|
Jangja-puri
Life replacement narratives or life extension narratives refer to three Korean shamanic narratives chanted during religious rituals, all from different regional traditions of mythology but with a similar core story: the ''Menggam bon-puri'' of the Jeju tradition, the ''Jangja-puri'' of the Jeolla tradition, and the ''Honswi-gut'' narrative of the South Hamgyong tradition. As oral literature, all three narratives exist in multiple versions. In all three narratives, a man (or men) is forewarned of his impending death and makes offerings to the ''chasa'', the gods of death who kill those whose time is due and take away their souls to the afterlife. The ''chasa'' unwittingly accept the offerings before realizing that they have accepted gifts from the man that they were supposed to kill. As they cannot ignore his gifts, they decide to spare his life and take the soul of another human or animal in his place. Other parts of the story differ significantly between the three narratives. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Shamanic Narrative
Korean mythology ( ) is the group of myths told by historical and modern Koreans. There are two types: the written, literary mythology in traditional histories, mostly about the founding monarchs of various historical kingdoms, and the much larger and more diverse oral mythology, mostly narratives sung by shamans or priestesses (mansin) in rituals invoking the gods and which are still considered sacred today. The historicized state-foundation myths that represent the bulk of the literary mythology are preserved in Classical Chinese-language works such as ''Samguk sagi'' and ''Samguk yusa''. One state's foundation myth, that of Dan'gun, has come to be seen as the founding myth of the whole Korean nation. State-foundation myths are further divided into northern, such as that of the kingdom of Goguryeo and its founder Jumong, where the founder is the son of a celestial male figure and an earthly female figure, and southern, such as that of the kingdom of Silla and its founder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Mythology
Korean mythology ( ) is the group of myths told by historical and modern Koreans. There are two types: the written, literary mythology in traditional histories, mostly about the founding monarchs of various historical kingdoms, and the much larger and more diverse oral mythology, mostly narratives sung by shamans or priestesses (mansin) in rituals invoking the gods and which are still considered sacred today. The historicized state-foundation myths that represent the bulk of the literary mythology are preserved in Classical Chinese-language works such as ''Samguk sagi'' and ''Samguk yusa''. One state's foundation myth, that of Dan'gun, has come to be seen as the founding myth of the whole Korean nation. State-foundation myths are further divided into northern, such as that of the kingdom of Goguryeo and its founder Jumong, where the founder is the son of a celestial male figure and an earthly female figure, and southern, such as that of the kingdom of Silla and its foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
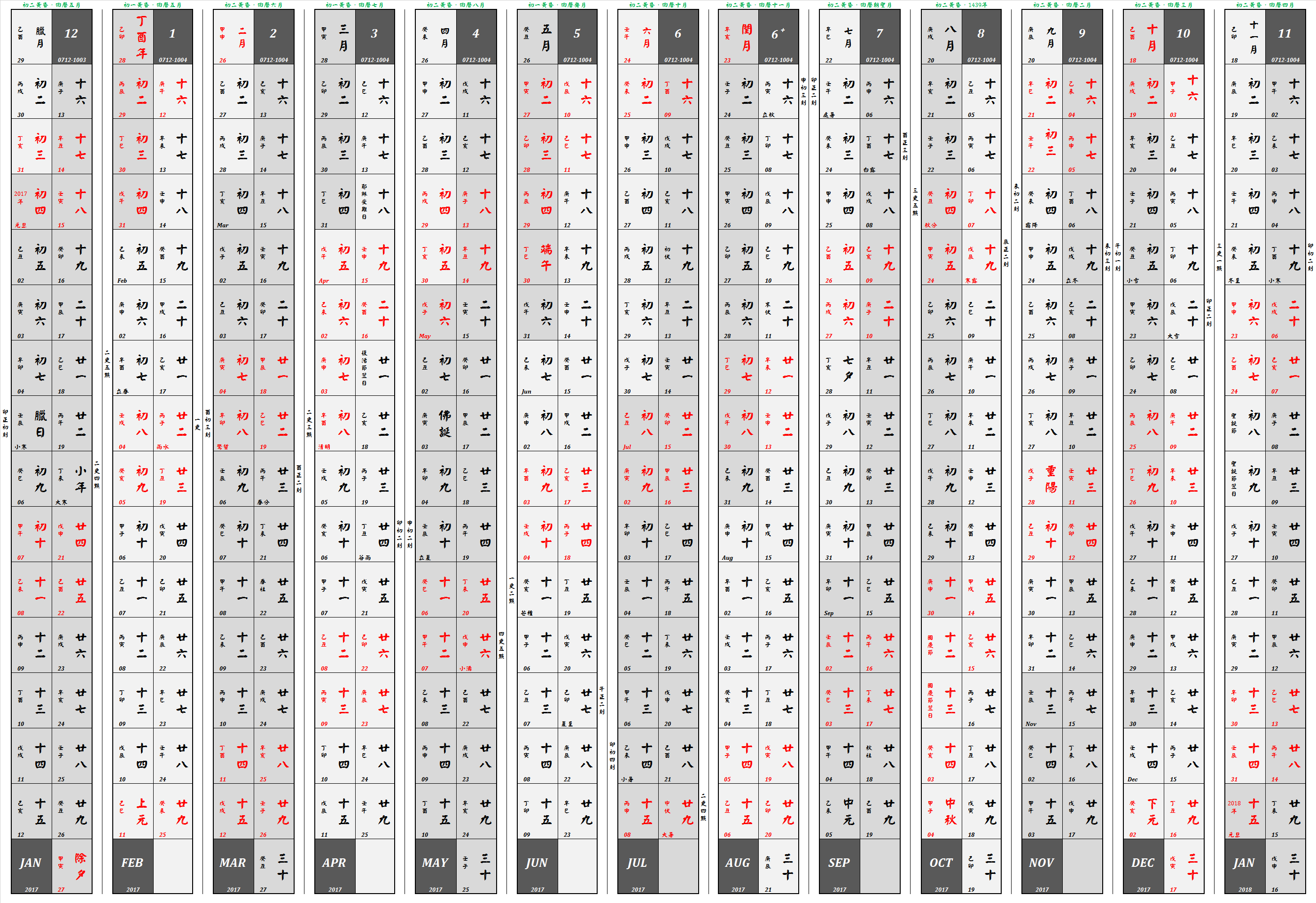
Chinese Calendar
The traditional Chinese calendar (also known as the Agricultural Calendar ��曆; 农历; ''Nónglì''; 'farming calendar' Former Calendar ��曆; 旧历; ''Jiùlì'' Traditional Calendar ��曆; 老历; ''Lǎolì'', is a lunisolar calendar which identifies years, months, and days according to astronomical phenomena. In China, it is defined by the Chinese national standard GB/T 33661–2017, "Calculation and Promulgation of the Chinese Calendar", issued by the Standardization Administration of China on May 12, 2017. Although modern-day China uses the Gregorian calendar, the traditional Chinese calendar governs holidays, such as the Chinese New Year and Lantern Festival, in both China and overseas Chinese communities. It also provides the traditional Chinese nomenclature of dates within a year which people use to select auspicious days for weddings, funerals, moving or starting a business. The evening state-run news program '' Xinwen Lianbo'' in the P.R.C. continues to anno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Language
