|
Jacob Neusner
Jacob Neusner (July 28, 1932 – October 8, 2016) was an American academic scholar of Judaism. He was named as one of the most published authors in history, having written or edited more than 900 books. Life and career Neusner was born in Hartford, Connecticut, to Reform Jewish parents. He graduated from William H. Hall High School in West Hartford. He then attended Harvard University, where he met Harry Austryn Wolfson and first encountered Jewish religious texts. After graduating from Harvard in 1953, Neusner spent a year at the University of Oxford. Neusner then attended the Jewish Theological Seminary of America, where he was ordained as a Conservative Jewish rabbi. After spending a year at Hebrew University of Jerusalem, he returned to the Jewish Theological Seminary and studied the Talmud under Saul Lieberman, who would later write a famous, and highly negative, critique of Neusner's translation of the Jerusalem Talmud.Saul Lieberman,A Tragedy or a Comedy? ''Journal of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Wisconsin–Milwaukee
The University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee (UW–Milwaukee, UWM, or Milwaukee) is a public urban research university in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. It is the largest university in the Milwaukee metropolitan area and a member of the University of Wisconsin System. It is also one of the two doctoral degree-granting public universities and the second largest university in Wisconsin. The university consists of 14 schools and colleges, including the only graduate school of freshwater science in the U.S., the first CEPH accredited dedicated school of public health in Wisconsin, and the state's only school of architecture. As of the 2015–2016 school year, the University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee had an enrollment of 27,156, with 1,604 faculty members, offering 191 degree programs, including 94 bachelor's, 64 master's and 33 doctorate degrees. The university is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Highest research activity". In 2018, the university had a research expenditure of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
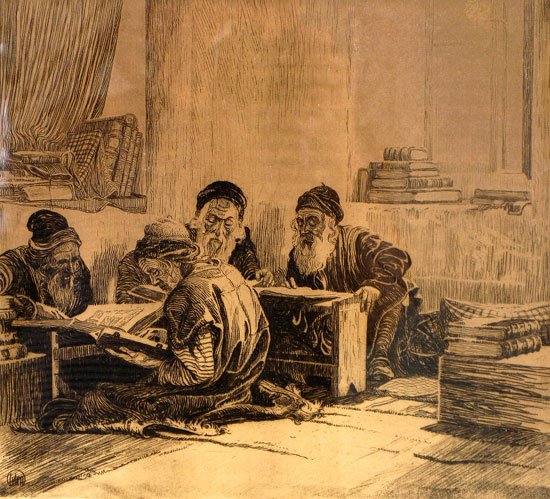
Rabbinic Texts
Rabbinic literature, in its broadest sense, is the entire spectrum of rabbinic writings throughout Jewish history. However, the term often refers specifically to literature from the Talmudic era, as opposed to medieval and modern rabbinic writing, and thus corresponds with the Hebrew term ''Sifrut Chazal'' ( he, ספרות חז״ל "Literature f oursages," where ''Hazal'' normally refers only to the sages of the Talmudic era). This more specific sense of "Rabbinic literature"—referring to the Talmudim, Midrash ( he, מדרש), and related writings, but hardly ever to later texts—is how the term is generally intended when used in contemporary academic writing. The terms ''meforshim'' and ''parshanim'' (commentaries/commentators) almost always refer to later, post-Talmudic writers of rabbinic glosses on Biblical and Talmudic texts. Mishnaic literature The Midr'she halakha, Mishnah, and Tosefta (compiled from materials pre-dating the year 200 CE) are the earliest e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Form Criticism
Form criticism as a method of biblical criticism classifies units of scripture by literary pattern and then attempts to trace each type to its period of oral transmission."form criticism." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2007. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 2 Dec. 2007read online/ref> "Form criticism is the endeavor to get behind the written sources of the Bible to the period of oral tradition, and to isolate the oral forms that went into the written sources. Insofar as this attempts to trace the history of the tradition, it is known as tradition criticism." Form criticism seeks to determine a unit's original form and the historical context of the literary tradition. Hermann Gunkel (1862-1932), Martin Noth, Gerhard von Rad, and other scholars originally developed form criticism for Old Testament studies; they used it to supplement the documentary hypothesis with reference to its oral foundations.Cross, F. L., ed. The Oxford dictionary of the Christian church. New York: Oxford Univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mishna
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Torah. It is also the first major work of rabbinic literature. The Mishnah was redacted by Judah ha-Nasi probably in Beit Shearim or Sepphoris at the beginning of the 3rd century CE in a time when, according to the Talmud, the persecution of the Jews and the passage of time raised the possibility that the details of the oral traditions of the Pharisees from the Second Temple period (516 BCE – 70 CE) would be forgotten. Most of the Mishnah is written in Mishnaic Hebrew, but some parts are in Aramaic. The Mishnah consists of six orders (', singular ' ), each containing 7–12 tractates (', singular ' ; lit. "web"), 63 in total, and further subdivided into chapters and paragraphs. The word ''Mishnah'' can also indicate a single paragraph of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabbinic Judaism
Rabbinic Judaism ( he, יהדות רבנית, Yahadut Rabanit), also called Rabbinism, Rabbinicism, or Judaism espoused by the Rabbanites, has been the mainstream form of Judaism since the 6th century CE, after the codification of the Babylonian Talmud. Rabbinic Judaism has its roots in Pharisaic Judaism and is based on the belief that Moses at Mount Sinai received both the Written Torah (''Torah she-be-Khetav'') and the Oral Torah (''Torah she-be-al Peh'') from God. The Oral Torah, transmitted orally, explains the Written Torah. At first, it was forbidden to write down the Oral Torah because the rabbis feared that it would become rigid and lose its flexibility, but after the destruction of the Second Temple they decided to write it down in the Talmud and other rabbinic texts. Rabbinic Judaism contrasts with the Sadducees, Karaite Judaism and Samaritanism, which do not recognize the Oral Torah as a divine authority nor the rabbinic procedures used to interpret Jewish scripture. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Endowment For The Arts
The National Endowment for the Arts (NEA) is an independent agency of the United States federal government that offers support and funding for projects exhibiting artistic excellence. It was created in 1965 as an independent agency of the federal government by an act of the U.S. Congress, signed by President Lyndon B. Johnson on September 29, 1965 (20 U.S.C. 951). It is a sub-agency of the National Foundation on the Arts and the Humanities, along with the National Endowment for the Humanities, the Federal Council on the Arts and the Humanities, and the Institute of Museum and Library Services. The NEA has its offices in Washington, D.C. It was awarded Tony Honors for Excellence in Theatre in 1995, as well as the Special Tony Award in 2016. In 1985, the NEA won an honorary Oscar from the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences for its work with the American Film Institute in the identification, acquisition, restoration and preservation of historic films. In 2016 and again in 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Endowment For The Humanities
The National Endowment for the Humanities (NEH) is an independent federal agency of the U.S. government, established by thNational Foundation on the Arts and the Humanities Act of 1965(), dedicated to supporting research, education, preservation, and public programs in the humanities. The NEH is housed at 400 7th St SW, Washington, D.C. From 1979 to 2014, NEH was at 1100 Pennsylvania Avenue, N.W., Washington, D.C. in the Nancy Hanks Center at the Old Post Office. History and purpose The NEH provides grants for high-quality humanities projects to cultural institutions such as museums, archives, libraries, colleges, universities, public television, and radio stations, and to individual scholars. According to its mission statement: "Because democracy demands wisdom, NEH serves and strengthens our republic by promoting excellence in the humanities and conveying the lessons of history to all Americans." The NEH was created in 1965 as a sub-agency of the National Foundation on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University
, mottoeng = Literal: From here, light and sacred draughts. Non literal: From this place, we gain enlightenment and precious knowledge. , established = , other_name = The Chancellor, Masters and Scholars of the University of Cambridge , type = Public research university , endowment = £7.121 billion (including colleges) , budget = £2.308 billion (excluding colleges) , chancellor = The Lord Sainsbury of Turville , vice_chancellor = Anthony Freeling , students = 24,450 (2020) , undergrad = 12,850 (2020) , postgrad = 11,600 (2020) , city = Cambridge , country = England , campus_type = , sporting_affiliations = The Sporting Blue , colours = Cambridge Blue , website = , logo = University of Cambridge logo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clare Hall, Cambridge
Clare Hall is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge, England. Founded in 1966 by Clare College, Clare Hall is a college for advanced study, admitting only postgraduate students alongside postdoctoral researchers and fellows. It was established to serve as an Institute of Advanced Studies and has slowly grown and developed into a full constituent college. Clare Hall is one of the smallest colleges with 200 graduate students, but around 125 Fellows, making it the highest Fellow to Student ratio at Cambridge University. Notwithstanding its small size, the college is also notable for its high number of Nobel Laureate affiliates. Clare Hall maintains many Cambridge traditions including formal hall and the tutorial system. History Clare Hall was founded by Clare College (which had previously been known as "Clare Hall" from 1338 to 1856) as a centre for advanced study, but was also intended to become a social group of men and women with their families that would inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruce Chilton
Bruce D. Chilton (born September 27, 1949 Roslyn, NY) is an American scholar of early Christianity and Judaism. He is Bernard Iddings Bell Professor of Religion at Bard College, former Rector of the Church of St John the Evangelist and formerly Lillian Claus Professor of New Testament at Yale University. He holds a PhD in New Testament from Cambridge University ( St. John's College). He has previously held academic positions at the Universities of Cambridge, Sheffield, and Münster. He wrote the first critical commentary on the Aramaic version of Isaiah (''The Isaiah Targum'', 1987), as well as academic studies that analyze Jesus in his Judaic context (''A Galilean Rabbi and His Bible'', 1984; ''The Temple of Jesus'', 1992; ''Pure Kingdom'', 1996), and explain the Bible critically (''Redeeming Time: The Wisdom of Ancient Jewish and Christian Festal Calendars'', 2002; ''The Cambridge Companion to the Bible'', 2007). He founded two academic periodicals, Journal for the Study of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
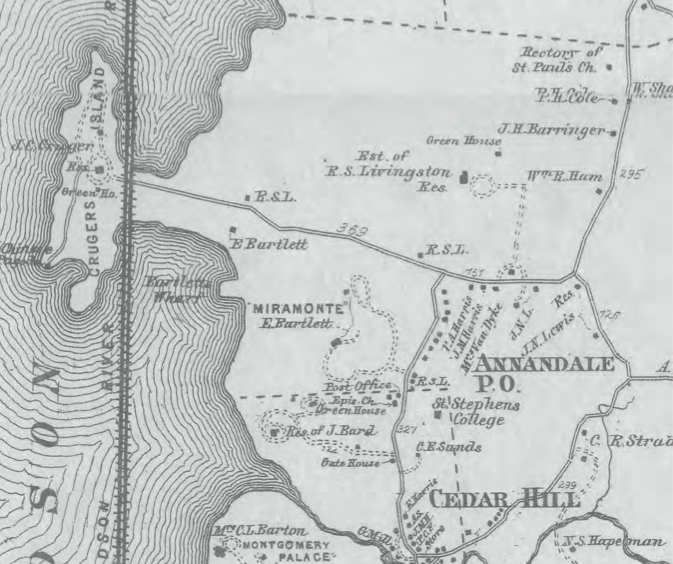
Bard College
Bard College is a private college, private Liberal arts colleges in the United States, liberal arts college in Annandale-on-Hudson, New York. The campus overlooks the Hudson River and Catskill Mountains, and is within the Hudson River Historic District—a National Historic Landmark. Founded in 1860, the institution consists of a liberal arts college and a Bard College Conservatory of Music, conservatory, as well as eight graduate programs offering over 20 graduate degrees in the arts and sciences. The college has a network of over 35 affiliated programs, institutes, and centers, spanning twelve city, cities, five U.S. states, states, seven country, countries, and four continents. History Origins and early years During much of the nineteenth century, the land now owned by Bard was mainly composed of several estate (land), country estates. These estates were called Blithewood, Bartlett, Sands, Cruger's Island, and Ward Manor/Almont. In 1853, John Bard (philanthropist), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |