|
James H. Fowler
James H. Fowler (born February 18, 1970) is an American social sciences, social scientist specializing in social networks, cooperation, political participation, and genopolitics (the study of the genetic basis of political behavior). He is currently Professor of Medical Genetics in the UC San Diego School of Medicine, School of Medicine and Professor of Political Science in the Division of Social Science at the University of California, San Diego. He was named a List of Guggenheim Fellowships awarded in 2010, 2010 Fellow of the John Simon Guggenheim Foundation. Background Fowler earned a bachelor's degree from Harvard College in 1992, a master's degree in International Relations from Yale University in 1997, and a Ph.D. in Government from the Harvard Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, Harvard University in 2003. He was also a Peace Corps volunteer in Ecuador from 1992 to 1994. In 2010, he was named by Foreign Policy magazine to its list of top global thinkers. Research Fowler' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
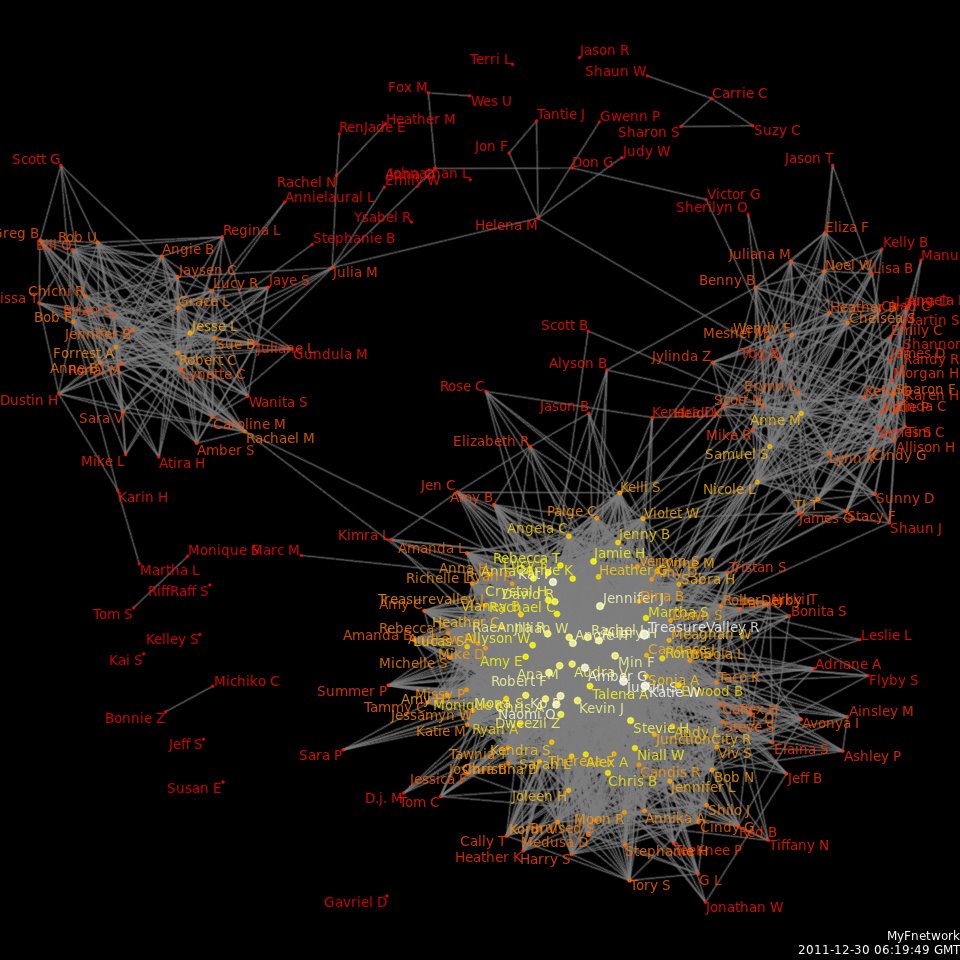
Social Network Analysis
Social network analysis (SNA) is the process of investigating social structures through the use of networks and graph theory. It characterizes networked structures in terms of ''nodes'' (individual actors, people, or things within the network) and the ''ties'', ''edges'', or ''links'' (relationships or interactions) that connect them. Examples of social structures commonly visualized through social network analysis include social media networks, memes spread, information circulation, friendship and acquaintance networks, business networks, knowledge networks, difficult working relationships, social networks, collaboration graphs, kinship, disease transmission, and sexual relationships. These networks are often visualized through ''sociograms'' in which nodes are represented as points and ties are represented as lines. These visualizations provide a means of qualitatively assessing networks by varying the visual representation of their nodes and edges to reflect attributes of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genopolitics
Genopolitics is the study of the genetic basis of political behavior and attitudes. It combines behavior genetics, psychology, and political science and it is closely related to the emerging fields of neuropolitics (the study of the neural basis of political attitudes and behavior) and political physiology (the study of biophysical correlates of political attitudes and behavior). In 2008, ''The Chronicle of Higher Education'' reported on the increase in academicians' recognition of and engagement in genopolitics as a discrete field of study, and ''New York Times Magazine'' included genopolitics in its "Eighth Annual Year in Ideas" for the same year, noting that the term was originally coined by James Fowler. Critics of genopolitics have argued that it is "a fundamentally misguided undertaking", and that it is inconsistent with evidence in the fields of genetics, neuroscience, and evolutionary psychology. Twin studies of political attitudes Psychologists and behavior geneticists b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Correlation Does Not Imply Causation
The phrase "correlation does not imply causation" refers to the inability to legitimately deduce a cause-and-effect relationship between two events or variables solely on the basis of an observed association or correlation between them. The idea that "correlation implies causation" is an example of a questionable-cause logical fallacy, in which two events occurring together are taken to have established a cause-and-effect relationship. This fallacy is also known by the Latin phrase ''cum hoc ergo propter hoc'' ('with this, therefore because of this'). This differs from the fallacy known as ''post hoc ergo propter hoc'' ("after this, therefore because of this"), in which an event following another is seen as a necessary consequence of the former event, and from conflation, the errant merging of two events, ideas, databases, etc., into one. As with any logical fallacy, identifying that the reasoning behind an argument is flawed does not necessarily imply that the resulting con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas A
