|
Jacques Bouveresse
Jacques Bouveresse (; 20 August 1940 – 9 May 2021) was a French philosopher who wrote on subjects including Ludwig Wittgenstein, Robert Musil, Karl Kraus, philosophy of science, epistemology, philosophy of mathematics and analytical philosophy. Bouveresse was called "an '' avis rara'' among the better known French philosophers in his championing of critical standards of thought." He was Professor Emeritus at the Collège de France where until 2010 he held the chair of philosophy of language and epistemology. His disciple Claudine Tiercelin was appointed to a chair of metaphysics and philosophy of knowledge upon his retirement. Education and career Born on 20 August 1940 in Épenoy in the Doubs département of France into a farming family, Jacques Bouveresse completed his secondary education at the seminary of Besançon. He spent two years of preparation for the baccalauréat in philosophy and scholastic theology at Faverney in Haute-Saône. He followed his preparatory literar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Philosophy
Western philosophy encompasses the philosophical thought and work of the Western world. Historically, the term refers to the philosophical thinking of Western culture, beginning with the ancient Greek philosophy of the pre-Socratics. The word ''philosophy'' itself originated from the Ancient Greek (φιλοσοφία), literally, "the love of wisdom" grc, φιλεῖν , "to love" and σοφία '' sophía'', "wisdom"). History Ancient The scope of ancient Western philosophy included the problems of philosophy as they are understood today; but it also included many other disciplines, such as pure mathematics and natural sciences such as physics, astronomy, and biology (Aristotle, for example, wrote on all of these topics). Pre-Socratics The pre-Socratic philosophers were interested in cosmology; the nature and origin of the universe, while rejecting mythical answers to such questions. They were specifically interested in the (the cause or first principle) of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytical Philosophy
Analytic philosophy is a branch and tradition of philosophy using analysis, popular in the Western world and particularly the Anglosphere, which began around the turn of the 20th century in the contemporary era in the United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and Scandinavia, and continues today. Analytic philosophy is often contrasted with continental philosophy, coined as a catch-all term for other methods prominent in Europe. Central figures in this historical development of analytic philosophy are Gottlob Frege, Bertrand Russell, G. E. Moore, and Ludwig Wittgenstein. Other important figures in its history include the logical positivists (particularly Rudolf Carnap), W. V. O. Quine, and Karl Popper. After the decline of logical positivism, Saul Kripke, David Lewis, and others led a revival in metaphysics. Elizabeth Anscombe, Peter Geach, Anthony Kenny and others brought analytic approach to Thomism. Analytic philosophy is characterized by an empha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
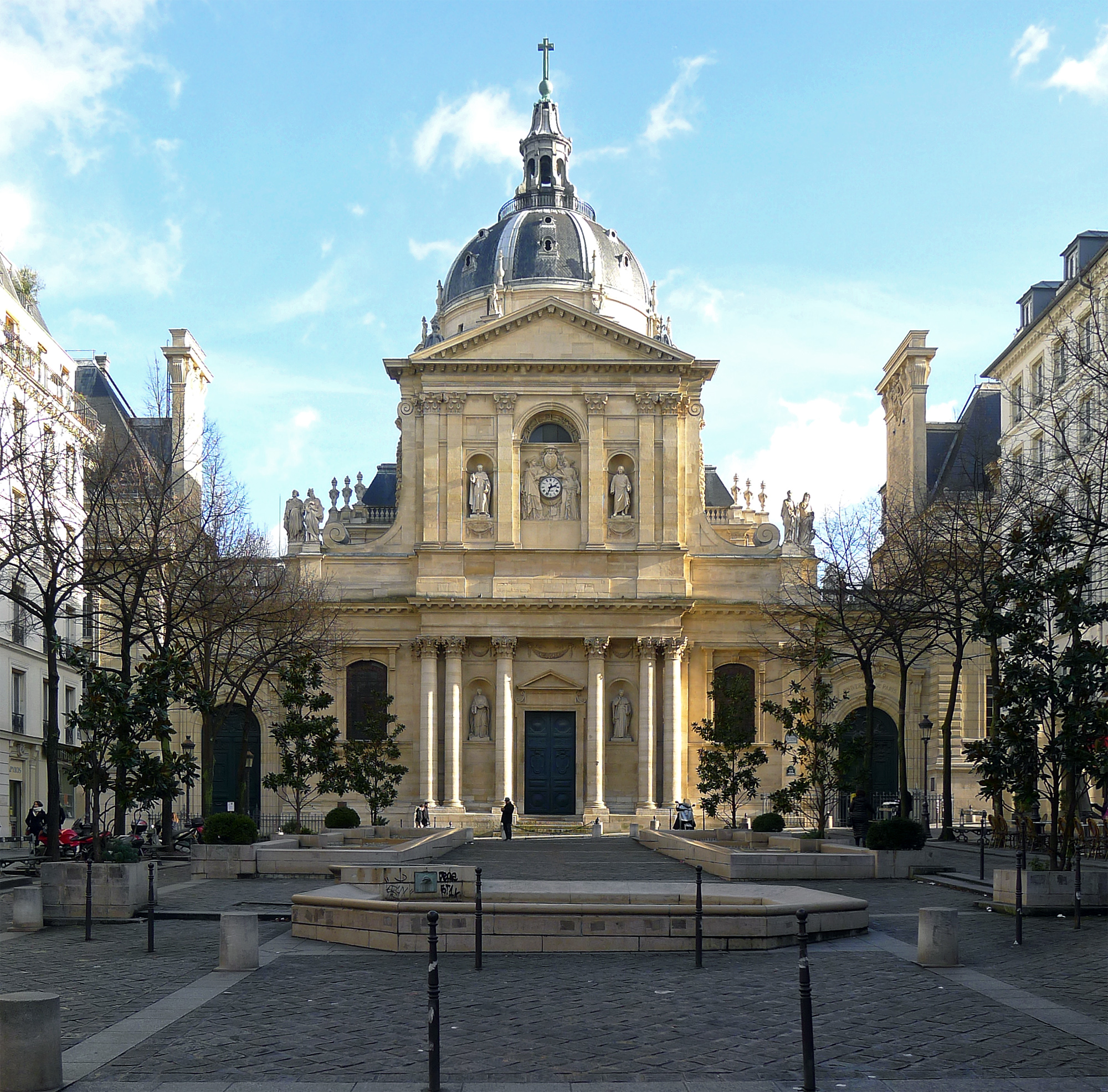
Sorbonne University
Sorbonne University (french: Sorbonne Université; la Sorbonne: 'the Sorbonne') is a public research university located in Paris, France. The institution's legacy reaches back to 1257 when Sorbonne College was established by Robert de Sorbon as one of the first universities in Europe. Sorbonne University is considered one of the most prestigious universities in Europe and the world. It has a world-class reputation in academia and industry; as of 2021, its alumni and professors have won 33 Nobel Prizes, six Fields Medals, and one Turing Award. In the 2021 edition of the '' Academic Ranking of World Universities'', Sorbonne University ranked 35th in the world, placing it as the 4th best university in continental Europe, 3rd in Mathematics and Oceanography. In the 2023 edition of ''QS World University Rankings'', the Sorbonne ranked 60th in the world, placing it 8th in continental Europe, 14th in Natural Sciences and Mathematics, and 7th in Classics and Ancient History. K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Paris
, image_name = Coat of arms of the University of Paris.svg , image_size = 150px , caption = Coat of Arms , latin_name = Universitas magistrorum et scholarium Parisiensis , motto = ''Hic et ubique terrarum'' (Latin) , mottoeng = Here and anywhere on Earth , established = Founded: c. 1150Suppressed: 1793Faculties reestablished: 1806University reestablished: 1896Divided: 1970 , type = Corporative then public university , city = Paris , country = France , campus = Urban The University of Paris (french: link=no, Université de Paris), metonymically known as the Sorbonne (), was the leading university in Paris, France, active from 1150 to 1970, with the exception between 1793 and 1806 under the French Revolution. Emerging around 1150 as a corporation associated with the cathedral school of Notre Dame de Paris, it was considered the second-oldest university in Europe. Haskins, C. H.: ''The Rise of Universities'', Henry Holt and Company, 1923, p. 292. Officially chartered i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilles Gaston Granger
Gilles-Gaston Granger (; ; 28 January 1920 – 24 August 2016) was a French philosopher. Work His works discuss the philosophy of logic, mathematics, human and social sciences, Aristotle, Jean Cavaillès, and Ludwig Wittgenstein. He produced the most authoritative French translation of Wittgenstein's ''Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus'' and published more than 150 scientific articles. In 1968 he co-founded with Jules Vuillemin the journal ''L'Âge de la Science''.Bibliography He was president of the scientific committee of Jules Vuillemin's Archives. Biography *Studied at |
Ludwig Josef Johann Wittgenstein
Ludwig Josef Johann Wittgenstein ( ; ; 26 April 1889 – 29 April 1951) was an Austrians, Austrian-British people, British philosopher who worked primarily in logic, the philosophy of mathematics, the philosophy of mind, and the philosophy of language. He is considered by some to be the greatest philosopher of the 20th century. From 1929 to 1947, Wittgenstein taught at the University of Cambridge. In spite of his position, during his entire life only one book of #Legacy, his philosophy was published, the 75-page ''Logisch-Philosophische Abhandlung'' (''Logical-Philosophical Treatise'', 1921), which appeared, together with an English translation, in 1922 under the Latin title ''Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus''. His only other published works were an article, "Some Remarks on Logical Form" (1929); a book review; and a children's dictionary. #Works, His voluminous manuscripts were edited and published posthumously. The first and best-known of this posthumous series is the 1953 b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sceaux (Hauts-de-Seine)
Sceaux () is a commune in the Hauts-de-Seine department in the southern suburbs of Paris, France. It is located from the centre of Paris. In 2019, Sceaux had a population of 20,004. A wealthy city Sceaux is famous for the Château de Sceaux, set in its large park (''Parc départemental de Sceaux''), designed by André Le Nôtre, measuring . The original ''château'' was transformed into a School of Agriculture during the Revolution and lost much of its luster. It was demolished at the beginning of the 19th century following its sale by the then French government. Sceaux castle was originally built by Jean-Baptiste Colbert, the minister of finance to Louis XIV and purchased by Louis' illegitimate son, the Duke of Maine in 1699. His duchesse held court in a glittering salon at Sceaux in the first decades of the eighteenth century. The present-day château, rebuilt between 1856 and 1862 in a Louis XIII style, is now the museum of Île-de-France open for visits. Housing costs are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycée Lakanal
Lycée Lakanal is a public secondary school in Sceaux, Hauts-de-Seine, France, in the Paris metropolitan area. It was named after Joseph Lakanal, a French politician, and an original member of the Institut de France. The school also offers a middle school and highly ranked " classes préparatoires" undergraduate training. Famous French scientists and writers have graduated from lycée Lakanal, such as Jean Giraudoux, Alain-Fournier and Frédéric Joliot-Curie. The school includes a science building, a large park, a track, and dormitories for the Pôle Espoir Rugby and the boarding students. Several teachers also live at the school along with boarding students. The main classrooms and the dormitories are in one building, and the school uses space heaters in every classroom except the science building's classrooms and the gymnasium. the school has about 2,550 students in all levels, from junior high school to preparatory classes. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haute-Saône
Haute-Saône (; Arpitan: ''Hiôta-Sona''; English: Upper Saône) is a department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region of northeastern France. Named after the river Saône, it had a population of 235,313 in 2019.Populations légales 2019: 70 Haute-Saône INSEE Its prefecture is ; its sole is Lure. History ...
|
Faverney
Faverney () is a commune in the Haute-Saône department in the region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in eastern France. See also *Communes of the Haute-Saône department The following is a list of the 539 communes in the French department of Haute-Saône. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):Communes of Haute-Saône {{HauteSaône-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scholastic Theology
Scholasticism was a medieval school of philosophy that employed a critical organic method of philosophical analysis predicated upon the Aristotelian 10 Categories. Christian scholasticism emerged within the monastic schools that translated scholastic Judeo—Islamic philosophies, and thereby "rediscovered" the collected works of Aristotle. Endeavoring to harmonize his metaphysics and its account of a prime mover with the Latin Catholic dogmatic trinitarian theology, these monastic schools became the basis of the earliest European medieval universities, and scholasticism dominated education in Europe from about 1100 to 1700. The rise of scholasticism was closely associated with these schools that flourished in Italy, France, Portugal, Spain and England. Scholasticism is a method of learning more than a philosophy or a theology, since it places a strong emphasis on dialectical reasoning to extend knowledge by inference and to resolve contradictions. Scholastic thought is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Besançon
Besançon (, , , ; archaic german: Bisanz; la, Vesontio) is the prefecture of the department of Doubs in the region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté. The city is located in Eastern France, close to the Jura Mountains and the border with Switzerland. Capital of the historic and cultural region of Franche-Comté, Besançon is home to the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté regional council headquarters, and is an important administrative centre in the region. It is also the seat of one of the fifteen French ecclesiastical provinces and one of the two divisions of the French Army. In 2019 the city had a population of 117,912, in a metropolitan area of 280,701, the second in the region in terms of population. Established in a meander of the river Doubs, the city was already important during the Gallo-Roman era under the name of ''Vesontio'', capital of the Sequani. Its geography and specific history turned it into a military stronghold, a garrison city, a political centre, and a religious c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |