|
James R. Hall
James Reginald Hall Jr. (born July 15, 1936) is a retired senior officer in the United States Army who served as the final commander of the Fourth United States Army before its inactivation in 1991. Prior to serving as commander of the Fourth Army, Hall served as the director of enlisted personnel management at the United States Army Military Personnel Center, the Deputy Inspector General of the Army, and commander of the 197th Infantry Brigade. Early life and education Hall was born on July 15, 1936, in Anniston, Alabama, and attended Morehouse College, where he received a Bachelor of Arts degree in political science in 1957. After graduation, Hall enlisted in the United States Army and, after completing basic training, entered officer candidate school. He was commissioned as a second lieutenant in the United States Army on December 19, 1958. Hall also holds an advanced degree in public administration from Shippensburg State College and has attended the Armed Forces Staff Colleg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
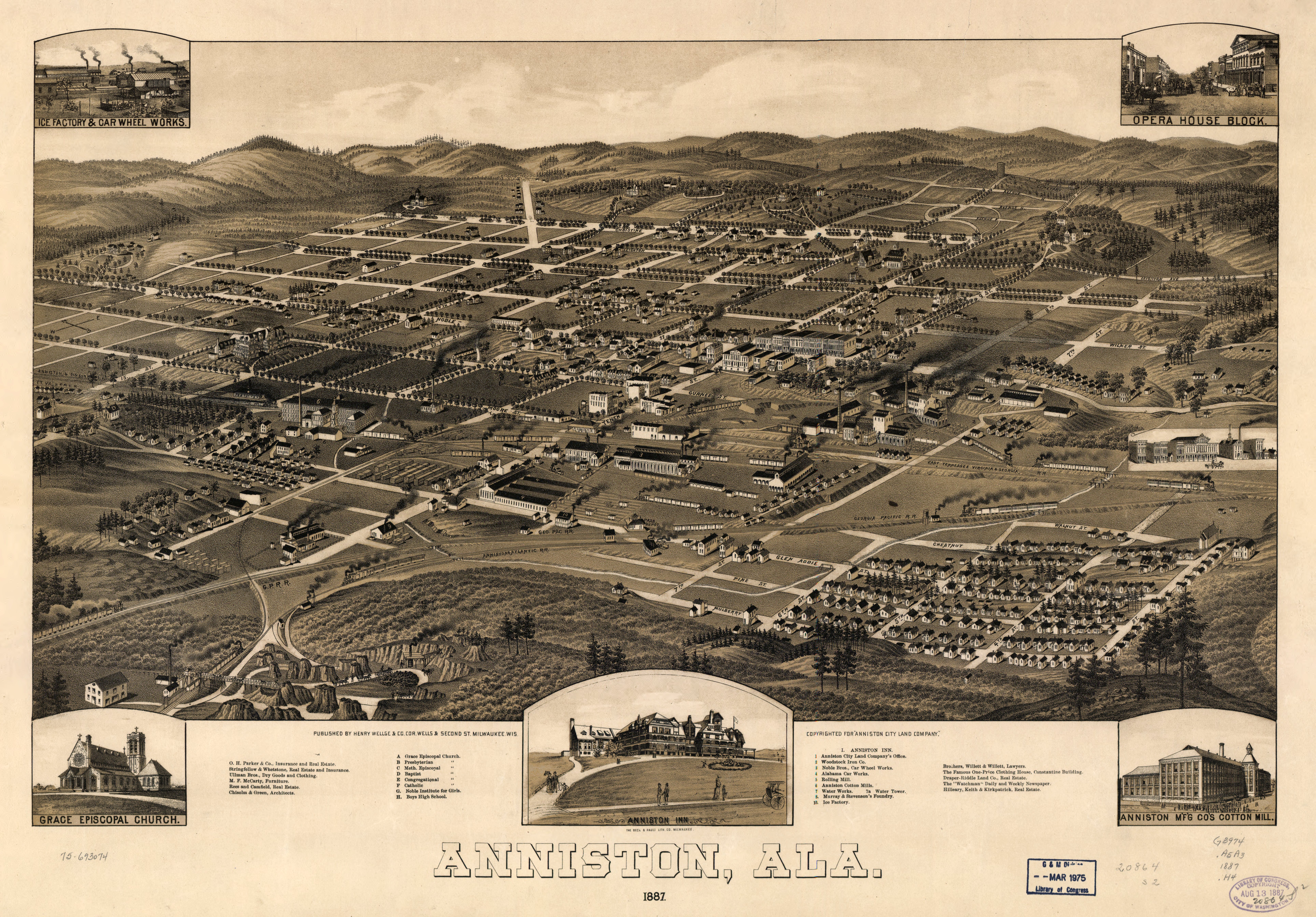
Anniston, Alabama
Anniston is the county seat of Calhoun County in Alabama and is one of two urban centers/principal cities of and included in the Anniston-Oxford Metropolitan Statistical Area. As of the 2010 census, the population of the city was 23,106. According to 2019 Census estimates, the city had a population of 21,287. Named "The Model City" by Atlanta newspaperman Henry W. Grady for its careful planning in the late 19th century, the city is situated on the slope of Blue Mountain. History Civil War Though the surrounding area was settled much earlier, the mineral resources in the area of Anniston were not exploited until the Civil War. The Confederate States of America then operated an iron furnace near present-day downtown Anniston, until it was finally destroyed by raiding Union cavalry in early 1865. Later, cast iron for sewer systems became the focus of Anniston's industrial output. Cast iron pipe, also called soil pipe, was popular until the advent of plastic pipe in the 1960s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Née
A birth name is the name of a person given upon birth. The term may be applied to the surname, the given name, or the entire name. Where births are required to be officially registered, the entire name entered onto a birth certificate or birth register may by that fact alone become the person's legal name. The assumption in the Western world is often that the name from birth (or perhaps from baptism or ''brit milah'') will persist to adulthood in the normal course of affairs—either throughout life or until marriage. Some possible changes concern middle names, diminutive forms, changes relating to parental status (due to one's parents' divorce or adoption by different parents). Matters are very different in some cultures in which a birth name is for childhood only, rather than for life. Maiden and married names The French and English-adopted terms née and né (; , ) denote an original surname at birth. The term ''née'', having feminine grammatical gender, can be u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1936 Births
Events January–February * January 20 – George V of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions and Emperor of India, dies at his Sandringham Estate. The Prince of Wales succeeds to the throne of the United Kingdom as King Edward VIII. * January 28 – Britain's King George V state funeral takes place in London and Windsor. He is buried at St George's Chapel, Windsor Castle * February 4 – Radium E (bismuth-210) becomes the first radioactive element to be made synthetically. * February 6 – The 1936 Winter Olympics, IV Olympic Winter Games open in Garmisch-Partenkirchen, Germany. * February 10–February 19, 19 – Second Italo-Ethiopian War: Battle of Amba Aradam – Italian forces gain a decisive tactical victory, effectively neutralizing the army of the Ethiopian Empire. * February 16 – 1936 Spanish general election: The left-wing Popular Front (Spain), Popular Front coalition takes a majority. * February 26 – February 26 Inci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1996 Summer Olympics
The 1996 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXVI Olympiad, also known as Atlanta 1996 and commonly referred to as the Centennial Olympic Games) were an international multi-sport event held from July 19 to August 4, 1996, in Atlanta, Georgia, United States. These were the fourth Summer Olympics to be hosted by the United States, and marked the centennial of the 1896 Summer Olympics in Athens, the inaugural edition of the modern Olympic Games. These were also the first Summer Olympics since 1924 to be held in a different year than the Winter Olympics, as part of a new IOC practice implemented in 1994 to hold the Summer and Winter Games in alternating, even-numbered years. The 1996 Games were the first of the two consecutive Summer Olympics to be held in a predominantly English-speaking country preceding the 2000 Summer Olympics in Sydney, Australia. These were also the last Summer Olympics to be held in North America until 2028, when Los Angeles will host the gam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Staff Identification Badge
The United States Army Staff Identification Badge is a badge of the United States Army worn by personnel who serve at the Office of the Secretary of the Army and the Army Staff at Headquarters, Department of the Army ( HQDA) and its agencies. Neither an award nor a decoration, the badge is a distinguishing emblem of service. Initially issued as a temporary badge, officers and enlisted personnel demonstrating outstanding performance of duty and meeting all eligibility requirements can be processed after one complete year (365 days cumulative) of assignment and receive a certificate authorizing permanent wear of the badge.DA Memo 672-1, Eligibility criteria for wear and permanent issue |
Parachutist Badge (United States)
The Parachutist Badge, also commonly referred to as "Jump Wings" is a military badge of the United States Armed Forces. The United States Space Force and United States Coast Guard are the only branches that do not award the Parachutist Badge, but their members are authorized to receive the Parachutist Badges of other services in accordance with their prescribed requirements. The DoD military services are all awarded the same Basic Parachutist Badge. The U.S. Army and U.S. Air Force issue the same Senior and Master Parachutist Badges while the U.S. Navy and U.S. Marine Corps issue the Navy and Marine Corps Parachutist Badge to advanced parachutists. The majority of the services earn their Basic Parachutist Badge through the U.S. Army Airborne School. Army The Army's Basic Parachutist Badge is awarded to all military personnel of any service who complete the US Army Basic Airborne Course at Fort Benning, Georgia. It signifies that the soldier is a trained military parachutist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combat Infantryman Badge
The Combat Infantryman Badge (CIB) is a United States Army military decoration. The badge is awarded to infantrymen and Special Forces soldiers in the rank of colonel and below, who fought in active ground combat while assigned as members of either an Infantry or Special Forces unit of brigade size or smaller at any time after 6 December 1941. For those soldiers who are not members of an infantry, or Special Forces unit, the Combat Action Badge (CAB) is awarded instead. For soldiers with an MOS in the medical field they would, with the exception of a Special Forces Medical Sergeant (18D), receive the Combat Medical Badge. 18D Special Forces Medics would receive the Combat Infantryman badge instead. The CIB and its non-combat contemporary, the Expert Infantryman Badge (EIB), were created in November 1943 during World War II to boost morale and increase the prestige of service in the Infantry. Specifically, it recognizes the inherent sacrifices of all infantrymen, and that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commendation Medal
