|
Jakhanke
The Jakhanke -- also spelled Jahanka, Jahanke, Jahanque, Jahonque, Diakkanke, Diakhanga, Diakhango, Dyakanke, Diakhanké, Diakanké, or Diakhankesare -- are a Manding-speaking ethnic group in the Senegambia region, often classified as a subgroup of the larger Soninke. The Jakhanke have historically constituted a specialized caste of professional Muslim clerics (''ulema'') and educators.Lamin O. Sanneh. ''The Jakhanke: The history of an Islamic clerical people of the Senegambia''. London (1979) They are centered on one larger group in Guinea, with smaller populations in the eastern region of The Gambia, Senegal, and in Mali near the Guinean border. Although generally considered a branch of the Soninke (also known as Serahule, Serakhulle or Sarakollé), their language is closer to Western Manding languages such as Mandinka. Since the fifteenth century the Jakhanke clerical communities have constituted an integral part of the region and have exercised a high level of economic and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
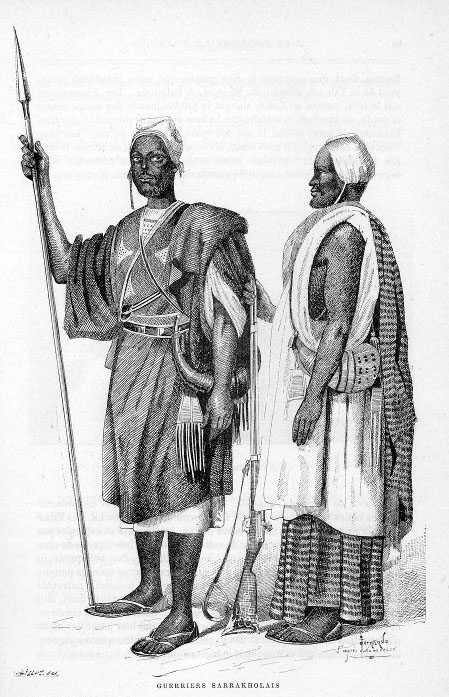
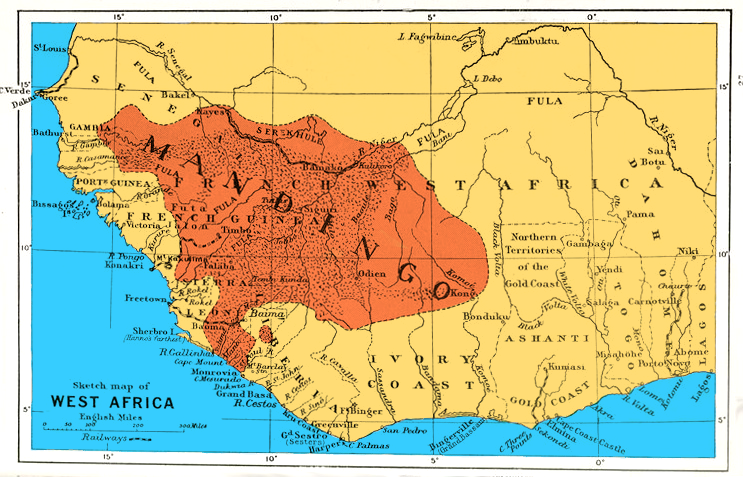
Soninke People
The Soninke people are a West African Mande-speaking ethnic group found in Mali, Fouta Djallon, southern Mauritania, eastern Senegal, Guinea and The Gambia. They speak the Soninke language, also called the Serakhulle or Azer language, which is one of the Mande languages. Soninke people were the founders of the ancient empire of Ghana or Wagadou c. 300–1240 CE, Subgroups of Soninke include the Maraka and Wangara. When the Ghana empire was destroyed, the resulting diaspora brought Soninkes to Mali, Mauritania, Senegal, Gambia, Burkina Faso, Côte d'Ivoire, Guinée-Conakry, modern-day Republic of Ghana, and Guinea-Bissau where some of this trading diaspora was called Wangara. Predominantly Muslims, the Soninke were one of the early ethnic groups from West Africa to convert to Islam in about the 10th century. The contemporary population of Soninke people is estimated to be over 2 million. The cultural practices of Soninke people are similar to the Mandé peoples, and those of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wagadu
The Ghana Empire, also known as Wagadou ( ar, غانا) or Awkar, was a West African empire based in the modern-day southeast of Mauritania and western Mali that existed from c. 300 until 1100. The Empire was founded by the Soninke people, and was based in the capital city of Koumbi Saleh. Complex societies, some based on trans-Saharan trade in salt and gold had existed in the region for centuries at the time of the empire's formation. The introduction of the camel to the western Sahara in the 3rd century AD served as a major catalyst for the transformative social changes that resulted in the empire's formation. By the time of the Muslim conquest of North Africa in the 7th century the camel had changed the ancient, more irregular trade routes into a trade network running from Morocco to the Niger River. The Ghana Empire grew rich from this increased trans-Saharan trade in gold and slaves and salt, allowing for larger urban centers to develop. The traffic furthermore encouraged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandinka People
The Mandinka or Malinke are a West African ethnic group primarily found in southern Mali, the Gambia and eastern Guinea. Numbering about 11 million, they are the largest subgroup of the Mandé peoples and one of the largest ethnic-linguistic groups in Africa. They speak the Manding languages in the Mande language family and a ''lingua franca'' in much of West Africa. Over 99% of Mandinka adhere to Islam. They are predominantly subsistence farmers and live in rural villages. Their largest urban center is Bamako, the capital of Mali. The Mandinka are the descendants of the Mali Empire, which rose to power in the 13th century under the rule of king Sundiata Keita, who founded an empire that would go on to span a large part of West Africa. They migrated west from the Niger River in search of better agricultural lands and more opportunities for conquest. Nowadays, the Mandinka inhabit the West Sudanian savanna region extending from The Gambia and the Casamance region in Senegal to Iv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
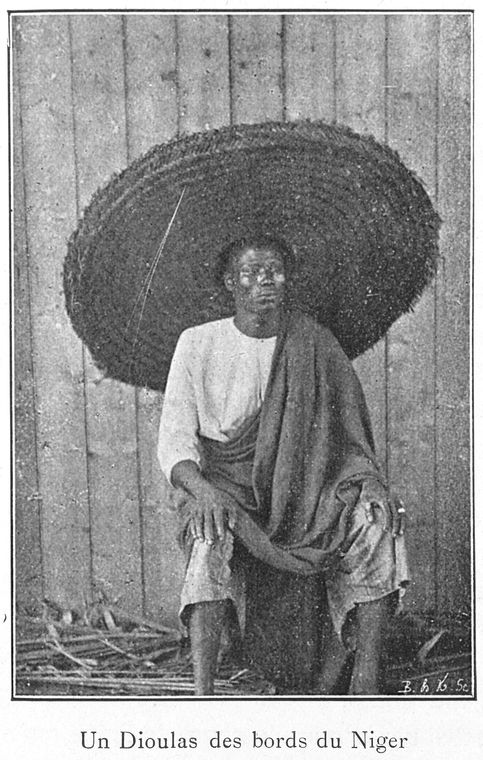
Dyula People
The Dyula (Dioula or Juula) are a Mande ethnic group inhabiting several West African countries, including Mali, Cote d'Ivoire, Ghana, and Burkina Faso. Characterized as a highly successful merchant caste, ''Dyula'' migrants began establishing trading communities across the region in the fourteenth century. Since business was often conducted under non-Muslim rulers, the ''Dyula'' developed a set of theological principles for Muslim minorities in non-Muslim societies. Their unique contribution of long-distance commerce, Islamic scholarship and religious tolerance were significant factors in the peaceful expansion of Islam in West Africa. Historical background The Mandé embraced Islam during the thirteenth century following introduction to the faith through contact with the North African traders. By the 14th century, the Malian empire (c.1230-1600) had reached its apogee, acquiring a considerable reputation for the Islamic rulings of its court and the pilgrimages of several emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bambuk
Bambouk (sometimes Bambuk or Bambuhu) is a traditional name for the territory in eastern Senegal and western Mali, encompassing the Bambouk Mountains on its eastern edge, the valley of the Faleme River and the hilly country to the east of the river valley. It was a formally described district in French Sudan, but in 1895, the border between Sudan and Senegal was moved to the Faleme River, placing the western portion of the district within Senegal. The term is still used to designate the region, but there is no formal administrative area with that name. Bambouk is primarily home to the Malinké people, and a distinctive dialect of the Maninkakan language is spoken there. History According to Martin Meredith, the Carthaginians used Berber nomads to establish a packhorse trade route across the Sahara between Lixus and "the goldfields of Bambuk in the Senegal River valley." The Diakhanke established Diakha-ba and became Muslim clerics for the Malinke chiefs after Bambuk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dia, Mali
Dia (''Jà'') is a small town and seat of the commune of Diaka in the Cercle of Ténenkou in the Mopti Region of southern-central Mali.. Tomo Kan and also some Fulfulde are spoken in Dia. According to Levtzion, the Diakhanke "remember Dia in Massina as the town of their ancestor, Suware, a great ''marabout'' and a saint." Local surnames include Sangaré, Cissé, Sidibé. The three settlement mound complex, near the Inland Niger Delta, predates Djenne and Timbuktu Timbuktu ( ; french: Tombouctou; Koyra Chiini: ); tmh, label=Tuareg, script=Tfng, ⵜⵏⴱⴾⵜ, Tin Buqt a city in Mali, situated north of the Niger River. The town is the capital of the Tombouctou Region, one of the eight administrativ .... Dia-Shoma, as the earliest settlement mound, dates to the 9th century BCE. Dia-Mara dates to sixth century CE. The height of settlement at this complex is reached around the tenth century CE. References Further reading *. *. *. *. Populated places in Mopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. It is the smallest country within mainland AfricaHoare, Ben. (2002) ''The Kingfisher A-Z Encyclopedia'', Kingfisher Publications. p. 11. . and is surrounded by Senegal, except for its western coast on the Atlantic Ocean. The Gambia is situated on both sides of the lower reaches of the Gambia River, the nation's namesake, which flows through the centre of the Gambia and empties into the Atlantic Ocean, thus the long shape of the country. It has an area of with a population of 1,857,181 as of the April 2013 census. Banjul is the Gambian capital and the country's largest metropolitan area, while the largest cities are Serekunda and Brikama. The Portugal, Portuguese in 1455 entered the Gambian region, the first Europeans to do so, but never established important trade there. In 1765, the Gambia was made a part of the British Empire by establishment of the Gambia Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mali Empire
