|
Istanbul Zoology Museum
Istanbul Zoology Museum, more precisely Zoology Museum of Istanbul University ( tr, İstanbul Üniversitesi Zooloji Müzesi) is a natural history museum, located in Istanbul University's Vezneciler Campus at Fatih, Istanbul featuring animal collections. It was founded in 1933 and rearranged in 1989. The museum is owned and maintained by the Department of Biology at Faculty of Science. History The museum was established by the Swiss scientist, Prof. Dr. André Naville, who was appointed head of the Biology Department at Istanbul University right after the reformation of the universities in 1933. Zoological objects donated from Germany were placed in a small hall situated in the Zoology Department of the university. After the sudden death of Naville in 1937, German hydrologist and zoologist Curt Kosswig took over the department. During his 15-year-long scientific research on the fauna of Anatolia, he collected examples of mammals, birds, reptiles, frogs, fish and various invertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Istanbul University
, image = Istanbul_University_logo.svg , image_size = 200px , latin_name = Universitas Istanbulensis , motto = tr, Tarihten Geleceğe Bilim Köprüsü , mottoeng = Science Bridge from Past to the Future , established = 1453 1846 1933 , type = Public university Research university , rector = Prof. Dr. Mahmut Ak , students = 69,411 , undergrad = 51,714 , postgrad = 16,669 , academic_staff = 4,101 , city = Istanbul , country = Turkey , campus = Beyazıt CampusVezneciler CampusAvcılar CampusÇapa CampusKadıköy Campus , coor = , colors = Green Yellow , affiliations = Coimbra Group EUA UNIMED , website = , free_label = Founder , free = Mehmed II Istanbul University ( tr, İstanbul Üniversitesi) is a prominent public research university located in Istanbul, Turkey. Founded by Mehmed II on May 30, 1453, a day after the conquest of Constantinople by the Turks, it was reformed in 1846 as the first Ottoman higher education institution based on Europea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with Saur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dodos, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Māori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
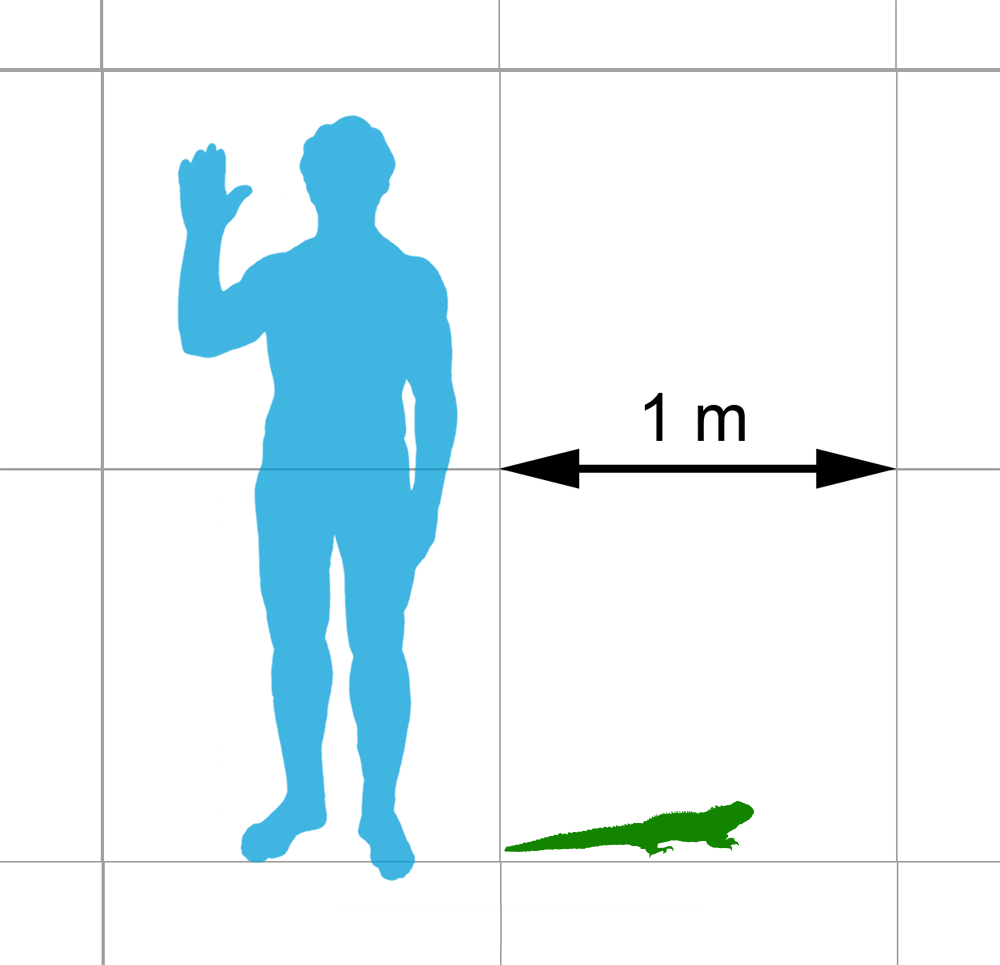
Sphenodon Punctatus
Tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') are reptiles endemic to New Zealand. Despite their close resemblance to lizards, they are part of a distinct lineage, the order Rhynchocephalia. The name ''tuatara'' is derived from the Māori language and means "peaks on the back". The single extant species of tuatara is the only surviving member of its order. Rhynchocephalians originated during the Triassic (~250 million years ago), reached worldwide distribution and peak diversity during the Jurassic and, with the exception of tuatara, were extinct by 60 million years ago. Their closest living relatives are squamates (lizards and snakes). For this reason, tuatara are of interest in the study of the evolution of lizards and snakes, and for the reconstruction of the appearance and habits of the earliest diapsids, a group of amniote tetrapods that also includes dinosaurs (including birds) and crocodilians. Tuatara are greenish brown and grey, and measure up to from head to tail-tip and wei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatteria
Tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') are reptiles Endemism, endemic to New Zealand. Despite their close resemblance to lizards, they are part of a distinct lineage, the order Rhynchocephalia. The name ''tuatara'' is derived from the Māori language and means "peaks on the back". The single extant species of tuatara is the only surviving member of its order. Rhynchocephalians originated during the Triassic (~250 million years ago), reached worldwide distribution and peak diversity during the Jurassic and, with the exception of tuatara, were extinct by Paleogene, 60 million years ago. Their closest living relatives are Squamata, squamates (lizards and snakes). For this reason, tuatara are of interest in the study of the evolution of lizards and snakes, and for the reconstruction of the appearance and habits of the earliest diapsids, a group of amniote tetrapods that also includes dinosaurs (including birds) and crocodilians. Tuatara are greenish brown and grey, and measure up to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yıldız Palace
Yıldız Palace ( tr, Yıldız Sarayı, ) is a vast complex of former imperial Ottoman pavilions and villas in Istanbul, Turkey, built in the 19th and early 20th centuries. It was used as a residence by the sultan and his court in the late 19th century. Origin Yıldız Palace, meaning "Star Palace", was built in 1880 and was used by the Ottoman Sultan Abdülhamid II. The area of the palace was originally made of natural woodlands and became an imperial estate during the reign of Sultan Ahmed I (1603–1617). Various sultans after Ahmed I enjoyed vacationing on these lands and Sultans Abdülmecid I and Abdülaziz built mansions here. The Yildiz Palace was a complex over a large area of hills and valleys. This was an example of traditional Ottoman architecture consisting of a complex of different buildings across a piece of land. The first pavilion was built by Sultan Selim III from 1798 to 1808, for his mother, Mihrişah Sultan. In the 1870s, the surrounding area of the pala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madrassah
Madrasa (, also , ; Arabic: مدرسة , pl. , ) is the Arabic word for any type of educational institution, secular or religious (of any religion), whether for elementary instruction or higher learning. The word is variously transliterated ''Madrasah arifah'', ''medresa'', ''madrassa'', ''madraza'', ''medrese'', etc. In countries outside the Arab world, the word usually refers to a specific type of religious school or college for the study of the religion of Islam, though this may not be the only subject studied. In an architectural and historical context, the term generally refers to a particular kind of institution in the historic Muslim world which primarily taught Islamic law and jurisprudence (''fiqh''), as well as other subjects on occasion. The origin of this type of institution is widely credited to Nizam al-Mulk, a vizier under the Seljuks in the 11th century, who was responsible for building the first network of official madrasas in Iran, Mesopotamia, and Khorasan. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuyucu Murad Pasha
Kuyucu Murad Pasha (Ottoman Turkish for "Murad Pasha the Well-digger", i.e. "Gravedigger"; sh, Murat-paša Kujudžić; 1535 – 1611) was an Ottoman statesman who served as Grand Vizier of the Ottoman Empire during the reign of Ahmed I between December 9, 1606, and August 5, 1611. Early life He was born in Bosnia.Safvet Bašagić: Znameniti Hrvati Bošnjaci i Hercegovci u turskoj carevini He is thought to have been a Slav or Albanian either born as a Muslim or converted later on during Devshirme conscription. Career He was '' beylerbey'' (governor-general) of Karaman in 1585 and Cyprus before being appointed to Damascus in 1593, as well as Aleppo. Upon arriving at the port of Sidon to take up his Damascus office he was received by the Druze chieftain of the Chouf, Fakhr al-Din, who furnished him with numerous gifts. He reciprocated by appointing Fakhr al-Din ''sanjak-bey'' (district governor) of Sidon-Beirut. Murad Pasha and Fakhr al-Din eliminated the latter's rival ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate subphylum Vertebrata. Familiar examples of invertebrates include arthropods, mollusks, annelids, echinoderms and cnidarians. The majority of animal species are invertebrates; one estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxa have a greater number and variety of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata. Invertebrates vary widely in size, from 50 μm (0.002 in) rotifers to the 9–10 m (30–33 ft) colossal squid. Some so-called invertebrates, such as the Tunicata and Cephalochordata, are more closely related to vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the invertebrates paraphyletic, so the term has little meaning in taxonomy. Etymology The word "invertebrate" comes from the Latin word ''vertebra'', whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) became formidable marine predators rather than just the prey of arthropods. Mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)