The Commendation Medal is a mid-level United States military decoration presented for sustained acts of heroism or meritorious service. Each branch of the United States Armed Forces issues its own version of the Commendation Medal, with a fifth version existing for acts of joint military service performed under the Department of Defense. The Commendation Medal was originally only a service ribbon and was first awarded by the U.S. Navy and U.S. Coast Guard in 1943. An Army Commendation Ribbon followed in 1945 and in 1949 the Navy, Coast Guard, and Army Commendation ribbons were renamed the "Commendation Ribbon with Metal Pendant". By 1960 the Commendation Ribbons had been authorized as full medals and were subsequently referred to as Commendation Medals. Additional awards of the Army and Air Force Commendation Medals are denoted by bronze and silver oak leaf clusters. The Navy and Marine Corps Commendation Medal and Coast Guard Commendation Medal are authorized gold and si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jet (magazine)
''Jet'' is an American weekly digital magazine focusing on news, culture, and entertainment related to the African-American community. Founded in November 1951 by John H. Johnson of the Johnson Publishing Company in Chicago, Illinois, the magazine was billed as "The Weekly Negro News Magazine". ''Jet'' chronicled the civil rights movement from its earliest years, including the murder of Emmett Till, the Montgomery bus boycott, and the activities of civil rights leader Martin Luther King Jr. ''Jet'' was printed from November 1, 1951, in digest-sized format in all or mostly black-and-white until its December 27, 1999, issue. In 2009, ''Jet'' expanded one of the weekly issues to a double issue published once each month. Johnson Publishing Company struggled with the same loss of circulation and advertising as other magazines and newspapers in the digital age, and the final print issue of ''Jet'' was published on June 23, 2014, continuing solely as a digital magazine app. In 2016, J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midwestern United States
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. It was officially named the North Central Region by the Census Bureau until 1984. It is between the Northeastern United States and the Western United States, with Canada to the north and the Southern United States to the south. The Census Bureau's definition consists of 12 states in the north central United States: Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, Ohio, South Dakota, and Wisconsin. The region generally lies on the broad Interior Plain between the states occupying the Appalachian Mountains, Appalachian Mountain range and the states occupying the Rocky Mountains, Rocky Mountain range. Major rivers in the region include, from east to west, the Ohio River, the Upper Mississippi River, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific (APAC) is the part of the world near the western Pacific Ocean. The Asia-Pacific region varies in area depending on context, but it generally includes East Asia, Russian Far East, South Asia, Southeast Asia, Australia and Pacific Islands. Definition The term may include countries in North America and South America that are on the coast of the Eastern Pacific Ocean; the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, for example, includes Canada, Chile, Mexico, Peru, and the United States. Alternatively, the term sometimes comprises all of Asia and Australasia as well as Pacific island nations (Asia-Pacific and Australian continent)—for example, when dividing the world into large regions for commercial purposes (e.g., into APAC, EMEA, LATAM, and NA). Central Asia and Western Asia are almost never included. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_NRT_09JUL01_(6896202880).jpg)