The Mali Empire ( Manding: ''Mandé''Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: ''UNESCO General History of Africa, Vol. IV, Abridged Edition: Africa from the Twelfth to the Sixteenth Century'', p. 57. University of California Press, 1997. or Manden; ar, مالي, Mālī) was an empire in West Africa from 1226 to 1670. The empire was founded by Sundiata Keita (c. 1214 – c. 1255) and became renowned for the wealth of its rulers, especially Mansa Musa (Musa Keita). The Manding languages were spoken in the empire. At its peak, Mali was the largest empire in West Africa, widely influencing the culture of the region through the spread of its language, laws and customs. Much of the recorded information about the Mali Empire comes from 14th-century Tunisian historian Ibn Khaldun, 14th-century Moroccan traveller Ibn Battuta and 16th-century Andalusian traveller Leo Africanus. The other major source of information is Mandinka oral tradition, as recorded by storytellers known as griots. The empire began as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Côte D'Ivoire
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is the port city of Abidjan. It borders Guinea to the northwest, Liberia to the west, Mali to the northwest, Burkina Faso to the northeast, Ghana to the east, and the Gulf of Guinea (Atlantic Ocean) to the south. Its official language is French, and indigenous languages are also widely used, including Bété, Baoulé, Dioula, Dan, Anyin, and Cebaara Senufo. In total, there are around 78 different languages spoken in Ivory Coast. The country has a religiously diverse population, including numerous followers of Christianity, Islam, and indigenous faiths. Before its colonization by Europeans, Ivory Coast was home to several states, including Gyaaman, the Kong Empire, and Baoulé. The area became a protectorate of France in 1843 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mande Languages
The Mande languages are spoken in several countries in West Africa by the Mandé peoples and include Maninka, Mandinka, Soninke, Bambara, Kpelle, Dioula, Bozo, Mende, Susu, and Vai. There are "60 to 75 languages spoken by 30 to 40 million people", chiefly in Burkina Faso, Mali, Senegal, the Gambia, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Sierra Leone, Liberia, and Ivory Coast, and also in northwestern Nigeria and northern Benin. The Mande languages show lexical similarities with the Atlantic–Congo language family, and the two have been classified together as a Niger–Congo language family since the 1950s. However, the Mande languages lack the noun-class morphology that is the primary identifying feature of the Atlantic–Congo languages. Without the help of that feature, a demonstration of the validity of Niger–Congo will require reconstructing both Proto-Mande and Proto-Atlantic–Congo. Until that work is done, linguists have increasingly decided to treat Mande and Atlantic–Cong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gambia River
The Gambia River (formerly known as the River Gambra) is a major river in West Africa, running from the Fouta Djallon plateau in north Guinea westward through Senegal and The Gambia to the Atlantic Ocean at the city of Banjul. It is navigable for about half that length. The river is strongly associated with The Gambia, the smallest country in mainland Africa, which occupies the downstream half of the river and its two banks. Geography The Gambia River runs a total length of . From the Fouta Djallon, it runs northwest into the Tambacounda Region of Senegal, where it flows through the Parc National du Niokolo Koba, then is joined by the Nieri Ko and and passing through the Barrakunda Falls before entering the Gambia at Koina. At this point, the river runs generally west, but in a meandering course with a number of oxbows, and about from its mouth it gradually widens, to over wide where it meets the sea. Crossings There are several bridges crossing the river. The largest an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |