|
Jacques D'Albon, Seigneur De Saint André
Jacques d'Albon, Seigneur de Saint-André (c. 1505–1562) was a French governor, Marshal, and favourite of Henri II of France, Henri II. He began his career as a confident of the dauphin during the reign of François I of France, François I, reared with the prince under the governorship of his father at court. In 1547 at the advent of Henri's reign he was appointed as his father's deputy, serving as lieutenant general for the Lyonnais. Concurrently he entered the king's ''conseil privé'' and was made a Marshal and Grand Chamberlain. With the resumption of the Italian Wars, Saint André found himself serving to protect the recently acquired city of Verdun during the emperor's campaign into the region in 1552. In 1553 he was subordinate to Anne de Montmorency in the French campaign in Picardy, however neither he nor Montmorency achieved much of note. In 1557 he was present during the disaster at Battle of Saint-Quentin (1557), Saint-Quentin and was captured, while much of the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musée D'Histoire De France
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, under the direction of the French Ministry of Culture, by the Public Establishment of the Palace, Museum and National Estate of Versailles. Some 15,000,000 people visit the palace, park, or gardens of Versailles every year, making it one of the most popular tourist attractions in the world. Louis XIII built a simple hunting lodge on the site of the Palace of Versailles in 1623 and replaced it with a small château in 1631–34. Louis XIV expanded the château into a palace in several phases from 1661 to 1715. It was a favorite residence for both kings, and in 1682, Louis XIV moved the seat of his court and government to Versailles, making the palace the ''de facto'' capital of France. This state of affairs was continued by Kings Louis XV an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conspiracy Of Amboise
The Amboise conspiracy, also called Tumult of Amboise, was a failed attempt by a Huguenot faction in France to gain control over the young king Francis II and to reverse the policies of the current administration of Francis, Duke of Guise and Charles, Cardinal of Lorraine through their arrest, and potentially execution. Malcontent factions of Huguenots had been chafing under the French crown since the reign of Henry II and with the arrival of a new young king, saw their chance to take power for themselves. However the plot was uncovered ahead of time, and the Guise were ready for them. As such hundreds would be arrested, and many killed. Louis, Prince of Condé was suspected of involvement, however he was able to flee south, and it was only after some months that the Guise were able to put him on trial. Shortly thereafter, the sickly Francis II died, their hold on the administration collapsed, and with it the conviction of Condé. This tumult would be one of the key steps in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Bishoprics
The Three Bishoprics (french: les Trois-Évêchés ) constituted a government of the Kingdom of France consisting of the dioceses of Metz, Verdun, and Toul within the Lorraine region. The three dioceses had been Prince-bishoprics of the Holy Roman Empire until they were seized by King Henry II of France between April and June 1552. At the end of the Thirty Years' War, they were officially ceded to France by the 1648 Peace of Westphalia. History In the course of the rebellion against the Habsburg emperor Charles V, several Protestant Imperial princes met at Lochau Castle near Torgau in May 1551. Here the receiving Wettin elector Maurice of Saxony forged an alliance with Duke John Albert I of Mecklenburg, Prince William IV of Hesse, whose father Landgrave Philip I was jailed by the emperor, the Hohenzollern margrave Albert Alcibiades of Brandenburg-Kulmbach and his cousin Duke Albert of Prussia. Dissatisfied with the Interim decreed by Charles V at the 1548 Diet of Augsburg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marche (France)
The County of La Marche (; oc, la Marcha) was a medieval French county, approximately corresponding to the modern ''département'' of Creuse. La Marche first appeared as a separate fief about the middle of the 10th century, when William III, Duke of Aquitaine, gave it to one of his vassals, Boson, who took the title of Count. In the 12th century, the countship passed to the House of Lusignan. They also were sometimes counts of Angoulême and counts of Limousin. With the death of the childless Count Guy in 1308, his possessions in La Marche were seized by Philip IV of France. In 1314, the king made La Marche an ''appanage'' for his youngest son the Prince, afterwards Charles IV. Several years later in 1327, La Marche passed into the hands of the House of Bourbon. The family of Armagnac held it from 1435 to 1477, when it reverted to the Bourbons. In 1527 La Marche was seized by Francis I and became part of the domains of the French crown. It was divided into ''Haute Marche' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
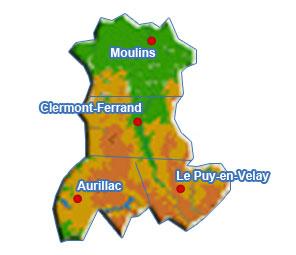
Auvergne
Auvergne (; ; oc, label=Occitan, Auvèrnhe or ) is a former administrative region in central France, comprising the four departments of Allier, Puy-de-Dôme, Cantal and Haute-Loire. Since 1 January 2016, it has been part of the new region Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes.. The administrative region of Auvergne is larger than the historical province of Auvergne, one of the seven counties of Occitania, and includes provinces and areas that historically were not part of Auvergne. The Auvergne region is composed of the following old provinces: * Auvergne: departments of Puy-de-Dôme, Cantal, northwest of Haute-Loire, and extreme south of Allier. The province of Auvergne is entirely contained inside the Auvergne region * Bourbonnais: department of Allier. A small part of Bourbonnais lies outside Auvergne, in the neighbouring Centre-Val de Loire region (south of the department of Cher). * Velay: centre and southeast of department of Haute-Loire. Velay is entirely contained inside the Auvergne r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaujolais (province)
Beaujolais (; frp, Biôjolês) is a historical province and wine-producing region in France. It is located north of Lyon, and covers parts of the departments of Rhône and Saône-et-Loire. The region is known internationally for its long tradition of winemaking, and more recently for the Beaujolais nouveau. Geography The historical capital of the province is Beaujeu ( frp, Bôjor / Biôjœr) and the economic capital of the area is Villefranche-sur-Saône Villefranche-sur-Saône (, ; frp, Velafranche) is a commune in the Rhône department in eastern France. It lies 1 mile (1.6 km) west of the river Saône, and is around north of Lyon. The inhabitants of the town are called ''Caladois''. ... (). Wine Almost all the wine produced in the region is red wine from the Gamay grape, of which the heavily marketed Beaujolais Nouveau is the most well-known, and the village crus the most prized. Notes and references * Mathieu Méras, ''Le Beaujolais au Moyen Age'', Lyon, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forez
Forez is a former province of France, corresponding approximately to the central part of the modern Loire ''département'' and a part of the Haute-Loire and Puy-de-Dôme ''départements''. The final "z" in Forez () is not pronounced in the Loire département; however, it is pronounced in the western part of the former province, essentially when referring to the correspondent Forez Mountains (on the border between Puy-de-Dôme and Loire. The name is derived from the city of Feurs. Franco-Provençal is the language that was historically spoken in the region. The city of Montbrison, Loire is considered the historical capital of the Forez. Residents of the Forez are called Foréziens. The rue du Forez in the third arrondissement of Paris was built in the late 16th century and appears on Turgot's map of Paris. List of counts of Forez The origins of the county of Forez are obscure. There are several early figures who are sometimes supposed to have been counts of Forez. Whether thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude D'Annebault
Claude d'Annebault (1495 – 2 November 1552) was a French military officer; Marshal of France (1538–52); Admiral of France (1543–1552); and Governor of Piedmont in 1541. He led the French invasion of the Isle of Wight in 1545. Annebault was governor of Normandy and a very powerful figure during the reign of King Francis. Claude was a commissioner for the Anglo-French Treaty of Ardres, also known as the Treaty of Camp, which was signed on 7 June 1546 and a step towards the conclusion of the Italian War of 1542–1546. After a delay which the English found frustrating, Claude then visited England as a special ambassador for the peace treaty 20–30 August 1546. Four cannon at Walmer Castle burst while firing his salute. Claude wrote from London to his ally, Mary of Guise, in Scotland on 28 August, explaining his difficulties in forwarding their mutual interest. Family Claude married Françoise Tournemine, daughter and heiress of George, sieur de la Hunaudaye. Their only son Jea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François De Scépeaux
François de Scépeaux de Vieilleville (1509 – 30 November 1571), lord of Vieilleville, 1st comte of Durtal, was a French governor, diplomat, ambassador, conseillé du roi and marshal. During his career, he would serve four French kings. He fought throughout the later years of the Italian Wars, acquiring for himself the key frontier governorship of Metz in 1553. Under King Charles IX he would be elevated to marshal and would serve the crown in the early religious wars, increasingly in the role of peacemaker and diplomat, though with scattered military service as with the recapture of Le Havre in 1563. He died in 1571, shortly before France would be shaken by the St Bartholomew's Day Massacre. Early life and family François de Scépaux de Vielleville, was born in 1509 to his father Seignory René de Scépeaux de Vieilleville and mother Marguerite de La Jaille. He was eldest to his sister named Françoise, and grandson of his namesake François , chamberlain of King Char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catherine De Medici
Catherine de' Medici ( it, Caterina de' Medici, ; french: Catherine de Médicis, ; 13 April 1519 – 5 January 1589) was an Florentine noblewoman born into the Medici family. She was Queen of France from 1547 to 1559 by marriage to King Henry II and the mother of French Kings Francis II, Charles IX, and Henry III. The years during which her sons reigned have been called "the age of Catherine de' Medici" since she had extensive, if at times varying, influence in the political life of France. Catherine was born in Florence to Lorenzo de' Medici, Duke of Urbino, and Madeleine de La Tour d'Auvergne. In 1533, at the age of 14, Catherine married Henry, the second son of King Francis I and Queen Claude of France. Catherine's marriage was arranged by her uncle Pope Clement VII. Henry excluded Catherine from participating in state affairs and instead showered favours on his chief mistress, Diane de Poitiers, who wielded much influence over him. Henry's death in 1559 thrust Cathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis, Prince Of Condé (1530-1569)
{{hndis ...
Louis, Prince of Condé may refer to: * Louis, Prince of Condé (1530–1569), Huguenot leader and general * Louis, Prince of Condé (1621–1686) * Louis, Prince of Condé (1668–1710) Louis, Prince of Condé may refer to: * Louis, Prince of Condé (1530–1569), Huguenot leader and general * Louis, Prince of Condé (1621–1686) * Louis, Prince of Condé (1668–1710) {{hndis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Dreux
The Battle of Dreux was fought on 19 December 1562 between Catholics and Huguenots. The Catholics were led by Anne de Montmorency while Louis I, Prince of Condé, led the Huguenots. Though commanders from both sides were captured, the French Catholics won the battle which would constitute the first major engagement of the French Wars of Religion. Opening moves This was the first major engagement of the French Wars of Religion. The Protestant army encountered the Catholic royal army on the road to Dreux while attempting to move north into Normandy. They began with a slight disadvantage because they had not posted sufficient scouts around their march, largely because Coligny had persuaded Condé that the Catholics would not attack and therefore there was some confusion about the line of battle. Although the Catholics were superior in numbers and their infantry was much more experienced they were severely lacking in heavy cavalry, the main offensive weapon of set battles in the per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |