|
James River Squadron
The James River Squadron was formed shortly after the secession of Virginia during the American Civil War. The squadron was part of the Virginia Navy before being transferred to the Confederate States Navy. The squadron is most notable for its role in patrolling the James River, which was the main water approach to the Confederate capital, Richmond. It had two phases: early war, when it consisted mostly of wooden ships (besides the famous CSS ''Virginia'') which ended with the Battle of Drewry's Bluff on May 15, 1862; and its later ironclad composition with the flagship CSS ''Virginia II''. History Background The Provisional Navy of Virginia was established by an ordinance of the Convention of Virginia on 27 April 27, 1861, when Virginia seceded from the Union. The James River Squadron was formed as part of this navy. When Virginia joined the Confederate States of America, Governor John Letcher issued a proclamation on 6 June 1861, transferring "all officers, seamen, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virginia State Navy
A Virginia State Navy (or Virginia Navy) existed twice. During the American Revolutionary War, the provisional government of the Virginia Colony authorized the purchase, outfitting, and manning of armed vessels to protect the colony's waters from threats posed it by the Royal Navy. Early in the American Civil War, after the state of Virginia seceded from the Union on April 17, 1861, it briefly had naval forces of its own known as the Virginia State Navy, which existed in tandem to the Provisional Army of Virginia. Both of these forces had been absorbed by the Confederate States Navy and the Confederate Army by the end of 1861. American Revolutionary War Virginia, along with the other Thirteen Colonies, was increasingly dissatisfied with the actions of Lord Dunmore, the royal governor of the colony. After the Gunpowder Incident in April 1775 and the news of the war's outbreak with the Battles of Lexington and Concord, Dunmore, fearing for his safety, fled with his family to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union (American Civil War)
During the American Civil War, the Union, also known as the North, referred to the United States led by President Abraham Lincoln. It was opposed by the secessionist Confederate States of America (CSA), informally called "the Confederacy" or "the South". The Union is named after its declared goal of preserving the United States as a constitutional union. "Union" is used in the U.S. Constitution to refer to the founding formation of the people, and to the states in union. In the context of the Civil War, it has also often been used as a synonym for "the northern states loyal to the United States government;" in this meaning, the Union consisted of 20 free states and five border states. The Union Army was a new formation comprising mostly state units, together with units from the regular U.S. Army. The border states were essential as a supply base for the Union invasion of the Confederacy, and Lincoln realized he could not win the war without control of them, especially Maryla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Army
During the American Civil War, the Union Army, also known as the Federal Army and the Northern Army, referring to the United States Army, was the land force that fought to preserve the Union (American Civil War), Union of the collective U.S. state, states. It proved essential to the preservation of the United States as a working, viable republic. The Union Army was made up of the permanent Regular Army (United States), regular army of the United States, but further fortified, augmented, and strengthened by the many temporary units of dedicated United States Volunteers, volunteers, as well as including those who were drafted in to service as Conscription in the United States, conscripts. To this end, the Union Army fought and ultimately triumphed over the efforts of the Confederate States Army in the American Civil War. Over the course of the war, 2,128,948 men enlisted in the Union Army, including 178,895 United States Colored Troops, colored troops; 25% of the white men who s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was the primary military force of the Confederate States of America in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was also the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most often arrayed against the Union Army of the Potomac. Origin The name ''Army of Northern Virginia'' referred to its primary area of operation, as did most Confederate States Army names. The Army originated as the Army of the Potomac, which was organized on June 20, 1861, from all operational forces in northern Virginia. On July 20 and July 21, the Army of the Shenandoah and forces from the District of Harpers Ferry were added. Units from the Army of the Northwest were merged into the Army of the Potomac between March 14 and May 17, 1862. The Army of the Potomac was renamed ''Army of Northern Virginia'' on March 14. The Army of the Peninsula was merged into it on April 12, 1862.Eicher, pp. 889–90. Robert E. Lee's biographer, Douglas S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSS Richmond
CSS ''Richmond'' was the name ship of her class of six casemate ironclads built for the Confederate States Navy during the American Civil War. Completed during 1862 the ship was assigned to the James River Squadron where she mostly supported Confederate forces near Richmond, Virginia. She was burned in April 1865 to prevent her capture by Union forces. Background and description The ship was built to a design by the Chief Naval Constructor, John L. Porter, based on his earlier work on the ironclad , retaining the traditional curving ship-type hull, but with flat ends to the casemate. As usual for Confederate ships, dimensions vary slightly between sources. The plan showed an overall length of and a length between perpendiculars of with a maximum beam of , a moulded beam of and a depth of hold of about . The consensus figure for the ship's draft is MarcelloSilverstone 2006, p. 152 She was fitted with a pilothouse at the forward end of the casemate roof.Canney, p. 39 The p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drewry's Bluff
Drewry's Bluff is located in northeastern Chesterfield County, Virginia, in the United States. It was the site of Confederate Fort Darling during the American Civil War. It was named for a local landowner, Confederate Captain Augustus H. Drewry, who owned the property. At Richmond, Virginia, location of the fall line at the head of navigation, the generally west-to-east course of the James River turns almost due south for a distance of about before turning eastward again towards the Chesapeake Bay. At this sharp bend, Drewry's Bluff on the west side of the James River rose above the water, commanding a view of several miles' distance downstream and making it a logical site for defensive fortifications. During the American Civil War On March 17, 1862, the men of Captain Drewry's Southside Artillery arrived at the bluff and began fortifying the area. They constructed earthworks, erected barracks, dug artillery emplacements, and mounted three large seacoast guns (one 10-inch Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Nicholson Barney
Joseph Nicholson Barney (1818 – June 16, 1899) was a career United States Navy officer (1835–1861) who served in the Confederate States Navy in the American Civil War (1861–1865). Personal life and family Barney was born in Baltimore in 1818, the son of U.S. Congressman John Barney and Elizabeth Nicholson Hindman and the grandson of United States Navy Commodore Joshua Barney. He married Eliza Jacobs Rogers on June 9, 1846 in New Castle County, Delaware, with whom he had one daughter before her death in 1848. He married a second time in 1858 to Anne (Nannie) Seddon Dornin, daughter of Thomas Aloysius Dornin, with whom he had eight children. He died at his home in Fredericksburg, Virginia, aged 81, on June 16, 1899, after a month-long illness.Genealogy of the Barney family in Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSS Raleigh
CSS ''Raleigh'' may refer to: * was a gunboat that served as a tender to CSS ''Virginia'' during the Battle of Hampton Roads * was an ironclad ram which patrolled the Cape Fear River near Wilmington, North Carolina See also * {{DEFAULTSORT:Raleigh, Css ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSS Beaufort
The CSS ''Beaufort'' ( ) was an iron-hull gunboat that served in North Carolina and Virginia during the Civil War. The ''Beaufort'' was originally called the ''Caledonia''. She was built at the Pusey & Jones Company of Wilmington, Delaware in 1854. The ''Caledonia'' operated out of Edenton, North Carolina. (Lytle 1975: 28) In 1856 her home port changed from Edenton to Plymouth. At the outbreak of the American Civil War, the ''Caledonia'', now renamed ''Beaufort'', was put in commission at Norfolk, Virginia on July 9, 1861 by Lieutenant Robert C. Duvall, North Carolina Navy, and sailed immediately for New Bern, North Carolina. While en route she engaged the large steamer USS ''Albatross'' in an inconclusive battle off Oregon Inlet. (ORN 6: 21, 790ff) After North Carolina seceded, ''Beaufort'' was turned over to the Confederate States Navy, and on September 9 Lieutenant William Harwar Parker, CSN, was placed in command. Thereafter she participated in the battles of Roano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
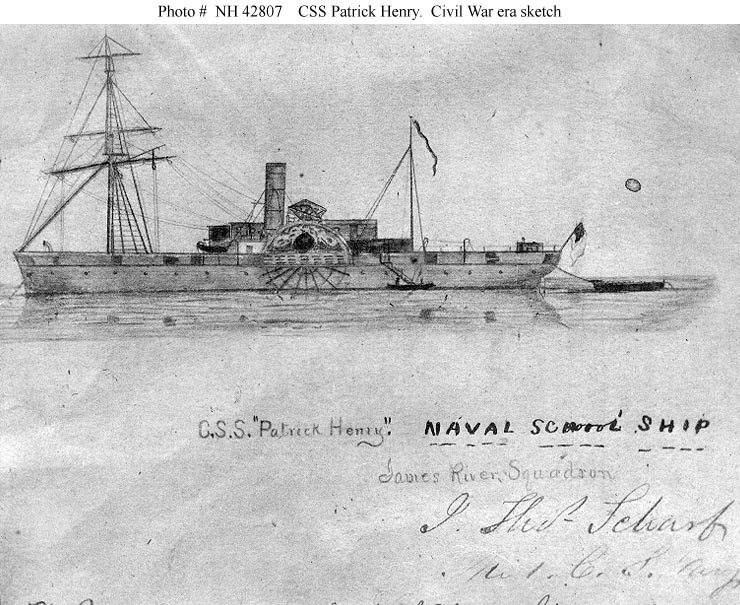
CSS Patrick Henry
CSS ''Patrick Henry'' was a ship built in New York City in 1859 by the renowned William H. Webb for the Old Dominion Steam Ship Line as the civilian steamer ''Yorktown'', a brigantine-rigged side-wheel steamer. She carried passengers and freight between Richmond, Virginia and New York City. ''Yorktown'' was anchored in the James River when Virginia seceded from the Union on 17 April 1861 and was seized by the Virginia Navy and later turned over to the Confederate Navy on 8 June 1861. Commander John Randolph Tucker, who commanded the ship, directed that ''Yorktown'' be converted into a gunboat and renamed ''Patrick Henry'' in honor of Patrick Henry, the revolutionary patriot and Founding Father. She also served as the first flagship of the James River Squadron. Library of Virginia. Retrieved 27 Dece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSS Jamestown
CSS ''Jamestown'', originally a side-wheel, passenger steamer, was built at New York City in 1853, and seized at Richmond, Virginia in 1861 for the Virginia Navy during the early days of the American Civil War. She was commissioned by the Confederate States Navy (CSN) the following July (after the Virginia Navy was transferred to the CSN), and renamed CSS ''Thomas Jefferson'' but was generally referred to as ''Jamestown'', after Jamestown, Virginia. Brigantine-rigged ''Jamestown'' was designed and constructed by the well-known shipbuilder William H. Webb for the New York and Old Dominion Line as a sister to ''Yorktown'', which became CSS ''Patrick Henry''. Career With Lt. Joseph Nicholson Barney, CSN, in command, she was actively employed until the end of her career in May 1862. Her service was highlighted by the Battle of Hampton Roads on March 8–9 1862, during which she assisted CSS ''Virginia'' in attacking USS ''Congress'' and USS ''Cumberland'' and stood by duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norfolk, Virginia
Norfolk ( ) is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. Incorporated in 1705, it had a population of 238,005 at the 2020 census, making it the third-most populous city in Virginia after neighboring Virginia Beach and Chesapeake, and the 94th-largest city in the nation. Norfolk holds a strategic position as the historical, urban, financial, and cultural center of the Hampton Roads region, which has more than 1.8 million inhabitants and is the thirty-third largest Metropolitan Statistical area in the United States. Officially known as ''Virginia Beach-Norfolk-Newport News, VA-NC MSA'', the Hampton Roads region is sometimes called "Tidewater" and "Coastal Virginia"/"COVA," although these are broader terms that also include Virginia's Eastern Shore and entire coastal plain. Named for the eponymous natural harbor at the mouth of the Chesapeake Bay, Hampton Roads has ten cities, including Norfolk; seven counties in Virginia; and two counties in No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |