|
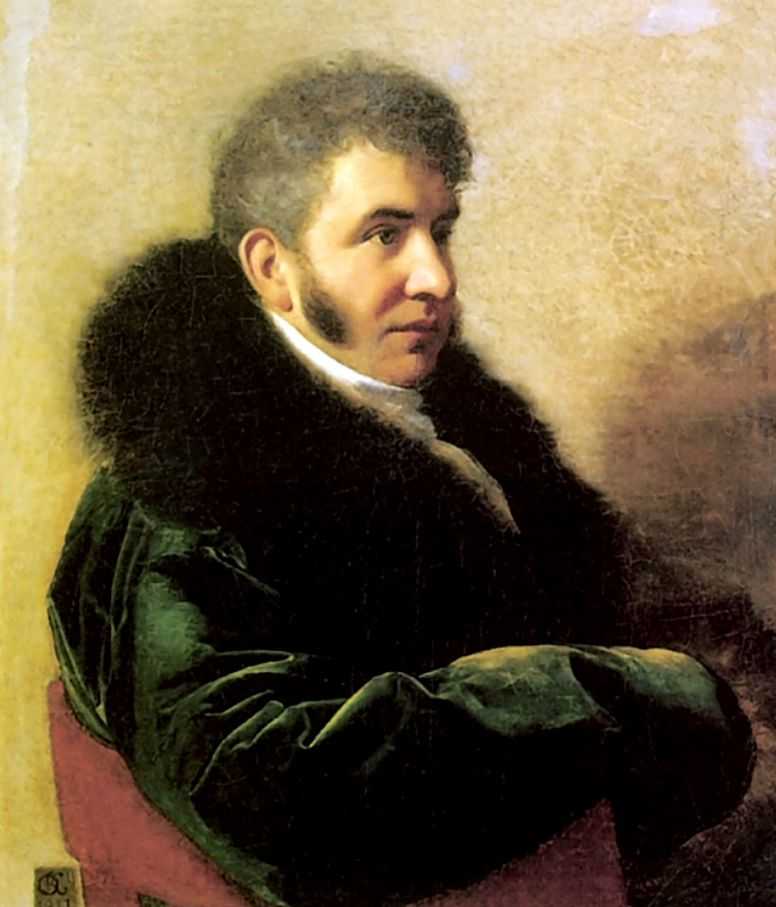
Ivan Alexeyevich Gagarin
Ivan Alexeyevich Gagarin (russian: Иван Алексеевич Гагарин; 16 September 1771, Moscow12 October 1832, Moscow) was a Russian Imperial Senator and Active Privy Councillor, from the princely Gagarin family. Biography He was born to the Privy Councilor, Alexei Ivanovich Gagarin, and his wife, Irina Grigorievna, daughter of the military officer and statesman, . At the age of only two, he was enrolled in the Preobrazhensky Regiment then, at the age of five, in the Izmaylovsky Regiment. When he began his active service, in 1790, he became a Praporshchik (Ensign), and was sent to fight in the Russo-Turkish War. For his participation in the Siege of Izmail, he was promoted to Podporuchik (Second-Lieutenant), and was awarded the Order of St. George, 4th degree. Further promotions followed and, in 1795, he was named a Chamberlain. In 1799, he was appointed an Equerry at the court of Grand Duchess Elena Pavlovna and later held the same position under Grand Duchess Cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Gagarin
Prince Ivan Sergeyevich Gagarin SJ (Иван Сергеевич Гагарин; born in Moscow, 1 August 1814; died in Paris, 19 July 1882) was a Russian Jesuit, known also as ''Jean-Xavier'' after his conversion from Orthodoxy to Roman Catholicism. He was of the Gagarin family, which traces its origin to the medieval rulers of Starodub-on-the-Klyazma. He was the founding editor of '' Études''. Life He was the son of the Russian state-councillor, Prince Sergey Gagarin, and Varvara Pushkina. He entered the service of the state at an early age, and was first named attaché to his uncle, Prince Gregory Gagarin, at Munich, on whose death, in 1837, he acted as secretary to the legation at Vienna. He was afterwards transferred to the Russian embassy at Paris, where his services were requisitioned in a similar capacity. He frequented the salon of his near relation, Madame Sophie Swetchine, and was on terms of familiar intercourse with Father de Ravignan, Lacordaire's successor in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchess Elena Pavlovna Of Russia
