country was facing: it did not report the extraordinary accounts, where the real cost of the war was to be found and which showed France in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Monarchy
Absolute monarchy (or Absolutism as a doctrine) is a form of monarchy in which the monarch rules in their own right or power. In an absolute monarchy, the king or queen is by no means limited and has absolute power, though a limited constitution may exist in some countries. These are often hereditary monarchies. On the other hand, in constitutional monarchies, in which the authority of the head of state is also bound or restricted by the constitution, a legislature, or unwritten customs, the king or queen is not the only one to decide, and their entourage also exercises power, mainly the prime minister. Absolute monarchy in Europe declined substantially following the French Revolution and World War I, both of which led to the popularization of theories of government based on the notion of popular sovereignty. Absolute monarchies include Brunei, Eswatini, Oman, Saudi Arabia, Vatican City, and the individual emirates composing the United Arab Emirates, which itself is a fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venal Office
In the context of the French Ancien Régime, a venal office refers to an office sold by the state to raise money. These offices, which were mostly in areas of the judicial system, were retained in exchange for an annual tax of one-sixtieth of the value known as the paulette. These offices provided access to power and opportunities for profit for those who bought them. The more important offices, which were more expensive, also conferred on their holders personal noble status that became hereditary, generally after three generations. Through venality of office, many bourgeoisie could hope for eventual noble status, and this provided an important avenue of social mobility for the expanding middle class. Prior to the French Revolution the bourgeoisie occupied 47,000 of the 51,000 venal offices, though this accounted for less than half of the total amount invested in venality. Louis XIV replenished his treasury by proliferating the amount of offices, as did his successors. In the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)