Korean (South Korean: , ''hangugeo''; North Korean: , ''chosŏnmal'') is the native language for about 80 million people, mostly of Koreans, Korean descent. It is the official language, official and national language of both North Korea and South Korea (geographically Korea), but over the past years of political division, the North–South differences in the Korean language, two Koreas have developed some noticeable vocabulary differences. Beyond Korea, the language is recognised as a minority language in parts of China, namely Jilin, Jilin Province, and specifically Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture, Yanbian Prefecture and Changbai Korean Autonomous County, Changbai County. It is also spoken by Sakhalin Koreans in parts of Sakhalin, the Russian island just north of Japan, and by the in parts of Central Asia. The language has a few Extinct language, extinct relatives which—along with the Jeju language (Jejuan) of Jeju Island and Korean itself—form the compact Koreanic l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soot
Soot ( ) is a mass of impure carbon particles resulting from the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons. It is more properly restricted to the product of the gas-phase combustion process but is commonly extended to include the residual pyrolysed fuel particles such as coal, cenospheres, charred wood, and petroleum coke that may become airborne during pyrolysis and that are more properly identified as cokes or char. Soot causes various types of cancer and lung disease. Sources Soot as an airborne contaminant in the environment has many different sources, all of which are results of some form of pyrolysis. They include soot from coal burning, internal-combustion engines, power-plant boilers, hog-fuel boilers, ship boilers, central steam-heat boilers, waste incineration, local field burning, house fires, forest fires, fireplaces, and furnaces. These exterior sources also contribute to the indoor environment sources such as smoking of plant matter, cooking, oil lamps, can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gangnim
The ''Chasa Bonpuri'', known in other versions as the ''Chesa Bonpuri'' (1933 version) or the ''Cheseo Bonpuri'' (2006 and 2008 versions), is a Korean myth of Jeju Island. It is a myth that tells how Gangnim, the death god, came to be. As one of the best-known myths in the Korean peninsula, the ''Chasa Bonpuri'' is a characteristic hero epic. Etymology The term ''Chasa Bonpuri'' (차사 본풀이) means "Solving the origins of the death god"; modern academic circles synonymize "Bonpuli" with "myth". ''Chasa'' is the Standard Korean pronunciation of the Chinese word ''Chaishi'' (差使), meaning "messenger". In the Jeju language however, ''chaishi'' is pronounced ''Chesɒ'' or ''Cheshi'', leading to the different names per each version. Collections The Chasa Bonpuli has been directly collected from shamans nine times; below is a chart of these collections. Major plot Like all oral myths, there are multiple versions of the Chasa Bonpuli. The best-known version, introduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Council Of Joseon
The State Council of Joseon or Uijeongbu was the highest organ of government under the Joseon Dynasty of Korea. It was led by three officials known as the High State Councillors. The Councilors were entrusted to deliberate over key problems of state, advising the king, and conveying royal decisions to the Six Ministries. The Council was formed under the reign of Jeongjong, just before Taejong seized power in 1400. It replaced an earlier institution called the "Privy Council," which had been dominated by Jeong Dojeon and other key figures behind the dynasty's founding. The State Council gradually declined in importance over the 500 years of Joseon's rule. Finally, the Council was replaced by the cabinet in 1907, forced by Japanese intervention Today, there's a city which was named after this organ (Uijeongbu) in Gyeonggi-do. Structure The State Council comprised: * the Chief State Councilor (영의정 領議政), rank 1a * the Left and Right State Councilors (좌ㆍ우의정 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Shaman
''Mu'' () is an ancient Korean word defining a shaman in the Korean traditional religion. Korean shamans hold rituals called '' gut'' (literally "good") for the welfare of the individuals and the society. In modern Korea different terms are used to define shamans, including mudang (mostly for females), baksu (only for males), tangol (for hereditary shamans), and musogin ("people who do shamanism", used in the context of organised shamanism). Etymology The Korean word 무 ''mu'' is related to the Chinese 巫 '' wu'', which defines shamans of either sex. Korean shamanic terminology has, however, at least a partial origin in Siberian languages. Already in records from the Yi dynasty, ''mudang'' has a prevalent usage. ''Mudang'' itself is explained in relation to Chinese characters, as originally referring to the "hall", 堂 ''tang'', of a shaman. A different etymology, however, explains ''mudang'' as stemming directly from the Siberian term for female shamans, ''utagan'' or ''ut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeju Language
Jeju (Jeju: , ; ko, 제주어, or , ), often called Jejueo or Jejuan in English-language scholarship, is a Koreanic language traditionally spoken on Jeju Island, South Korea. While often classified as a divergent Jeju dialect ( ko, 제주방언, links=no, ) of the Korean language, the variety is referred to as a language in local government and increasingly in both South Korean and foreign academia. Jeju is not mutually intelligible with the mainland dialects of South Korea. The consonants of Jeju are similar to those of Seoul Korean, but Jeju has a larger and more conservative vowel inventory. Jeju is a head-final, agglutinative, suffixing language like Korean. Nouns are followed by particles that may function as case markers. Verbs inflect for tense, aspect, mood, evidentiality, relative social status, formality, and other grammatical information. Korean and Jeju differ significantly in their verbal paradigms. For instance, the continuative aspect marker of Jeju and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeju Island Traditional Hunters
Jeju may refer to: * Jeju Island (Jejudo), an island near South Korea * Jeju Province (formerly transliterated Cheju), a province of South Korea comprising Jejudo **Jeju City, the biggest city on Jejudo **Jeju dog, a dog native to Jejudo **Jeju language, the Koreanic language spoken on Jejudo **Jeju people ** Jeju Black, a cattle breed from the island *Jeju Air, an airline operating from Jejudo * Jeju Bank, the subsidiary of Shinhan Bank * Jeju (woreda), one of the 180 ''woredas'' district in the Oromia Region of Ethiopia * Jeju Shinhwa World, a fully integrated South Korean resort located on Jeju Island * ''Hoplerythrinus unitaeniatus ''Hoplerythrinus unitaeniatus'' is a species of trahira (family Erythrinidae). It is a tropical, pelagic freshwater fish Freshwater fish are those that spend some or all of their lives in fresh water, such as rivers and lakes, with a salini ...'', an Amazonian fish known as jeju {{disambig, geo Language and nationality disambiguation pages< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |