|
Jaitsri
Jaitsri is an Indian classical raga that appears in the Sikh tradition from northern India and is part of the Guru Granth Sahib. It provided the setting for hymns by Guru Ram Das, Guru Arjan and Guru Tegh Bahadar Guru Tegh Bahadur ( Punjabi: ਗੁਰੂ ਤੇਗ਼ ਬਹਾਦਰ (Gurmukhi); ; 1 April 1621 – 11 November 1675) was the ninth of ten Gurus who founded the Sikh religion and the leader of Sikhs from 1665 until his beheading in 1 ... for a total of 30 hymns. It is the 26th raag, in order of appearance, in Guru Granth Sahib. Jaitsiri conveys the heartfelt emotion of not being able to live without someone. Its mood is preoccupied with feelings of dependence and an overwhelming sense of desperately reaching out to be with that person. The following represents the order of notes that can be used on the ascending and descending phase of the composition and the primary and secondary notes: See also * Kirtan References External links Sikh Kir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guru Granth Sahib
The Guru Granth Sahib ( pa, ਗੁਰੂ ਗ੍ਰੰਥ ਸਾਹਿਬ, ) is the central holy religious scripture of Sikhism, regarded by Sikhs as the final, sovereign and Guru Maneyo Granth, eternal Guru following the lineage of the Sikh gurus, ten human gurus of the religion. The Adi Granth ( pa, ਆਦਿ ਗ੍ਰੰਥ), its first rendition, was compiled by the fifth guru, Guru Arjan (1564–1606). Its compilation was completed on 29 August 1604 and first installed inside Golden Temple in Amritsar on 1 September 1604. Baba Buddha was appointed the first Granthi of the Golden Temple. Shortly afterwards Guru Hargobind added Ramkali Ki Vaar. Later, Guru Gobind Singh, the tenth Sikh guru, added hymns of Guru Tegh Bahadur to the Adi Granth and affirmed the text as his successor. This second rendition became known as the Guru Granth Sahib and is also sometimes referred to as the Adi Granth. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raga
A ''raga'' or ''raag'' (; also ''raaga'' or ''ragam''; ) is a melodic framework for improvisation in Indian classical music akin to a musical mode, melodic mode. The ''rāga'' is a unique and central feature of the classical Indian music tradition, and as a result has no direct translation to concepts in classical European music. Each ''rāga'' is an array of melodic structures with musical motifs, considered in the Indian tradition to have the ability to "colour the mind" and affect the emotions of the audience. Each ''rāga'' provides the musician with a musical framework within which to improvise. Improvisation by the musician involves creating sequences of notes allowed by the ''rāga'' in keeping with rules specific to the ''rāga''. ''Rāga''s range from small ''rāga''s like Bahar (raga), Bahar and Shahana that are not much more than songs to big ''rāga''s like Malkauns, Darbari and Yaman (raga), Yaman, which have great scope for improvisation and for which performances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Sikh'' has its origin in the word ' (), meaning 'disciple' or 'student'. Male Sikhs generally have ''Singh'' ('lion'/'tiger') as their last name, though not all Singhs are necessarily Sikhs; likewise, female Sikhs have ''Kaur'' ('princess') as their last name. These unique last names were given by the Gurus to allow Sikhs to stand out and also as an act of defiance to India's caste system, which the Gurus were always against. Sikhs strongly believe in the idea of "Sarbat Da Bhala" - "Welfare of all" and are often seen on the frontline to provide humanitarian aid across the world. Sikhs who have undergone the ''Amrit Sanchar'' ('baptism by Khanda (Sikh symbol), Khanda'), an initiation ceremony, are from the day of thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guru Ram Das
Guru Ram Das (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਰਾਮ ਦਾਸ, pronunciation: ; 24 September 1534 – 1 September 1581) was the fourth of the ten Ten Gurus of Sikhism, Gurus of Sikhism. He was born in a family based in Lahore. His birth name was Jetha, and he was orphaned at age seven; he there after grew up with his maternal grandmother in a village. At age 12, Bhai Jetha and his grandmother moved to Goindval, where they met Guru Amar Das. The boy thereafter accepted Guru Amar Das as his mentor and served him. The daughter of Guru Amar Das married Bhai Jetha, and he thus became part of Guru Amar Das's family. As with the first two Gurus of Sikhism, Guru Amar Das instead of choosing his own sons, chose Bhai Jetha, owing to Bhai Jetha's exemplary service, selfless devotion and unquestioning obedience to the commands of the Guru, as his successor and renamed him as Ram Das or "servant of god." Guru Ram Das became the Guru of Sikhism in 1574 and served as the 4th guru until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guru Arjan
Guru Arjan (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਅਰਜਨ, pronunciation: ; 15 April 1563 – 30 May 1606) was the first of the two Gurus martyred in the Sikh faith and the fifth of the ten total Sikh Gurus. He compiled the first official edition of the Sikh scripture called the Adi Granth, which later expanded into the Guru Granth Sahib. He was born in Goindval, in the Punjab, the youngest son of Bhai Jetha, who later became Guru Ram Das, and Mata Bhani, the daughter of Guru Amar Das. He completed the construction of Darbar Sahib at Amritsar, after the fourth Sikh Guru founded the town and built a sarovar. Guru Arjan compiled the hymns of previous Gurus and of other saints into Adi Granth, the first edition of the Sikh scripture, and installed it in the Harimandir Sahib. Guru Arjan reorganized the Masands system initiated by Guru Ram Das, by suggesting that the Sikhs donate, if possible, one-tenth of their income, goods or service to the Sikh organization (''dasvandh''). The ''Masan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
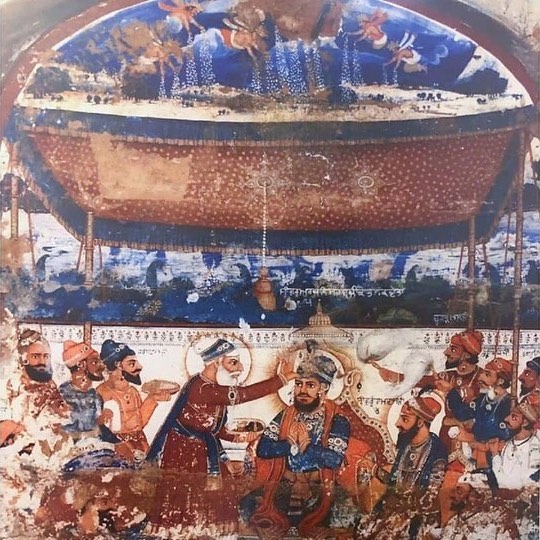
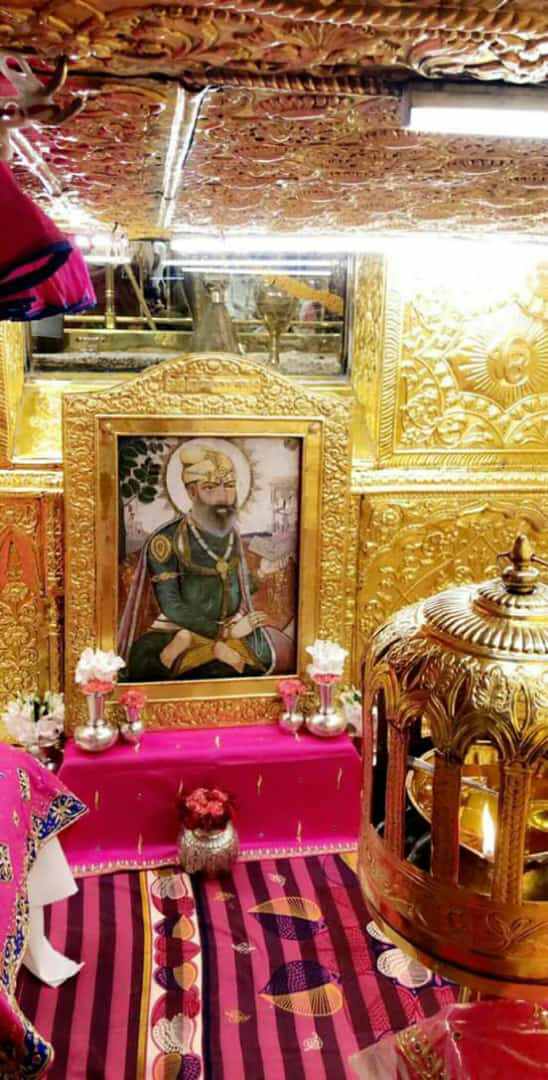
Guru Tegh Bahadar
Guru Tegh Bahadur ( Punjabi: ਗੁਰੂ ਤੇਗ਼ ਬਹਾਦਰ (Gurmukhi); ; 1 April 1621 – 11 November 1675) was the ninth of ten Gurus who founded the Sikh religion and the leader of Sikhs from 1665 until his beheading in 1675. He was born in Amritsar, Punjab, India in 1621 and was the youngest son of Guru Hargobind, the sixth Sikh guru. Considered a principled and fearless warrior, he was a learned spiritual scholar and a poet whose 115 hymns are included in ''Sri Guru Granth Sahib,'' the main text of Sikhism. Guru Tegh Bahadur was executed on the orders of Aurangzeb, the sixth Mughal emperor, in Delhi, India.;;; Sikh holy premises Gurudwara Sis Ganj Sahib and Gurdwara Rakab Ganj Sahib in Delhi mark the places of execution and cremation of Guru Tegh Bahadur. His martyrdom is remembered as the ''Shaheedi Divas of Guru Tegh Bahadur'' every year on 24 November. Biography Early life Guru Tegh Bahadur was the youngest son of Guru Hargobind, the sixth guru: Guru H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guru Arjan Dev
Guru Arjan (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਅਰਜਨ, pronunciation: ; 15 April 1563 – 30 May 1606) was the first of the two Gurus martyred in the Sikh faith and the fifth of the ten total Sikh Gurus. He compiled the first official edition of the Sikh scripture called the Adi Granth, which later expanded into the Guru Granth Sahib. He was born in Goindval, in the Punjab, the youngest son of Bhai Jetha, who later became Guru Ram Das, and Mata Bhani, the daughter of Guru Amar Das. He completed the construction of Darbar Sahib at Amritsar, after the fourth Sikh Guru founded the town and built a sarovar. Guru Arjan compiled the hymns of previous Gurus and of other saints into Adi Granth, the first edition of the Sikh scripture, and installed it in the Harimandir Sahib. Guru Arjan reorganized the Masands system initiated by Guru Ram Das, by suggesting that the Sikhs donate, if possible, one-tenth of their income, goods or service to the Sikh organization (''dasvandh''). The ''Masand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guru Teg Bahadur
Guru Tegh Bahadur ( Punjabi: ਗੁਰੂ ਤੇਗ਼ ਬਹਾਦਰ (Gurmukhi); ; 1 April 1621 – 11 November 1675) was the ninth of ten Gurus who founded the Sikh religion and the leader of Sikhs from 1665 until his beheading in 1675. He was born in Amritsar, Punjab, India in 1621 and was the youngest son of Guru Hargobind, the sixth Sikh guru. Considered a principled and fearless warrior, he was a learned spiritual scholar and a poet whose 115 hymns are included in ''Sri Guru Granth Sahib,'' the main text of Sikhism. Guru Tegh Bahadur was executed on the orders of Aurangzeb, the sixth Mughal emperor, in Delhi, India.;;; Sikh holy premises Gurudwara Sis Ganj Sahib and Gurdwara Rakab Ganj Sahib in Delhi mark the places of execution and cremation of Guru Tegh Bahadur. His martyrdom is remembered as the ''Shaheedi Divas of Guru Tegh Bahadur'' every year on 24 November. Biography Early life Guru Tegh Bahadur was the youngest son of Guru Hargobind, the sixth guru: Gur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhagat Ravidas
Ravidas or Raidas, was an Indian mystic poet-saint of the bhakti movement during the 15th to 16th century CE. Venerated as a ''guru'' (teacher) in the modern regions of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab and Haryana, he was a poet, social reformer and spiritual figure. The life details of Ravidas are uncertain and contested. Scholars believe he was born in 1450 CE. But some Scholars believe he was born in 1377 CE and dead in 1528 CE. He taught removal of social divisions of caste and gender, and promoted unity in the pursuit of personal spiritual freedom. Ravidas's devotional verses were included in the Sikh scriptures known as ''Guru Granth Sahib''. The ''Panch Vani'' text of the Dadu Panthi tradition within Hinduism also includes numerous poems of Ravidas. He is also the central figure within the Ravidassia religious movement. Life The details of Guru Ravidas's life are not well known. Scholars state he was born in 1377 CE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirtan
Kirtana ( sa, कीर्तन; ), also rendered as Kirtan, is a Sanskrit word that means "narrating, reciting, telling, describing" of an idea or story, specifically in Indian religions. It also refers to a genre of religious performance arts, connoting a musical form of narration or shared recitation, particularly of spiritual or religious ideas, native to the Indian subcontinent. With roots in the Vedic ''anukirtana'' tradition, a kirtan is a call-and-response style song or chant, set to music, wherein multiple singers recite or describe a legend, or express loving devotion to a deity, or discuss spiritual ideas. It may include dancing or direct expression of ''bhavas'' (emotive states) by the singer. Many kirtan performances are structured to engage the audience where they either repeat the chant,Sara Brown (2012), ''Every Word Is a Song, Every Step Is a Dance'', PhD Thesis, Florida State University (Advisor: Michael Bakan), pages 25-26, 87-88, 277 or reply to the call of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindustani Ragas
Hindustani may refer to: * something of, from, or related to Hindustan (another name of India) * Hindustani language, an Indo-Aryan language, whose two official norms are Hindi and Urdu * Fiji Hindi, a variety of Eastern Hindi spoken in Fiji, and is known locally as Hindustani * Caribbean Hindustani, a variety of Eastern Hindi spoken in the Caribbean * Hindustani classical music, a major style of Indian classical music * Hindustani (film), ''Hindustani'' (film) or ''Indian'', a 1996 film starring Kamal Haasan and Manisha Koirala * Muhammadjan Hindustani, Islamist teacher of Uzbekistan See also * South Asian ethnic groups * Hindustani Lal Sena or Indian Red Army, formed 1939 * Communist Ghadar Party of India, a political group founded in 1970 * ''Raja Hindustani'', a 1996 film starring Aamir Khan and Karishma Kapoor {{disambiguation, surname Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)