Elena Pavlovna (; 24 December 1784 S 13 December– 24 September 1803) was born a grand duchess of Russia as the daughter of Paul I, Emperor of all the Russias and later became the Hereditary Grand Duchess of Mecklenburg-Schwerin as the wife of Frederick Louis of Meclenburg-Schwerin (1778–1819). Early life Grand Duchess Elena Pavlovna Romanova of Russia was born in Saint Petersburg in the Russian Empire as the fourth child and second daughter of Tsesarevich Paul Petrovich of Russia (1754–1801) and his second wife, Tsesarevna Maria Feodorovna, born Duchess Sophie Dorothea of Württemberg (1759–1828). Out of her nine siblings, Elena was closest to her older sister Alexandra Pavlovna (1783–1801). She was educated privately at home, for the first years, under the supervision of her paternal grandmother, Catherine the Great (1729–1796). Her education was focused mainly on fine arts, literature and music. Marriage and life in Schwerin Marriage In 1798, negotiati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Biographical Dictionary
The ''Russian Biographical Dictionary'' (RBD, russian: Русский биографический словарь) is a Russian-language biographical dictionary published by the Russian Historian Society edited by a collective with Alexander Polovtsov as the editor-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The highest-ranking editor of a publication may also be titled editor, managing .... The dictionary was published in 25 volumes from 1896 to 1918 and considered one of the most comprehensive Russian biographical sources for the 19th and early 20th century period. External links *Online version {{Authority control Russian biographical dictionaries 1896 non-fiction books Reference works in the public domain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekaterina Semenova
Ekaterina Semenova (Russian: Екатерина Семёновна Семёнова; 18 November 1786–13 March 1849) was an actress in the Russian Empire. Life Semenova became a student in the Saint Petersburg Theatre School in 1790 where she was instructed by Ivan Dmitrevsky and debuted at the stage in 1797. She eventually became the leading interpreter of plays of William Shakespeare, Jean Racine, Friedrich Schiller and Vladislav Ozerov. She was coached by director Prince Alexander Shakhovskoy and the poet Nikolay Gnedich. Semenova was admired for her beauty, deep voice and passionate way of acting. She was mentioned in the poems of Alexander Pushkin, but also talked about because of her rivalry with Marguerite Georges, who was very popular in the Russian Empire at the time. She retired in 1820, but returned in 1822 and made a great success with ''Phèdre'' in 1823. In 1828, Semenova married Prince Ivan Alexeyevich Gagarin and afterwards only performed in private theatres. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Gagarin
Prince Alexander Ivanovich Gagarin (russian: Александр Иванович Гагарин) (1801 – 27 October 1857) was a Russian general and nobleman of Rurikid ancestry who was involved in the Caucasian and Crimean wars. In 1857, he served as a governor-general of Kutaisi and was killed by Constantine Dadeshkeliani, the deposed Prince of Svanetia, during a quarrel at Kutaisi. References His biography at Hronos.Ru 1801 births 1857 deaths Imperial Russian Army generals Alexander Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history. Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ... Russian military personnel of the Caucasian War Russian military personnel of the Crimean War {{Russia-mil-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
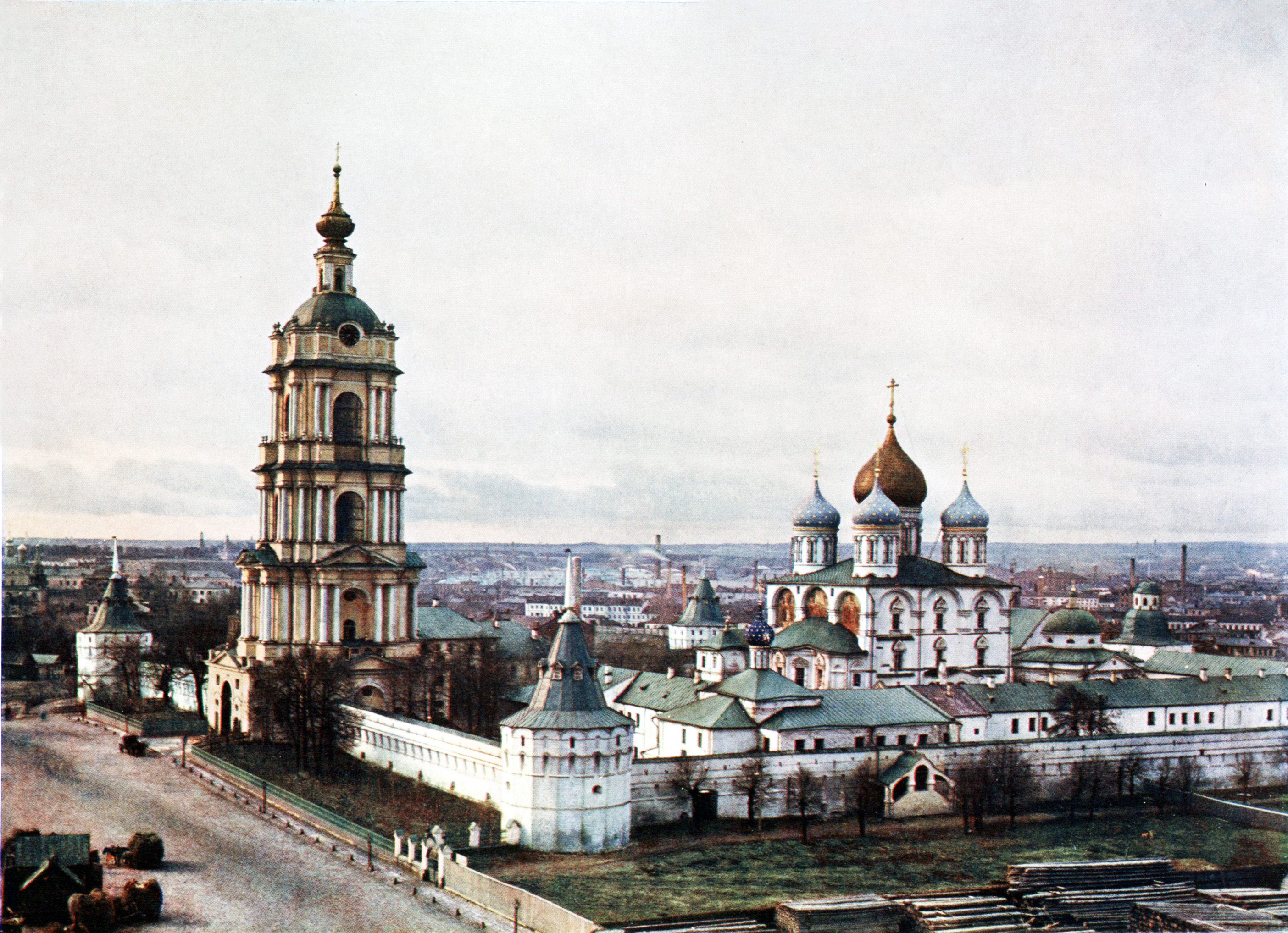
Novospassky Monastery
Novospassky Monastery (''New Monastery of the Savior'', russian: Новоспасский монастырь) is one of the fortified monasteries surrounding Moscow from the south-east. Like all medieval Russian monasteries, it was built by the Russian Orthodox Church. The abbey traces its history back to Moscow's first monastery established in the early 14th century at the location where the Danilov Monastery now stands. The Church of the Savior in the Wood (Собор Спаса на Бору) of the Kremlin, the oldest church of Moscow, was its original katholikon. Upon its removal to the left bank of the Moskva River in 1491, the abbey was renamed ''Abbey of the New Savior'', to distinguish it from the older one in the Kremlin. The monastery was patronized by Andrei Kobyla's descendants, including the Sheremetev and Romanov boyars, and served as their burial vault. Among the last Romanovs buried in the monastery were Xenia Shestova (the mother of the first Romanov Tsar), Pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decembrists
The Decembrist Revolt ( ru , Восстание декабристов, translit = Vosstaniye dekabristov , translation = Uprising of the Decembrists) took place in Russia on , during the interregnum following the sudden death of Emperor Alexander I. Alexander's heir apparent, Konstantin, had privately declined the succession, unknown to the court, and his younger brother Nicholas decided to take power as Emperor Nicholas I, pending formal confirmation. While some of the army had sworn loyalty to Nicholas, a force of about 3,000 troops tried to mount a military coup in favour of Konstantin. The rebels, although weakened by dissension between their leaders, confronted the loyalists outside the Senate building in the presence of a large crowd. In the confusion, the Emperor's envoy, Mikhail Miloradovich, was assassinated. Eventually, the loyalists opened fire with heavy artillery, which scattered the rebels. Many were sentenced to hanging, prison, or exile to Siberia. The consp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Saint Vladimir
The Imperial Order of Saint Prince Vladimir (russian: орден Святого Владимира) was an Imperial Russian order established on by Empress Catherine II in memory of the deeds of Saint Vladimir, the Grand Prince and the Baptizer of the Kievan Rus'. Grades The order had four degrees and was awarded for continuous civil and military service. People who had been awarded with the St. Vladimir Order for military merits bore it with a special fold on the ribbon – "with a bow". There was a certain hierarchy of Russian Orders. According to this, the First Class Order of Saint Vladimir was the second one—the first was the Saint George Order—by its significance. According to Russian laws on nobility, people who were awarded the Order of Saint Vladimir had the rights of hereditary nobility until the Emperor's decree of 1900 was issued. After this, only three first classes of the order gave such a right, the last one granting only personal nobility. Today, G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Society For The Encouragement Of The Arts
The Imperial Society for the Encouragement of the Arts (Russian: Императорское общество поощрения художеств (ОПХ)) was an organization devoted to promoting the arts that existed in Saint Petersburg from 1820 to 1929. It was the oldest society of its kind in Russia. Until 1882 it was called the "Society for the Encouragement of Artists". After 1917, it became the "All-Russian Society for the Encouragement of the Arts". History The Society was founded by a group of influential patrons (including Ivan Alexeyevich Gagarin, Pyotr Andreyevich Kikin and Alexander Dmitriev-Mamonov) with the aim of assisting development in the fine arts, the diffusion of knowledge related to the arts, and the education of painters and sculptors.History of the Society @ the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Ivanovich Dmitriev-Mamonov
Alexander Ivanovich Dmitriev-Mamonov (Russian: Александр Иванович Дмитриев-Мамонов; 24 December 1787 in Saint Petersburg – 9 December 1836 in Moscow) was the commander of a Belarusian Hussar regiment and a battle painter. Biography He was born into a noble family and was the son of Major-General Ivan Dmitriev-Mamonov (1754-1812). His mother, Mariya (1768-1794), died when he was only seven and his father remarried into the Tolstoy family. @ Geni.com. Most sources say that his father's second wife, Yelena (1772-1855), was his mother. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
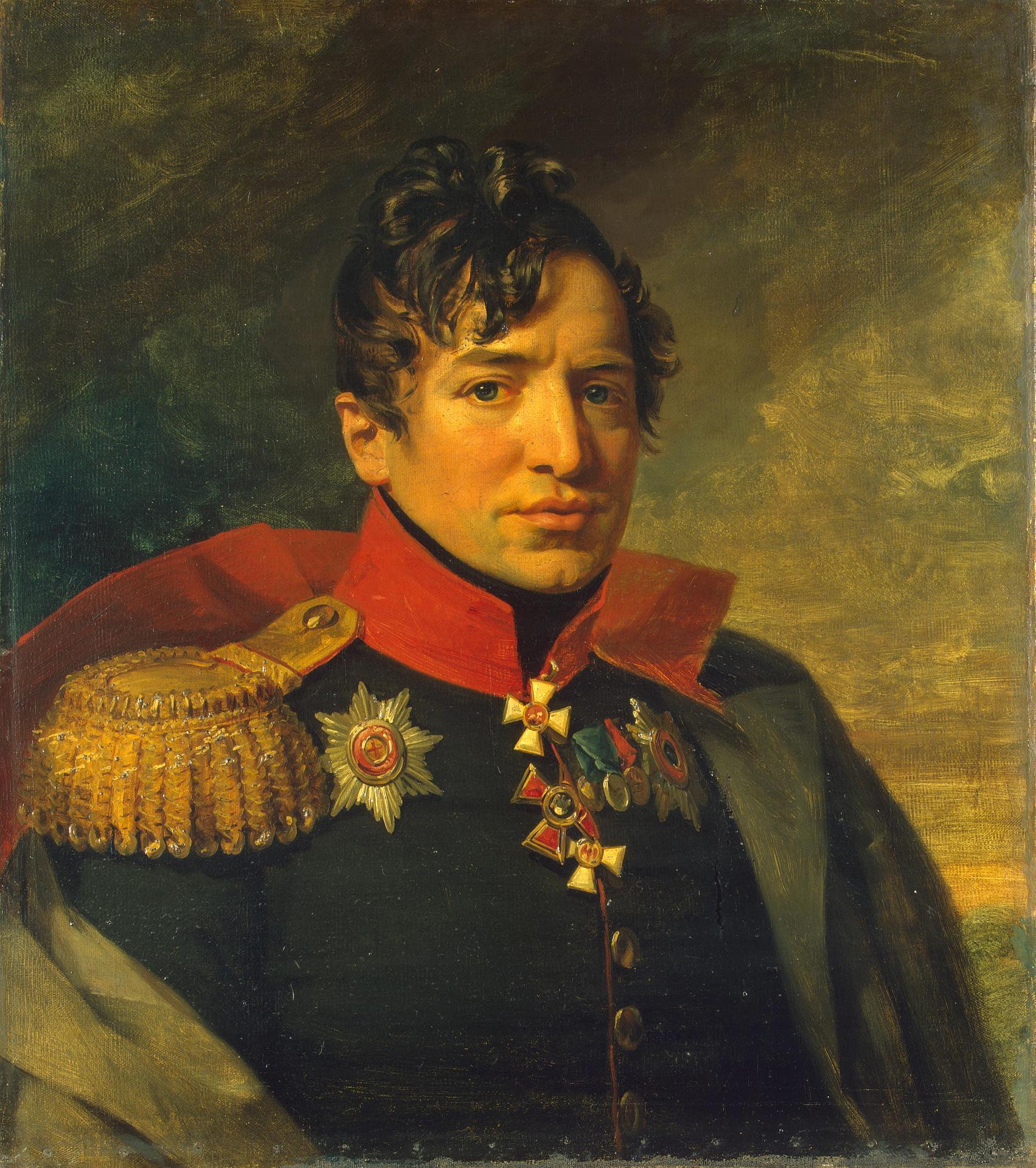
Pyotr Andreyevich Kikin
Pyotr Andreyevich Kikin (Russian: Пётр Андре́евич Ки́кин; 27 December 1775, Alatyr – 18 May 1834, Saint Petersburg?) was a Russian general and a Secretary of State under Tsar Alexander I. Biography He was one of twelve children born to Major Andrei Kikin (1747-1790) and his wife Maria Yermolova (1754-1819). His baptismal name was Bartholomei, but he never used it. As soon as he was old enough to take some responsibility, he was enrolled in the Guards and was a sergeant by the age of ten. He later studied in a boarding school at Moscow University and began his regular military career as an ensign in the Semyonovsky Regiment. From 1806 to 1812, he fought in the Russo-Turkish War, serving as an adjutant under General Michelson. He was promoted to colonel and almost immediately became involved in the French invasion of Russia, serving in the First Western Army. He was wounded in the eye at the Battle of Valutino and was injured in a counter-attack at the Bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Saint Alexander Nevsky
The Imperial Order of Saint Alexander Nevsky was an order of chivalry of the Russian Empire first awarded on by Empress Catherine I of Russia. History The introduction of the Imperial Order of Saint Alexander Nevsky was envisioned by Emperor Peter I of Russia (r. 1682–1721) for rewarding military bravery in battle. However, he died before he could create the order. It was established by Empress Catherine I of Russia, in memory of the deeds of Saint Alexander Nevsky, patron Saint of the Russian capital of Saint Petersburg, for defending Russia against foreign invaders. The order was originally awarded to distinguished Russian citizens who had served their country with honor, mostly through political or military service. It was first awarded on the occasion of the wedding of Grand Duchess Anna Petrovna of Russia and Charles Frederick, Duke of Holstein-Gottorp in 1725. A dozen guests received the reward, and the order quickly fell far behind the Order of Saint Andrew and the O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |