|
Japanese Submarine Ro-15
''Ro-15'', originally named ''Submarine No. 24'', was an Imperial Japanese Navy ''Kaichū''-Type submarine of the ''Kaichū'' II subclass. She was commissioned in 1921 and operated in the waters of Japan. She was stricken in 1933. Design and description The submarines of the ''Kaichu'' II sub-class were larger and had a greater range than the preceding ''Kaichu'' I subclass, but they had the same powerplant, so their greater size resulted in a loss of some speed.Gray, Randal, ed., ''Conway′s All the World′s Fighting Ships 1906–1921'', Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press, 1985, , p. 248. They also had a modified conning tower, bow, and stern, and the stern was overhanging. They displaced surfaced and submerged. The submarines were long and had a beam of and a draft of . They had a diving depth of . For surface running, the submarines were powered by two Sulzer Mark II diesel engines, each driving one propeller shaft. When submerged each propeller was driven by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kure Naval Arsenal
was one of four principal naval shipyards owned and operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy. History The Kure Naval District was established at Kure, Hiroshima in 1889, as the second of the naval districts responsible for the defense of the Japanese home islands. Along with the establishment of the navy base, a ship repair facility was also constructed, initially by moving the equipment from the Onohama shipyards near Kobe. Construction was supervised by the French engineer Louis-Émile Bertin. The first warship constructed at Kure, '' Miyako'', was launched in 1897. The "Kure Shipyards" were officially renamed the "Kure Naval Arsenal" in 1903. Kure developed into one of the largest shipbuilding facilities in the Empire of Japan, capable of working with the largest vessels. The Arsenal included a major steel works (built with British assistance), and also facilities for producing naval artillery and projectiles. The battleships ''Yamato'' and '' Nagato'' were designed and con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
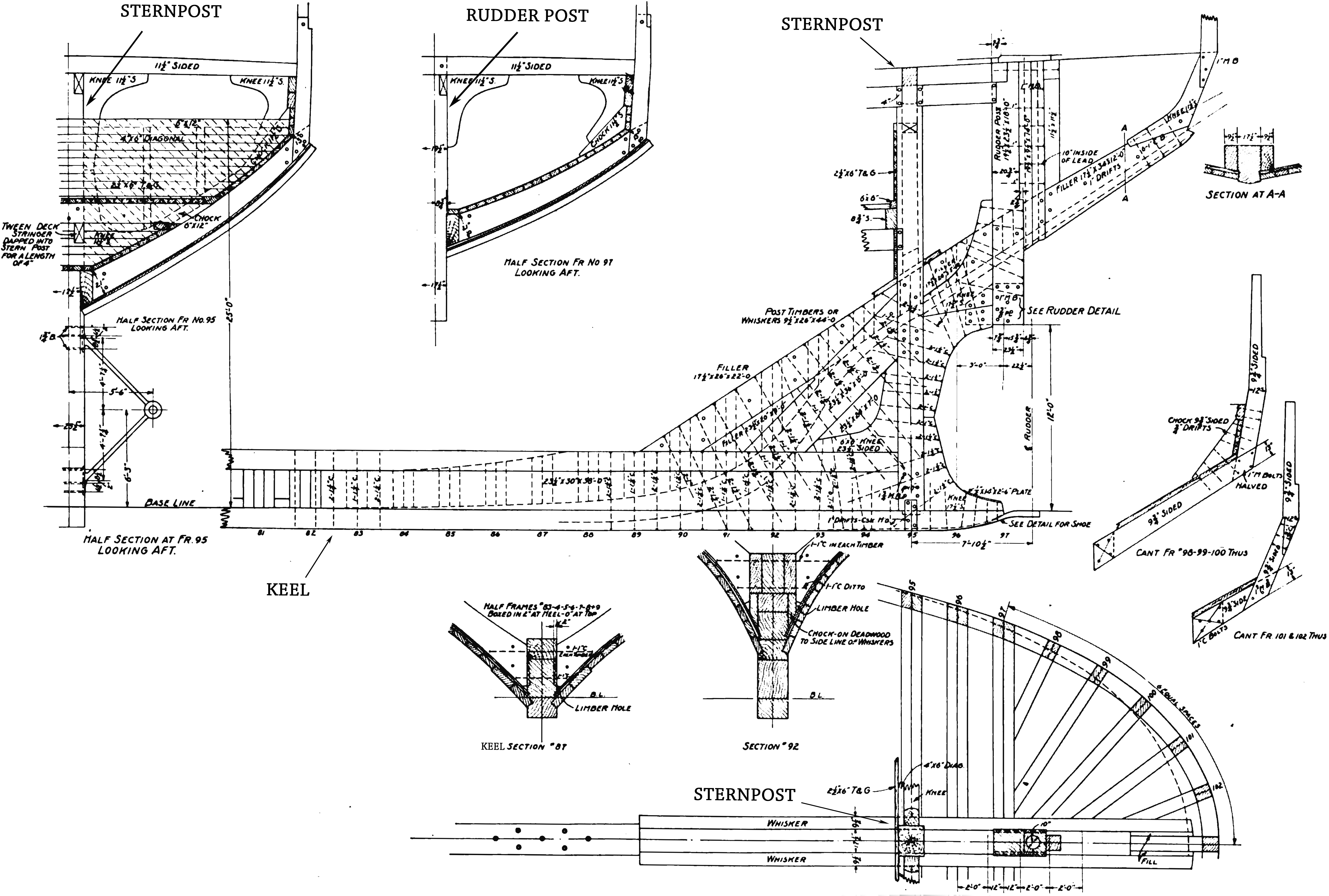
Stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night. Sterns on European and American wooden sailing ships began with two principal forms: the ''square'' or ''transom'' stern and the ''elliptical'', ''fantail'', or ''merchant'' stern, and were developed in that order. The hull sections of a sailing ship located before the stern were composed of a series of U-shaped rib-like frames set in a sloped or "cant" arrangement, with the last frame before the stern being called the ''fashion timber(s)'' or ''fashion piece(s)'', so called for "fashioning" the after part of the ship. This frame is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steamship
A steamship, often referred to as a steamer, is a type of steam-powered vessel, typically ocean-faring and seaworthy, that is propelled by one or more steam engines that typically move (turn) propellers or paddlewheels. The first steamships came into practical usage during the early 1800s; however, there were exceptions that came before. Steamships usually use the prefix designations of "PS" for ''paddle steamer'' or "SS" for ''screw steamer'' (using a propeller or screw). As paddle steamers became less common, "SS" is assumed by many to stand for "steamship". Ships powered by internal combustion engines use a prefix such as "MV" for ''motor vessel'', so it is not correct to use "SS" for most modern vessels. As steamships were less dependent on wind patterns, new trade routes opened up. The steamship has been described as a "major driver of the first wave of trade globalization (1870–1913)" and contributor to "an increase in international trade that was unprecedented in hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moji-ku, Kitakyūshū
is a Japanese ward of the city of Kitakyushu in Fukuoka Prefecture. It is the former city of Moji which was one of five merged to create Kitakyūshū in 1963. It faces the city of Shimonoseki across the Kanmon Straits between Honshū and Kyūshū. The ward's area is 73.37 km². It had a population of 114,754 as of 2000. History Moji was first made into a port by Suematsu Kenchō with the financial backing of Shibusawa Eiichi in 1889. It was chiefly used for the transportation of coal, though there is a traditional song about the sale of bananas imported into Moji from Southeast Asia which survives to this day (''Banana no tataki-uri''). An imperial decree in July 1899 established Moji as an open port for trading with the United States and the United Kingdom.US Department of State. (1906)''A digest of international law as embodied in diplomatic discussions, treaties and other international agreements'' (John Bassett Moore, ed.), Vol. 5, p. 759 In 1905, Moji was the departu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Wiring
Electrical wiring is an electrical installation of cabling and associated devices such as switches, distribution boards, sockets, and light fittings in a structure. Wiring is subject to safety standards for design and installation. Allowable wire and electrical cable, cable types and sizes are specified according to the circuit operating voltage and electric current capability, with further restrictions on the environmental conditions, such as ambient temperature range, moisture levels, and exposure to sunlight and chemicals. Associated circuit protection, control, and distribution devices within a building's wiring system are subject to voltage, current, and functional specifications. Wiring safety codes vary by locality, country, or region. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is attempting to harmonise wiring standards among member countries, but significant variations in design and installation requirements still exist. Wiring codes of practice and regulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galley (kitchen)
The galley is the compartment of a ship, train, or aircraft where food is cooked and prepared. It can also refer to a land-based kitchen on a naval base, or, from a kitchen design point of view, to a straight design of the kitchen layout. Ship's cooking area A galley is the cooking area aboard a vessel, usually laid out in an efficient typical style with longitudinal units and overhead cabinets. This makes the best use of the usually limited space aboard ships. It also caters for the rolling and heaving nature of ships, making them more resistant to the effects of the movement of the ship. For this reason galley stoves are often gimballed, so that the liquid in pans does not spill out. They are also commonly equipped with bars, preventing the cook from falling against the hot stove. A small cooking area on deck was called a caboose or ''camboose'', originating from the nl, kombuis, which is still in use today. In English it is a defunct term used only for a cooking area that is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kure Defense Division
is a port and major shipbuilding city situated on the Seto Inland Sea in Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan. With a strong industrial and naval heritage, Kure hosts the second-oldest naval dockyard in Japan and remains an important base for the Japan Maritime Self-Defence Force (JMSDF) named, JMSDF Kure Naval Base. , the city has an estimated population of 228,030 and a population density of 646 persons per km2. The total area is 352.80 km2. History The Kure Naval District was first established in 1889, leading to the construction of the Kure Naval Arsenal and the rapid growth of steel production and shipbuilding in the city. Kure was formally incorporated on October 1, 1902. From 1889 until the end of World War II, the city served as the headquarters of the Kure Naval District. Kure dockyards recorded a number of significant engineering firsts including the launching of the first major domestically built capital ship, the battlecruiser ''Tsukuba'' (1905) and the laun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kure Naval District
was the second of four main administrative districts of the pre-war Imperial Japanese Navy. Its territory included the Seto Inland Sea, Inland Sea of Japan and the Pacific Ocean, Pacific coasts of southern Honshū from Wakayama prefecture, Wakayama to Yamaguchi prefectures, eastern and northern Kyūshū and Shikoku. The area of the Kure Naval District encompassed Hashirajima Anchoring Area located at the south end of Hiroshima Bay, 30-40 kilometers southwest of Kure. When not in need of repairs ships usually anchored in this area to free up pier space at Kure. Hashirajima was also a major staging area for fleet operations. Tokuyama, Yamaguchi, Tokuyama port, was also part of Kure Naval District, and had the largest fuel depot in the Japanese Navy. History The location of Kure, Hiroshima, Kure within the sheltered Inland Sea of Japan was recognized of strategic importance in controlling the sea lanes around western Japan by the Meiji government and early Imperial Japanese Navy. Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Commissioning
Ship commissioning is the act or ceremony of placing a ship in active service and may be regarded as a particular application of the general concepts and practices of project commissioning. The term is most commonly applied to placing a warship in active duty with its country's military forces. The ceremonies involved are often rooted in centuries-old naval tradition. Ship naming and launching endow a ship hull with her identity, but many milestones remain before she is completed and considered ready to be designated a commissioned ship. The engineering plant, weapon and electronic systems, galley, and other equipment required to transform the new hull into an operating and habitable warship are installed and tested. The prospective commanding officer, ship's officers, the petty officers, and seamen who will form the crew report for training and familiarization with their new ship. Before commissioning, the new ship undergoes sea trials to identify any deficiencies needing corre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
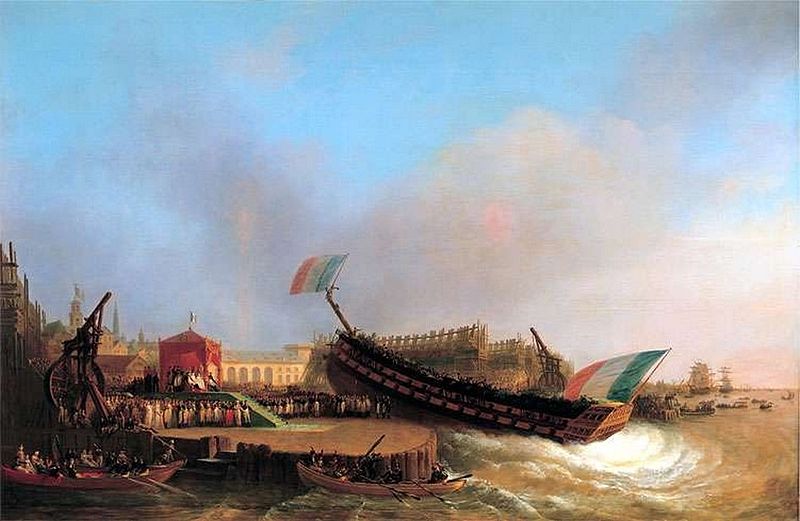
Ceremonial Ship Launching
Ceremonial ship launching involves the performance of ceremonies associated with the process of transferring a vessel to the water. It is a nautical tradition in many cultures, dating back thousands of years, to accompany the physical process with ceremonies which have been observed as public celebration and a solemn blessing, usually but not always, in association with the launch itself. Ship launching imposes stresses on the ship not met during normal operation and, in addition to the size and weight of the vessel, represents a considerable engineering challenge as well as a public spectacle. The process also involves many traditions intended to invite good luck, such as christening by breaking a sacrificial bottle of champagne over the bow as the ship is named aloud and launched. Methods There are three principal methods of conveying a new ship from building site to water, only two of which are called "launching". The oldest, most familiar, and most widely used is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keel-laying
Laying the keel or laying down is the formal recognition of the start of a ship's construction. It is often marked with a ceremony attended by dignitaries from the shipbuilding company and the ultimate owners of the ship. Keel laying is one of the four specially celebrated events in the life of a ship; the others are launching, commissioning and decommissioning. In earlier times, the event recognized as the keel laying was the initial placement of the central timber making up the backbone of a vessel, called the keel. As steel ships replaced wooden ones, the central timber gave way to a central steel beam. Modern ships are most commonly built in a series of pre-fabricated, complete hull sections rather than around a single keel. The event recognized as the keel laying is the first joining of modular components, or the lowering of the first module into place in the building dock. It is now often called "keel authentication", and is the ceremonial beginning of the ship's life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propeller Shaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft (Australian English), propeller shaft (prop shaft), or Cardan shaft (after Girolamo Cardano) is a component for transmitting mechanical power and torque and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drivetrain that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement between them. As torque carriers, drive shafts are subject to torsion and shear stress, equivalent to the difference between the input torque and the load. They must therefore be strong enough to bear the stress, while avoiding too much additional weight as that would in turn increase their inertia. To allow for variations in the alignment and distance between the driving and driven components, drive shafts frequently incorporate one or more universal joints, jaw couplings, or rag joints, and sometimes a splined joint or prismatic joint. History The term ''driveshaft'' first appeared during the mid-19th centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_underway_2009.jpg)