Nicholas is a male given name and a surname. The Eastern Orthodox Church, the Roman Catholic Church, and the Anglicanism, Anglican Churches celebrate Saint Nicholas every year on December 6, which is the name day for "Nicholas". In Greece, the name and its derivatives are especially popular in maritime regions, as St. Nicholas is considered the protector saint of seafarers. Origins The name is derived from the Greek language, Greek name Νικόλαος (''Nikolaos''), understood to mean 'victory of the people', being a compound of νίκη ''nikē'' 'victory' and λαός ''laos'' 'people'.. An ancient paretymology of the latter is that originates from λᾶς ''las'' (Synaeresis, contracted form of λᾶας ''laas'') meaning 'stone' or 'rock', as in Greek mythology, Deucalion and Pyrrha recreated the people after they had vanished in a catastrophic Deluge myth, deluge, by throwing stones behind their shoulders while they kept marching on. The name became popular through Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precedent
A precedent is a principle or rule established in a previous legal case that is either binding on or persuasive for a court or other tribunal when deciding subsequent cases with similar issues or facts. Common-law legal systems place great value on deciding cases according to consistent principled rules, so that similar facts will yield similar and predictable outcomes, and observance of precedent is the mechanism by which that goal is attained. The principle by which judges are bound to precedents is known as ''stare decisis'' (a Latin phrase with the literal meaning of "to stand in the-things-that-have-been-decided"). Common-law precedent is a third kind of law, on equal footing with statutory law (that is, statutes and codes enacted by legislative bodies) and subordinate legislation (that is, regulations promulgated by executive branch agencies, in the form of delegated legislation) in UK parlance – or regulatory law (in US parlance). Case law, in common-law jurisdictions, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Framingham Heart Study
The Framingham Heart Study is a long-term, ongoing cardiovascular cohort study of residents of the city of Framingham, Massachusetts. The study began in 1948 with 5,209 adult subjects from Framingham, and is now on its third generation of participants. Prior to the study almost nothing was known about the epidemiology of hypertensive or arteriosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Much of the now-common knowledge concerning heart disease, such as the effects of diet, exercise, and common medications such as aspirin, is based on this longitudinal study. It is a project of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, in collaboration with (since 1971) Boston University. Various health professionals from the hospitals and universities of Greater Boston staff the project. History In 1948, the study was commissioned by Congress, with a choice made between Framingham, Massachusetts and Paintsville, Kentucky. Framingham was chosen when residents showed more general interest in heart rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Happiness
Happiness, in the context of Mental health, mental or emotional states, is positive or Pleasure, pleasant emotions ranging from contentment to intense joy. Other forms include life satisfaction, well-being, subjective well-being, flourishing and eudaimonia. Since the 1960s, happiness research has been conducted in a wide variety of scientific disciplines, including gerontology, social psychology and positive psychology, Clinical research, clinical and medical research and happiness economics. Definitions "Happiness" is subject to debate on usage and meaning, and on possible differences in understanding by culture. The word is mostly used in relation to two factors: * the current experience of the feeling of an affect (psychology), emotion (affect) such as pleasure or joy, or of a more general sense of 'emotional condition as a whole'. For instance Daniel Kahneman has defined happiness as "''what I experience here and now''". This usage is prevalent in dictionary definiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is burned and the resulting smoke is typically breathed in to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have been rolled into a small rectangle of rolling paper to create a small, round cylinder called a cigarette. Smoking is primarily practised as a route of administration for recreational drug use because the combustion of the dried plant leaves vaporizes and delivers active substances into the lungs where they are rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream and reach bodily tissue. In the case of cigarette smoking, these substances are contained in a mixture of aerosol particles and gases and include the pharmacologically active alkaloid nicotine; the vaporization creates heated aerosol and gas into a form that allows inhalation and deep penetration into the lungs where absorption into the bloodstream of the active substances occurs. In some cultures, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's weight divided by the square of the person's height—is over ; the range is defined as overweight. Some East Asian countries use lower values to calculate obesity. Obesity is a major cause of disability and is correlated with various diseases and conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, and osteoarthritis. Obesity has individual, socioeconomic, and environmental causes. Some known causes are diet, physical activity, automation, urbanization, genetic susceptibility, medications, mental disorders, economic policies, endocrine disorders, and exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals. While a majority of obese individuals at any given time are attempting to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ''Ekuatur Nunka''), is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. Ecuador also includes the Galápagos Islands in the Pacific, about west of the mainland. The country's capital and largest city is Quito. The territories of modern-day Ecuador were once home to a variety of Indigenous groups that were gradually incorporated into the Inca Empire during the 15th century. The territory was colonized by Spain during the 16th century, achieving independence in 1820 as part of Gran Colombia, from which it emerged as its own sovereign state in 1830. The legacy of both empires is reflected in Ecuador's ethnically diverse population, with most of its mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peace Corps
The Peace Corps is an independent agency and program of the United States government that trains and deploys volunteers to provide international development assistance. It was established in March 1961 by an executive order of President John F. Kennedy Executive Order 10924 and authorized by Congress the following September by the Peace Corps Act. Kennedy first publicly proposed the Peace Corps during his 1960 presidential campaign as a means to improve America's global image and leadership in the Cold War; he cited the Soviet Union's deployment of skilled citizens "abroad in the service of world communism" and argued the U.S. must do the same to advance values such as democracy and liberty. The Peace Corps was formally established within three months of Kennedy's presidency, garnering both bipartisan congressional support and popular support, particularly among recent university graduates. The official goal of the Peace Corps is to assist developing countries by providing skil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard Graduate School Of Arts And Sciences
The Graduate School of Arts and Sciences (GSAS) is the largest of the twelve graduate schools of Harvard University. Formed in 1872, GSAS is responsible for most of Harvard's graduate degree programs in the humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences. The school offers Master of Arts (AM), Master of Science (SM), and Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degrees in approximately 58 disciplines. Academic programs offered by the Harvard Graduate School of Arts and Sciences have consistently ranked at the top of graduate programs in the United States. The School's graduates include a diverse set of prominent public figures and academics. The vast majority of Harvard's Nobel Prize-winning alumni earned a degree at GSAS. In addition to scholars and scientists, GSAS graduates have become U.S. Cabinet Secretaries, Supreme Court Justices, foreign heads of state, and heads of government. History and organization GSAS was formally created as the Graduate Department of Harvard University in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
