|
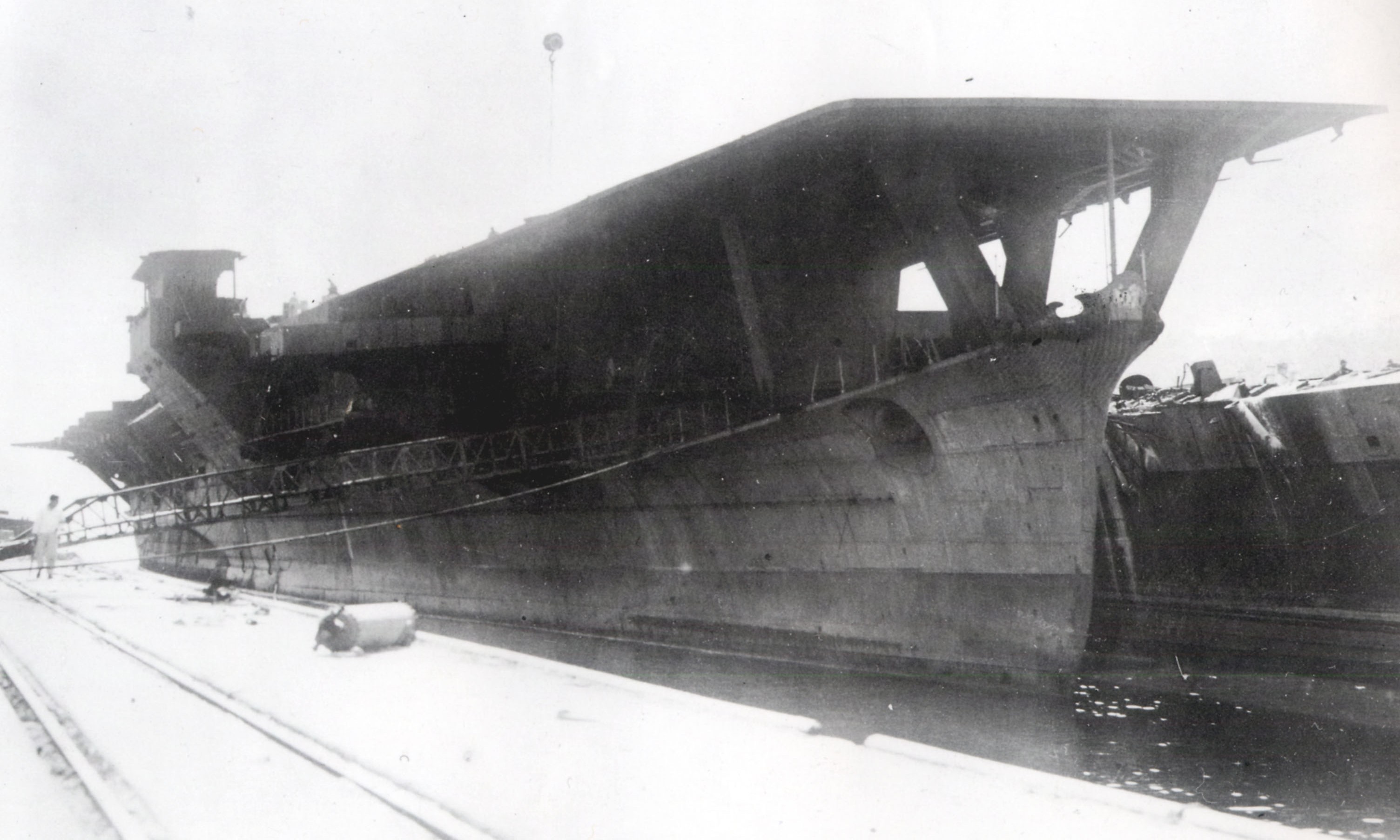
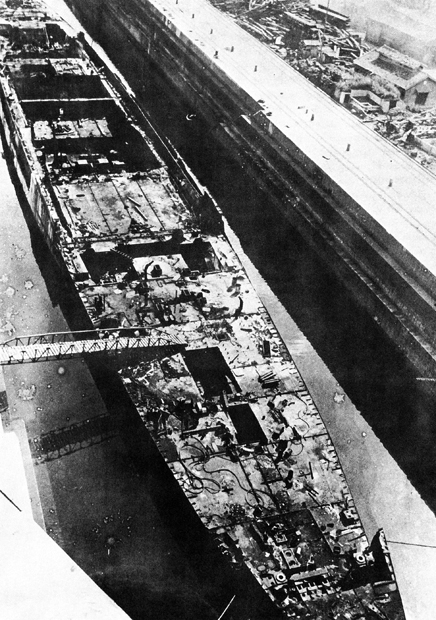
Japanese Cruiser Ibuki (1943)
The Japanese cruiser was a heavy cruiser built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during World War II. The lead ship of her class of two ships, she was ordered to be converted into a light aircraft carrier in 1943 before completion to help replace the aircraft carriers sunk during the Battle of Midway in mid-1942. The conversion was delayed and finally stopped in March 1945 in order to concentrate on building small submarines. ''Ibuki'' was scrapped in the Sasebo Naval Arsenal beginning in 1946. Background The ''Ibuki''-class cruisers were ordered in the Rapid Naval Armaments Supplement Programme of November 1941, and they were slightly improved versions of the preceding after those ships had been upgraded during the late 1930s. After the heavy losses suffered in the Battle of Midway in early June 1942, the IJN reorganized its current building programs to emphasize aircraft carrier construction. ''Ibuki'', which had only been laid down a few months earlier, had all work sus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasebo, Nagasaki
is a Core cities of Japan, core city located in Nagasaki Prefecture, Japan. It is also the second largest city in Nagasaki Prefecture, after its capital, Nagasaki. On 1 June 2019, the city had an estimated population of 247,739 and a population density of 581 persons per km2 (1,505 persons per square mile). The total area is . The city includes a part of Saikai National Park. Located in the southern part of the city is the Dutch-styled theme park ''Huis Ten Bosch (theme park), Huis Ten Bosch''. The island of Ukujima is also administered as part of Sasebo city. History The area of present-day Sasebo was a small fishing village under the control of nearby Hirado Domain until shortly after the start of the Meiji period. Imperial Japanese Navy Admiral Tōgō Heihachirō, when surveying the coasts of northwestern Kyūshū for the site of a navy base, selected his location based on its protected, deep-water harbor, geographic proximity to China and Korea, and the presence of nearby Coal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deck (ship)
A deck is a permanent covering over a compartment or a hull of a ship. On a boat or ship, the primary or upper deck is the horizontal structure that forms the "roof" of the hull, strengthening it and serving as the primary working surface. Vessels often have more than one level both within the hull and in the superstructure above the primary deck, similar to the floors of a multi-storey building, that are also referred to as decks, as are certain compartments and decks built over specific areas of the superstructure. Decks for some purposes have specific names. Structure The main purpose of the upper or primary deck is structural, and only secondarily to provide weather-tightness and support people and equipment. The deck serves as the lid to the complex box girder which can be identified as the hull. It resists tension, compression, and racking forces. The deck's scantling is usually the same as the topsides, or might be heavier if the deck is expected to carry heavier loads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shipyard
A shipyard, also called a dockyard or boatyard, is a place where ships are built and repaired. These can be yachts, military vessels, cruise liners or other cargo or passenger ships. Dockyards are sometimes more associated with maintenance and basing activities than shipyards, which are sometimes associated more with initial construction. The terms are routinely used interchangeably, in part because the evolution of dockyards and shipyards has often caused them to change or merge roles. Countries with large shipbuilding industries include Australia, Brazil, China, Croatia, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, India, Ireland, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, Norway, the Philippines, Poland, Romania, Russia, Singapore, South Korea, Sweden, Taiwan, Turkey, the United Arab Emirates, Ukraine, the United Kingdom, the United States and Vietnam. The shipbuilding industry is more fragmented in Europe than in Asia where countries tend to have fewer, larger companies. Many naval vessels ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laid Down
Laying the keel or laying down is the formal recognition of the start of a ship's construction. It is often marked with a ceremony attended by dignitaries from the shipbuilding company and the ultimate owners of the ship. Keel laying is one of the four specially celebrated events in the life of a ship; the others are launching, commissioning and decommissioning. In earlier times, the event recognized as the keel laying was the initial placement of the central timber making up the backbone of a vessel, called the keel. As steel ships replaced wooden ones, the central timber gave way to a central steel beam. Modern ships are most commonly built in a series of pre-fabricated, complete hull sections rather than around a single keel. The event recognized as the keel laying is the first joining of modular components, or the lowering of the first module into place in the building dock. It is now often called "keel authentication", and is the ceremonial beginning of the ship's life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Naval Armaments Supplement Programme
The was one of the armaments expansion plan of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). Background In August 1941, the IJN started building warships for war. It extended to 293 vessels, 300,000 tons. Table of vessels See also * 1st Naval Armaments Supplement Programme (Maru 1 Keikaku, 1931) * 2nd Naval Armaments Supplement Programme (Maru 2 Keikaku, 1934) * 3rd Naval Armaments Supplement Programme (Maru 3 Keikaku, 1937) *4th Naval Armaments Supplement Programme (Maru 4 Keikaku, 1939) * Temporal Naval Armaments Supplement Programme (Maru Rin Keikaku, 1940) * Additional Naval Armaments Supplement Programme (Maru Tui Keikaku, 1941) * 5th Naval Armaments Supplement Programme (Maru 5 Keikaku, 1941) *6th Naval Armaments Supplement Programme (Maru 6 Keikaku, 1942) * Modified 5th Naval Armaments Supplement Programme (Kai-Maru 5 Keikaku, 1942) * Wartime Naval Armaments Supplement Programme (Maru Sen Keikaku, 1944) References *''Rekishi Gunzō series'', Gakken (Japan) *''The Maru Special series' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasebo Naval Arsenal
was one of four principal naval shipyards owned and operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy. History The Sasebo Naval District was established at Sasebo, Nagasaki in 1886, as the third of the naval districts responsible for the defense of the Japanese home islands. After the establishment of the navy base, a ship repair facility was established in 1889 with a dry dock. With the addition of equipment and facilities for ship production by 1897, the "Sasebo Shipyards" were officially established, and renamed the "Sasebo Naval Arsenal" in 1903. Construction of the arsenal was supervised by the French engineer Louis-Émile Bertin. In 1913, a 250-ton crane was installed, and the shipbuilding facilities expanded to permit the construction of large warships. With the mothballing of the Maizuru Naval Arsenal due to restrictions by the Washington Naval Treaty, much of the design and prototype work for new classes of destroyers and torpedo boats formerly done at Maizuru was shifted to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely operated vehicles and Autonomous underwater vehicle, robots, as well as medium-sized or smaller vessels, such as the midget submarine and the wet sub. Submarines are referred to as ''boats'' rather than ''ships'' irrespective of their size. Although experimental submarines had been built earlier, submarine design took off during the 19th century, and they were adopted by several navies. They were first widely used during World War I (1914–1918), and are now used in many navy, navies, large and small. Military uses include attacking enemy surface ships (merchant and military) or other submarines, and for aircraft carrier protection, Blockade runner, blockade running, Ballistic missile submarine, nuclear deterrence, reconnaissance, conventio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Midway
The Battle of Midway was a major naval battle in the Pacific Theater of World War II that took place on 4–7 June 1942, six months after Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor and one month after the Battle of the Coral Sea. The U.S. Navy under Admirals Chester W. Nimitz, Frank J. Fletcher, and Raymond A. Spruance defeated an attacking fleet of the Imperial Japanese Navy under Admirals Isoroku Yamamoto, Chūichi Nagumo, and Nobutake Kondō north of Midway Atoll, inflicting devastating damage on the Japanese fleet. Military historian John Keegan called it "the most stunning and decisive blow in the history of naval warfare", while naval historian Craig Symonds called it "one of the most consequential naval engagements in world history, ranking alongside Salamis, Trafalgar, and Tsushima Strait, as both tactically decisive and strategically influential". Hoping to lure the American aircraft carriers into a trap and occupying Midway was part of an overall "barrier" strategy to extend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Aircraft Carrier
A light aircraft carrier, or light fleet carrier, is an aircraft carrier that is smaller than the standard carriers of a navy. The precise definition of the type varies by country; light carriers typically have a complement of aircraft only one-half to two-thirds the size of a full-sized fleet carrier. A light carrier was similar in concept to an escort carrier in most respects, however light carriers were intended for higher speeds to be deployed alongside fleet carriers, while escort carriers usually defended convoys and provided air support during amphibious operations. History In World War II (WWII), the United States Navy produced a number of light carriers by converting cruiser hulls. These s, converted from light cruisers, were unsatisfactory ships for aviation with their narrow, short decks and slender, high- sheer hulls; in virtually all respects the escort carriers were superior aviation vessels. These issues were superseded by ''Independence''-class ships' virtue of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibuki-class Cruiser
The cruisers were the last class of heavy cruisers built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). In order to save design time, the ships were essentially repeats of the earlier . Begun during World War II, only the lead ship, , was launched, but she was in the process of being converted into a light aircraft carrier when construction was suspended in 1945. She was scrapped the following year. The unnamed second ship was scrapped less than a month after being laid down in order to clear her slipway for an aircraft carrier. Design and description The design of the ''Ibuki'' class was a minor improvement over the last pair of the ''Mogami'' class after those ships had been upgraded during the late 1930s. The main improvement was the replacement of the triple torpedo tube mounts in the older ships with quadruple mounts. They cost 60,000,000 yen each and had a crew of 54 officers and 822 enlisted men. The ships had a length of overall. They had a beam of and a draft of . They dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead Ship
The lead ship, name ship, or class leader is the first of a series or class of ships all constructed according to the same general design. The term is applicable to naval ships and large civilian vessels. Large ships are very complex and may take as many as five to ten years to build. Improvements based on experience with building and operating the lead ship are likely to be incorporated into the design or construction of later ships in the class, so it is rare to have vessels that are identical. The second and later ships are often started before the first one is completed, launched and tested. Nevertheless, building copies is still more efficient and cost-effective than building prototypes, and the lead ship will usually be followed by copies with some improvements rather than radically different versions. The improvements will sometimes be retrofitted to the lead ship. Occasionally, the lead ship will be launched and commissioned for shakedown testing before following ship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |