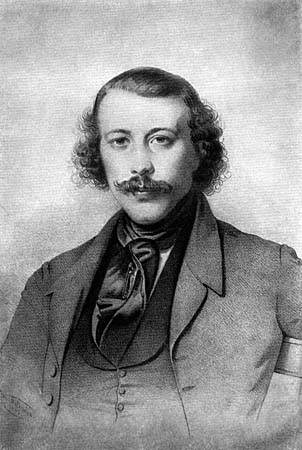|
Jaroslav Hašek
Jaroslav Hašek (; 1883–1923) was a Czechs, Czech writer, Humorism, humorist, Satire, satirist, journalist, Bohemianism, bohemian, first anarchist and then communist, and commissar of the Red Army against the Czechoslovak Legion. He is best known for his novel ''The Good Soldier Švejk, The Fateful Adventures of the Good Soldier Švejk During the World War'', an unfinished novel about a soldier in World War I and a satire on the ineptitude of authority figures. The novel has been translated into about 60 languages, making it the most translated novel in Czech literature. Life Jaroslav Hašek's paternal ancestors were farmers rooted in Mydlovary in South Bohemian Region, South Bohemia. Hašek's grandfather from his father's side, František Hašek, was a member of the Czech Landtag and later also the so-called Imperial Diet (Austria), Kromeriz convention. He was also involved in Prague uprising (1848), barricade fights in Prague in 1848. According to some rumors, he worked wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaroslav Hájek
Jaroslav Hájek (; 1926–1974) was a Czech people, Czech mathematician who worked in theoretical statistics, theoretical and nonparametric statistics, nonparametric statistics. The Hajek projection and Hájek–Le Cam convolution theorem are named after him (as well as collaborator Lucien Le Cam). Life Jaroslav Hájek studied statistical and insurance engineering at the Faculty of Special Sciences of the Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Technical University in Prague and in 1950 he successfully completed this study by obtaining an engineering degree. In 1955 he received the title of CSc. for the paper Contributions to the theory of statistical estimation, the supervisor of this thesis was Josef Novák. In 1963, he received a D.Sc. in the same year he received his habilitation at the Faculty of Mathematics and Physics of Charles University, in 1966 he was entitled professor at this faculty. In 1973, he was awarded the Klement Gottwald State Prize for his work on the asym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czechoslovak Legion
The Czechoslovak Legion ( Czech: ''Československé legie''; Slovak: ''Československé légie'') were volunteer armed forces consisting predominantly of Czechs and Slovaks fighting on the side of the Entente powers during World War I and the White Army during the Russian Civil War until November 1919. Their goal was to win the support of the Allied Powers for the independence of Lands of the Bohemian Crown from the Austrian Empire and of Slovak territories from the Kingdom of Hungary, which were then part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. With the help of émigré intellectuals and politicians such as the Czech Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk and the Slovak Milan Rastislav Štefánik, they grew into a force over 100,000 strong. In Russia, they took part in several victorious battles of the war, including the Zborov and Bakhmach against the Central Powers, and were heavily involved in the Russian Civil War fighting Bolsheviks, at times controlling the entire Trans-Siberian rail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Fanaticism
Religious fanaticism or religious extremism is a pejorative designation used to indicate uncritical zeal or obsessive enthusiasm that is related to one's own, or one's group's, devotion to a religion – a form of human fanaticism that could otherwise be expressed in one's other involvements and participation, including employment, role, and partisan affinities. In psychiatry, the term hyperreligiosity is used. Historically, the term was applied in Christian antiquity to denigrate non-Christian religions, and subsequently acquired its current usage with the Age of Enlightenment. Features Lloyd Steffen cites several features associated with religious fanaticism or extremism: * Spiritual needs: Human beings have a spiritual longing for understanding and meaning, and given the mystery of existence, that spiritual quest can only be fulfilled through some kind of relationship with ultimacy, whether or not that takes the form as a "transcendent other". Religion has power to mee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics Teacher
In contemporary education, mathematics education—known in Europe as the didactics or pedagogy of mathematics—is the practice of teaching, learning, and carrying out scholarly research into the transfer of mathematical knowledge. Although research into mathematics education is primarily concerned with the tools, methods, and approaches that facilitate practice or the study of practice, it also covers an extensive field of study encompassing a variety of different concepts, theories and methods. National and international organisations regularly hold conferences and publish literature in order to improve mathematics education. History Ancient Elementary mathematics were a core part of education in many ancient civilisations, including ancient Egypt, ancient Babylonia, ancient Greece, ancient Rome, and Vedic India. In most cases, formal education was only available to male children with sufficiently high status, wealth, or caste. The oldest known mathematics textbook is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Schwarzenberg
The House of Schwarzenberg () is a German (Franconian Circle, Franconian) and Czech (Kingdom of Bohemia, Bohemian) aristocratic family, formerly one of the most prominent European noble houses. The Schwarzenbergs are members of the German nobility, German and Czech nobility, and they once held the rank of Princes of the Holy Roman Empire. The family belongs to the high nobility and traces its roots to the Lords of Seinsheim during the Middle Ages. The secundogeniture branch of the Schwarzenbergs was among the foremost Czech patriotic houses. The current head of the family is (born 1967), son and heir of the late Karel Schwarzenberg, Karel, 12th Prince of Schwarzenberg (1937–2023), a Czech politician who served as Minister of Foreign Affairs (Czech Republic), Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Czech Republic. The family owns properties and lands across Austria, the Czech Republic, Germany, and Switzerland. History Origin The family stems from the Lords of Seinsheim, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaroslav Hasek - Pomnik V Lipnici Nad Sazavou - Detail
Jaroslav (also written as Yaroslav or Jarosław in other Slavic languages) is a Czech and Slovak first name, pagan in origin. Its feminine form is Jaroslava. There are several possible origins of the name Jaroslav. It is very likely that originally the two elements of the name referred to ''Jarilo'' - male Proto-Slavic deity of the sun, spring, and fertility, and ''slav'' meaning glory, i.e. "glory of the sun". However, with the adoption of Christianity in the Slavic countries the name began to be commonly understood not as a reference to a pagan deity, but rather to the "fervent worship of Go1of the Bible. ;People named Jaroslav: *Jaroslav Drobný, Czech tennis player *Jaroslav Drobný, Czech footballer *Jaroslav Filip, Slovak musician. *Jaroslav Foglar, Czech novelist *Jaroslav Halák, Slovak ice hockey player *Jaroslav Hašek, Czech author, writer of ''The Good Soldier Švejk'' *Jaroslav Heyrovský, Czech chemist and inventor, recipient of the Nobel prize *Jaroslav Jakubovič ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historically it could also refer to a wider area consisting of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the List of Bohemian monarchs, Bohemian kings, including Moravia and Czech Silesia, in which case the smaller region is referred to as Bohemia Proper as a means of distinction. Bohemia became a part of Great Moravia, and then an independent principality, which became a Kingdom of Bohemia, kingdom in the Holy Roman Empire. This subsequently became a part of the Habsburg monarchy and the Austrian Empire. After World War I and the establishment of an History of Czechoslovakia (1918–1938), independent Czechoslovak state, the whole of Bohemia became a part of Czechoslovakia, defying claims of the German-speaking inhabitants that regions with German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Bakunin
Mikhail Alexandrovich Bakunin. Sometimes anglicized to Michael Bakunin. ( ; – 1 July 1876) was a Russian revolutionary anarchist. He is among the most influential figures of anarchism and a major figure in the revolutionary socialist, social anarchist, and collectivist anarchist traditions. Bakunin's prestige as a revolutionary also made him one of the most famous ideologues in Europe, gaining substantial influence among radicals throughout Russia and Europe. Bakunin grew up in Pryamukhino, a family estate in Tver Governorate. From 1840, he studied in Moscow, then in Berlin hoping to enter academia. Later in Paris, he met Karl Marx and Pierre-Joseph Proudhon, who deeply influenced him. Bakunin's increasing radicalism ended hopes of a professorial career. He was expelled from France for opposing the Russian Empire's occupation of Poland. After participating in the 1848 Prague and 1849 Dresden uprisings, Bakunin was imprisoned, tried, sentenced to death, and extradit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prague Uprising (1848)
The Prague uprising (), also known as the Pentecostal Storm, was an armed conflict on 12–17 June 1848 in Prague, which culminated in the revolutionary process in the Czech lands. The uprising was a spontaneous unprepared uprising, which was suppressed by the army and killed about 43 people. Background From March 11, 1848 (Assembly in Svatováclavské lázně) there was a political unrest in Prague, by which Prague joined the wider revolutionary current in the whole of Europe. At that time, Czech politics had already split into a liberal current (František Palacký, Karel Havlíček Borovský) and a radically democratic one (Karel Sabina, Josef Václav Frič, Vincenc Vávra Haštalský, Vilém Gauč, Emanuel Arnold). In the first phase, the moderate liberals prevailed. They preferred constructive and cautious steps, such as the establishment of the St. Wenceslas Committee on March 12. On 19 and 31 March, the Committee prepared two petitions to the Emperor, which mainly incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Diet (Austria)
The Reichstag ("Imperial Diet"), also called Kremsier Parliament, was the first elected parliament in the Austrian Empire. It lasted for only a short time between July 1848 and 7 March 1849, but had an important effect on Austrian history. Its main product was the Kremsier Constitution which was preempted by the imposed March Constitution. Formed after the March Revolution of 1848 and in reaction to opposition to the Pillersdorf Constitution of 25 April 1848. The Diet consisted of 383 deputies from the German-speaking and Slavic crown lands of Habsburg Austria, that is, without representatives from the Kingdom of Hungary. It met for the first time on 22 July 1848 and was opened by Archduke Johann. On 22 October 1848, in the wake of the Vienna Uprising, it relocated to Kremsier and was finally dissolved on 7 March 1849. Its most important work was the abolition of the feudal system. Historical background The Kremsier Parliament had been elected in June, and convened in J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landtag
A ''Landtag'' (State Diet) is generally the legislative assembly or parliament of a federated state or other subnational self-governing entity in German-speaking nations. It is usually a unicameral assembly exercising legislative competence in non-federal matters. The States of Germany and Austria are governed by ''Landtage''. In addition, the legislature of the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol is known in German as a ''Landtag''. Historically, states of the German Confederation also established ''Landtage''. The Landtag of Liechtenstein is the nation's unicameral assembly. Name The German word Landtag is composed of the words ''Land'' (state, country or territory) and ''Tag'' (day). The German word ''Tagung'' (meeting) is derived from the German word ''Tag'', as such meetings were held at daylight and sometimes spanned several days. Historic Landtag assemblies States of the Holy Roman Empire In feudal society, the formal class system was reflected in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |