|
Jahriyya Revolt
In the Jahriyya revolt () of 1781 sectarian violence between two suborders of the Naqshbandi Sufis, the Jahriyya Sufi Muslims and their rivals, the Khafiyya Sufi Muslims, led to Qing intervention to stop the fighting between the two, which in turn led to a Jahriyya Sufi Muslim rebellion which the Qing dynasty of China crushed with the help of the Khufiyya (Khafiyya) Sufi Muslims. Due to street fighting and lawsuits between the Jahriyya and Khufiyya Sufi orders, Ma Mingxin was arrested to stop the sectarian violence between the Sufis. The Jahriyya then tried to violently jailbreak Ma Mingxin which led to his execution and the crushing of the Jahriyya rebels. The Qing used Xinjiang as a place to put deported Jahriyya rebels. The Khufiyya Sufis and Gedimu joined together against the Jahriyya Sufis whom they fiercely opposed and differed from in practices. Salar Jahriyyas were among those deported to Xinjiang. Some Han Chinese joined and fought alongside the Jahriyya Salar Musli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xining. Qinghai borders Gansu on the northeast, Xinjiang on the northwest, Sichuan on the southeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region on the southwest. Qinghai province was established in 1928 during the period of the Republic of China, and until 1949 was ruled by Chinese Muslim warlords known as the Ma clique. The Chinese name "Qinghai" is after Qinghai Lake, the largest lake in China. The lake is known as Tso ngon in Tibetan, and as Kokonor Lake in English, derived from the Mongol Oirat name for Qinghai Lake. Both Tso ngon and Kokonor are names found in historic documents to describe the region.Gangchen Khishong, 2001. ''Tibet and Manchu: An Assessment of Tibet-Manchu Relations in Five Phases of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khafiyya
Ma Laichi (1681? – 1766?; ), also known as Abu 'l-Futūh Ma Laichi, was a Chinese Sufi master, who brought the Khufiyya movement to China and created the Huasi ''menhuan'' ( Sufi order) - the earliest and most important Naqshbandi (نقشبندية,納克什班迪) order in Chinese Muslim history.Gladney (1996), pp. 47-48Lipman (1998), p. 65-67 Life Afaq Khoja's blessing Ma Laichi came from a Chinese Muslim family with a military background. His grandfather, Ma Congshan, was a general under the Ming dynasty; his father, Ma Jiujun, passed imperial examinations on the military track under the Qing, but instead of joining government service, made a fortune in business. His home was in Hezhou (now called Linxia), one of the main Muslim centers of Gansu. According to the legend told by Ma Laichi's followers, Ma Jiajun was still childless at the age of forty, and, desirous to have a son, he went to Xining, to ask for a blessing from Afaq Khoja, a Naqshbandi ''shaykh'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
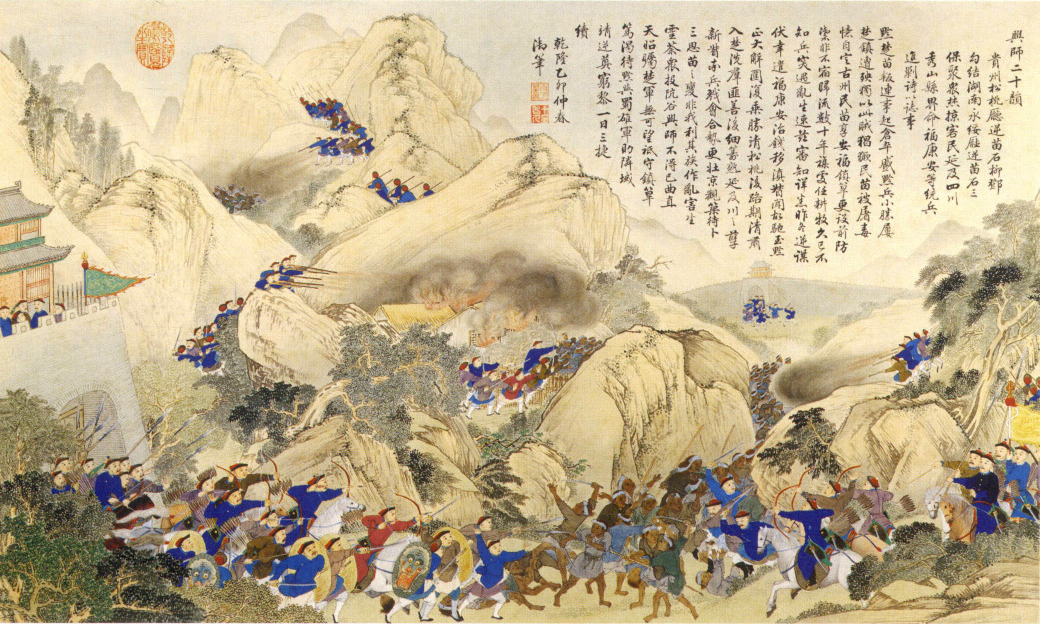
18th-century Rebellions
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected events. To historians who expand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam During The Qing Dynasty
During the Manchu-led Qing dynasty (1636–1912), there were five major Muslim rebellions. The first and last rebellions were caused by sectarian infighting between rival Sufi Muslim orders. Anti-Qing rebellions Ming loyalist Muslims When the Qing dynasty invaded the Ming dynasty in 1644, Muslim Ming loyalists in Gansu led by Muslim leaders Milayin and Ding Guodong led a revolt in 1646 against the Qing during the Milayin rebellion in order to drive the Qing out and restore the Ming Prince of Yanchang Zhu Sichuan to the throne as the emperor. The Muslim Ming loyalists were supported by Hami's Sultan Sa'id Baba and his son Prince Turumtay. The Muslim Ming loyalists were joined by Tibetan and Han peoples in the revolt. After fierce fighting, and negotiations, a peace agreement was agreed on in 1649, and Milayan and Ding nominally pledged allegiance to the Qing and were given ranks as members of the Qing military. When other Ming loyalists in southern China made a resurgence and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Islam In China
The history of Islam in China dates back to 1,300 years ago.. Currently, Chinese Muslims are a minority group in China, representing between 0.45% to 1.8% of the total population according to the latest estimates. Although Hui Muslims are the most numerous group, the greatest concentration of Chinese Muslims are located in Northwestern China, mostly in the autonomous region of Xinjiang, which holds a significant Uyghur population. Lesser but significant Chinese Muslim populations reside in the regions of Ningxia, Gansu, and Qinghai. Of China's 55 officially recognized minority peoples, ten groups are predominantly Sunnī Muslim. Origin of Islam in China The history of Islam in China goes back to the earliest years of Islam. According to Chinese Muslims' traditional accounts, Muslim missionaries reached China through an embassy sent by ʿUthmān ibn ʿAffān (644–656 CE), the third '' rāshidūn'' caliph, in 651 CE, less than twenty years after the death of Muhammad (632 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam In China
Islam has been practiced in China since the 7th century CE.. Muslims are a minority group in China, representing 1.6-2 percent of the total population (21,667,000- 28,210,795) according to various estimates. Though Hui people, Hui Muslims are the most numerous group, the greatest concentration of Muslims are in Xinjiang, which contains a significant Uyghurs, Uyghur population. Lesser yet significant populations reside in the regions of Ningxia, Gansu and Qinghai. Of Ethnic minorities in China, China's 55 officially recognized minority peoples, ten of these groups are predominantly Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim. History The Silk Road, which was a series of extensive inland trade routes that spread all over the Mediterranean to East Asia, was used since 1000 BCE and continued to be used for millennia. For more than half of this long period of time, most of the traders were Muslim and moved towards the East. Not only did these traders bring their goods, they also carried with them thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rebellions In China
This is an incomplete list of some of the rebellions, revolts and revolutions that have occurred in China. Zhou dynasty * Rebellion of the Three Guards (late 11th century BC) was a three-year rebellion of the Shang and three uncles of King Cheng of Zhou against their nephew and his regent, the Duke of Zhou. * Compatriots Rebellion (842 BC) was an uprising against King Li of Zhou, ending with the King's exile, establishing the interregnum Gonghe Regency until King Xuan of Zhou took the throne. Qin dynasty * The Dazexiang Uprising (; July – December 209 BC) was the first uprising against Qin rule following the death of Qin Shi Huang. Chen Sheng and Wu Guang were both army officers who were ordered to lead their bands of commoner soldiers north to participate in the defense of Yuyang (漁陽). However, they were stopped halfway in Dazexiang, Qixian (modern Suzhou, Anhui) by a severe rainstorm and flooding. Harsh Qin law stated that anyone who showed up l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
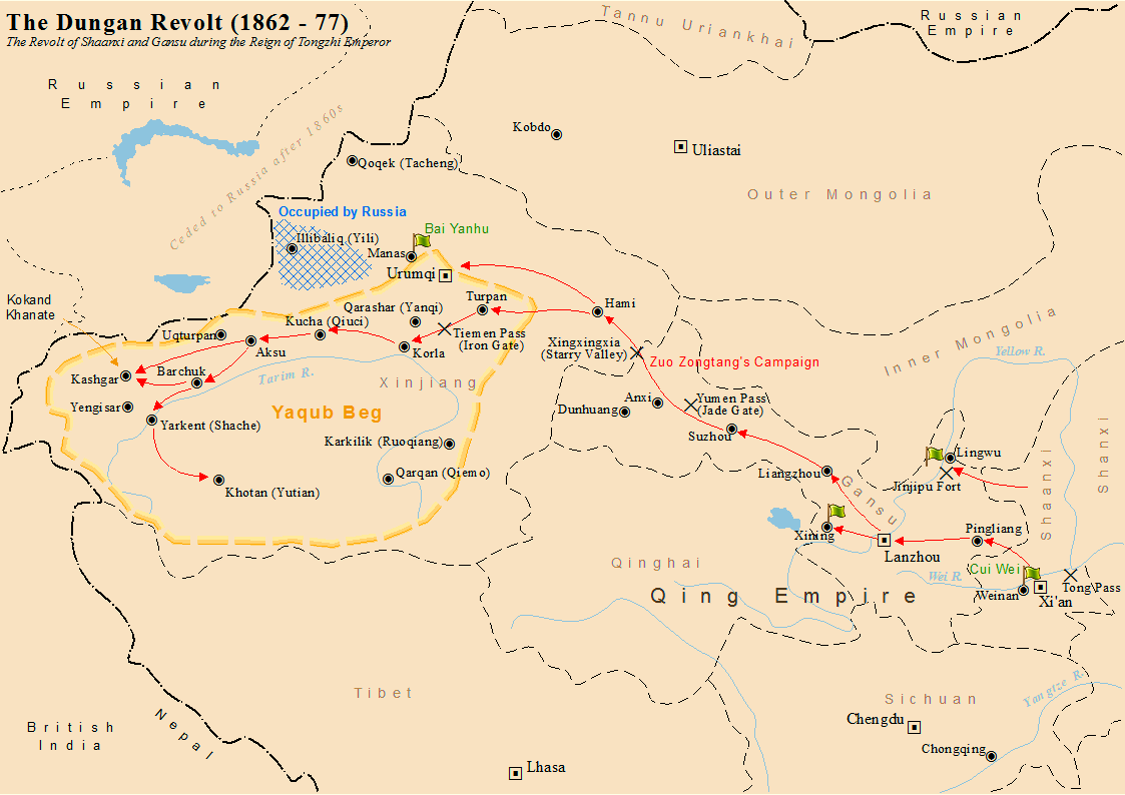
Dungan Revolt (1862–1877)
The Dungan Revolt (1862–1877) or Tongzhi Hui Revolt (, Xiao'erjing: تُجِ خُوِ لُوًا, dng, Тунҗы Хуэй Луан) or Hui (Muslim) Minorities War was a war fought in 19th-century western China, mostly during the reign of the Tongzhi Emperor (r. 1861–1875) of the Qing dynasty. The term sometimes includes the Panthay Rebellion in Yunnan, which occurred during the same period. However, this article refers specifically to two waves of uprising by various Chinese Muslims, mostly Hui people, in Shaanxi, Gansu and Ningxia provinces in the first wave, and then in Xinjiang in the second wave, between 1862 and 1877. The uprising was eventually suppressed by Qing forces led by Zuo Zongtang. The conflict began with riots by the Hui and massacres of the Han Chinese, followed by the revenge massacres of the Hui by the Han. It resulted in massive demographic shifts in Northwest China, and led to a population loss of 21 million people from a combination of massa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim Groups In China
The vast majority of China's Muslims are Sunni Muslims, although a small minority are Shia. Mosques The style of architecture of Hui mosques varies according to their sect. The traditionalist Gedimu Hanafi Sunnis, influenced by Chinese culture, build mosques that look like Chinese temples. The reformist modernist (but originally Wahhabi-inspired) Yihewani build their mosques to look like Middle Eastern Arab-style mosques. Hanafi Sunni Gedimu Gedimu or Qadim is the earliest school of Islam in China. It is a Hanafi non-Sufi school of the Sunni tradition. Its supporters are centered on local mosques, which function as relatively independent units. It is numerically the largest Islamic school of thought in China and most common school of Islam among the Hui. Since the introduction of Islam, first during the Tang dynasty in China, it continued to the Ming dynasty with no splits. At the end of the Ming and early Qing dynasty Sufism was introduced to China. Its members were sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Proper
China proper, Inner China, or the Eighteen Provinces is a term used by some Western writers in reference to the "core" regions of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China. This term is used to express a distinction between the "core" regions populated by the dominant Han population and the "frontier" regions of China, sometimes known as "Outer China". There is no fixed extent for China proper, as many administrative, cultural, and linguistic shifts have occurred in Chinese history. One definition refers to the original area of Chinese civilization, the Central Plain (in the North China Plain); another to the Eighteen Provinces of the Qing dynasty. There is no direct translation for "China proper" in the Chinese language due to differences in terminology used by the Qing to refer to the regions. The expression is controversial among scholars, particularly in China, due to issues pertaining to territorial integrity. Outer China usually includes the geographical regions of Dzungar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ma Yuanzhang
Ma Yuanzhang (Xiao'erjing: , ) was a Chinese Sufi master, of the Jahriyya ''menhuan'' (Naqshbandi Sufi order). Jiaozhu of the Jahriyya Ma Mingxin's descendant was Ma Yuanzhang. When Agui defeated Su Forty-three and the New teaching in the Jahriyya revolt of 1781, The family of Ma Mingxin was exiled to Yunnan. where they lived in the western Muslim community, converting the Yunnan Muslims to the Jahriyya sect. Ma Yuanzhang's father, Ma Shilin, travelled from Yunnan to Ningxia to visit Ma Hualong two times. After Du Wenxiu rebelled in the Panthay Rebellion, Ma Shilin joined him as a garrison commander and civil official. He defended Donggouzhai fort a year against Qing, and then committed suicide. Ma Shilin's son Ma Yuanzhang and his other sons went to Sichuan. Ma Yuanzhang searched for surviving children of Ma Hualong. Few of Ma Hualong's family survived the massacre at Jinjipu. Two of his grandsons, Ma Jincheng and Ma Jinxi, were sentenced to castration upon reaching the age of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dungan Revolt (1895–96) , rebellion of various Muslim ethnic groups in Qinghai and Gansu, China
{{disambiguation ...
Dungan revolt may refer to: * Dungan revolt (1862–77), rebellion of various Muslim ethnic groups in Shaanxi and Gansu, China * Dungan revolt (1895–96) Dungan revolt may refer to: * Dungan revolt (1862–77) Dungan revolt may refer to: * Dungan revolt (1862–77), rebellion of various Muslim ethnic groups in Shaanxi and Gansu, China * Dungan revolt (1895–96) Dungan revolt may refer to: * Dunga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |