|
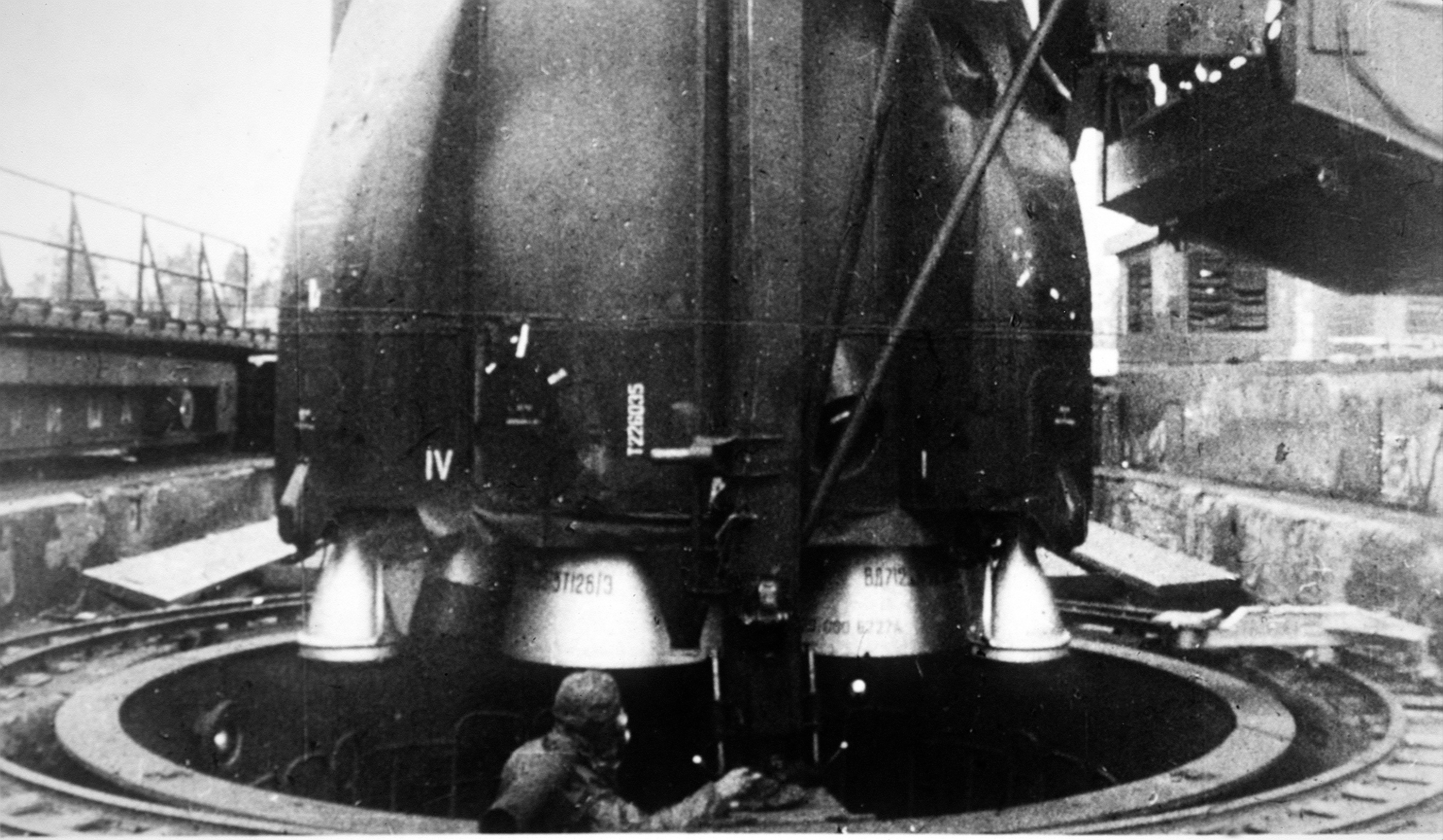
J-I Rocket
The J-I was a Solid-fuel rocket expendable launch vehicle developed by the National Space Development Agency of Japan and the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science. In an attempt to reduce development costs, it used the solid rocket booster from the H-II as the first stage, and the upper stages of the M-3SII. It flew only once on a suborbital flight taking place 11 February 1996 UTC from Tanegashima Space Center pad LA-N, in a partial configuration, to launch the demonstrator HYFLEX. The vehicle never flew in the final orbital capability configuration, which should have launched the OICETS satellite (OICETS was launched on a Russian R-36MUTTH Intercontinental ballistic missile-based Dnepr rocket instead). On the HYFLEX mission a load of 1,054 kg was launched 1,300 km downrange. Apogee was 110km; the HYFLEX payload achieved speed of approximately 3.8 km/s. See also * Epsilon (rocket) * Mu (rocket family) * M-V * Comparison of orbital launchers families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J-I Rocket
The J-I was a Solid-fuel rocket expendable launch vehicle developed by the National Space Development Agency of Japan and the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science. In an attempt to reduce development costs, it used the solid rocket booster from the H-II as the first stage, and the upper stages of the M-3SII. It flew only once on a suborbital flight taking place 11 February 1996 UTC from Tanegashima Space Center pad LA-N, in a partial configuration, to launch the demonstrator HYFLEX. The vehicle never flew in the final orbital capability configuration, which should have launched the OICETS satellite (OICETS was launched on a Russian R-36MUTTH Intercontinental ballistic missile-based Dnepr rocket instead). On the HYFLEX mission a load of 1,054 kg was launched 1,300 km downrange. Apogee was 110km; the HYFLEX payload achieved speed of approximately 3.8 km/s. See also * Epsilon (rocket) * Mu (rocket family) * M-V * Comparison of orbital launchers families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid-fuel Rocket
A solid-propellant rocket or solid rocket is a rocket with a rocket engine that uses solid propellants ( fuel/oxidizer). The earliest rockets were solid-fuel rockets powered by gunpowder; they were used in warfare by the Arabs, Chinese, Persians, Mongols, and Indians as early as the 13th century. All rockets used some form of solid or powdered propellant up until the 20th century, when liquid-propellant rockets offered more efficient and controllable alternatives. Solid rockets are still used today in military armaments worldwide, model rockets, solid rocket boosters and on larger applications for their simplicity and reliability. Since solid-fuel rockets can remain in storage for an extended period without much propellant degradation and because they almost always launch reliably, they have been frequently used in military applications such as missiles. The lower performance of solid propellants (as compared to liquids) does not favor their use as primary propulsion in mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Space Development Agency Of Japan
The , or NASDA, was a Japanese national space agency established on October 1, 1969 under the National Space Development Agency Law only for peaceful purposes. Based on the Space Development Program enacted by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), NASDA was responsible for developing satellites and launch vehicles as well as launching and tracking them. The first launch vehicles of NASDA (N-I (rocket), N-I, N-II (rocket), N-II, and H-I) were partially based on licensed technology from the United States, particularly the Delta (rocket family), Delta rocket family. The H-II was the first liquid fuel rocket to be fully developed in Japan. Hideo Shima, chief engineer of the original Shinkansen "bullet train" project, served as Chief of NASDA from 1969 to 1977. On October 1, 2003, NASDA merged with the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS) and the National Aerospace Laboratory of Japan (NAL) into one Independent Administrative Insti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Space And Astronautical Science
(ISAS) is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes which played a major role in Japan's space development. Since 2003, it is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). History The ISAS originated as part of the Institute of Industrial Science of the University of Tokyo, where Hideo Itokawa experimented with miniature solid-fuel rockets ( Pencil Rocket and Baby Rocket) in the 1950s. This experimentation eventually led to the development of the Κ (''Kappa'') sounding rocket, which was used for observations during the International Geophysical Year (IGY). By 1960, the Κ-8 rocket had reached an altitude of 200 km. In 1964, the rocket group and the ''Institute of Aeronautics'', along with scientific ballooning team, were merged to form within the University of Tokyo. The rocket evolved into the L (''Lambda'') series, and, in 1970, L-4S-5 was launched as Japan's firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Rocket Booster
A solid rocket booster (SRB) is a large solid propellant motor used to provide thrust in spacecraft launches from initial launch through the first ascent. Many launch vehicles, including the Atlas V, SLS and space shuttle, have used SRBs to give launch vehicles much of the thrust required to place the vehicle into orbit. The space shuttle used two space shuttle SRBs, which were the largest solid propellant motors ever built and the first designed for recovery and reuse. The propellant for each solid rocket motor on the space shuttle weighed approximately 500,000 kilograms.. Advantages Compared to liquid propellant rockets, the solid-propellant motors SRMs have been capable of providing large amounts of thrust with a relatively simple design. They provide greater thrust without significant refrigeration and insulation requirements, and produce large amounts of thrust for their size. Adding detachable SRBs to a vehicle also powered by liquid-propelled rockets known as staging re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mu (rocket Family)
The Mu, also known as M, was a series of Japanese solid-fueled carrier rockets, which were launched from Uchinoura between 1966 and 2006. Originally developed by Japan's Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, Mu rockets were later operated by Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency following ISAS becoming part of it. Early Japanese carrier rockets The first Mu rocket, the Mu-1 made a single, sub-orbital, test flight, on 31 October 1966. Subsequently, a series of rockets were produced, designated Mu-3 and Mu-4. In 1969 a suborbital test launch of the Mu-3D was conducted. The first orbital launch attempt for the Mu family, using a Mu-4S, was conducted on 25 September 1970, however the fourth stage did not ignite, and the rocket failed to reach orbit. On 16 February 1971, Tansei 1 was launched by another Mu-4S rocket. Two further Mu-4S launches took place during 1971 and 1972. The Mu-4S was replaced by the Mu-3C, was launched four times between 1974 and 1979, with three success ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into orbit, and is involved in many more advanced missions such as asteroid exploration and possible human exploration of the Moon. Its motto is ''One JAXA'' and its corporate slogan is ''Explore to Realize'' (formerly ''Reaching for the skies, exploring space''). History On 1 October 2003, three organizations were merged to form the new JAXA: Japan's Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), the National Aerospace Laboratory of Japan (NAL), and National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). JAXA was formed as an Independent Administrative Institution administered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC). Before the merger, ISA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanegashima Space Center
The (TNSC) is the largest rocket-launch complex in Japan with a total area of about 9.7 square kilometers. It is located on the southeast coast of Tanegashima, an island approximately south of Kyushu. It was established in 1969 when the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) was formed, and is now run by JAXA. The activities that take place at TNSC include assembly, testing, launching, and tracking satellites, as well as rocket engine firing tests. Facilities On-site main facilities include: * Yoshinobu Launch Complex is a launch site for launch vehicles like the H-IIA * Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) * Second Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building * Takesaki Range Control Center Those facilities are used for performing operations from assembling launch vehicles, maintenance, inspections, final checks of satellites, loading satellites onto launch vehicles, rocket launches, and tracking launch vehicles after liftoff. The TNSC plays a pivotal role in satellit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HYFLEX
HYFLEX (Hypersonic Flight Experiment) was a National Space Development Agency of Japan reentry demonstrator prototype which was launched in 1996 on the only flight of the J-I launcher. It was a successor of OREX and was a precursor for the Japanese space shuttle HOPE-X. HYFLEX tested the carbon-carbon heat shielding tiles that were intended to be used on HOPE, as well as having the same body shaping in order to gather data on hypersonic lifting. HYFLEX flew in space at altitude and succeeded in re-entry, but sank in the Pacific after splashdown before it could be recovered. Overview HYFLEX was an uncrewed lifting body space plane for gaining technological prowess in the design, production, and flight of hypersonic crafts, as well as technology validation of atmospheric reentry. The experimental vehicle was covered in carbon–carbon, ceramic tiles, and flexible thermal insulation, which were materials that was to be used for HOPE. Launched on 11 February 1996 (UTC) from Tane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OICETS
The Optical Inter-orbit Communications Engineering Test Satellite (OICETS), also called ''Kirari'', was an experimental satellite launched by JAXA to demonstrate interorbital communication between satellites through optical (laser) means. OICETS was originally slated for a launch on the second J-I launcher. Due to problems with that launcher, the launch had to be put on hold. Using the H-IIA was out of question: it would have been overkill to use the H-IIA to send a satellite into low Earth orbit, and there was no budget for another H-IIA launch. Finally, in order to be able to perform the tests during the lifetime of the European Artemis satellite (since 2014, sold to Avanti Communications to exploit its Ka, S, and L-band payloads), OICETS was successfully launched on an SS-18-based Dnepr rocket. The satellite was decommissioned and its mission terminated on 24 September 2009 at 05:48 UTC. Achievements *On 9 December 2005, JAXA succeeded in establishing optical links betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-36 (missile)
The R-36 (russian: Р-36) is a family of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) and space launch vehicles (Tsyklon) designed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. The original R-36 was deployed under the GRAU index 8K67 and was given the NATO reporting name SS-9 Scarp. It was able to carry three warheads and was the first Soviet MRV (multiple re-entry vehicle) missile. The later version, the R-36M was produced under the GRAU designations 15A14 and 15A18 and was given the NATO reporting name SS-18 Satan. This missile was viewed by certain United States analysts as giving the Soviet Union first strike advantage over the U.S., particularly because of its rapid silo-reload ability, very heavy throw weight and extremely large number of re-entry vehicles. Some versions of the R-36M were deployed with 10 warheads and up to 40 penetration aids and the missile's high throw-weight made it theoretically capable of carrying more warheads or penetration aids. Contemporary U.S. miss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_pre-launch.jpg)