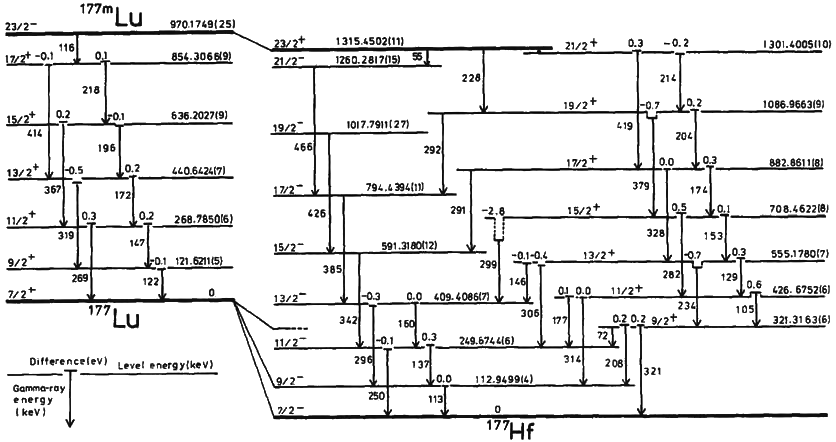
|
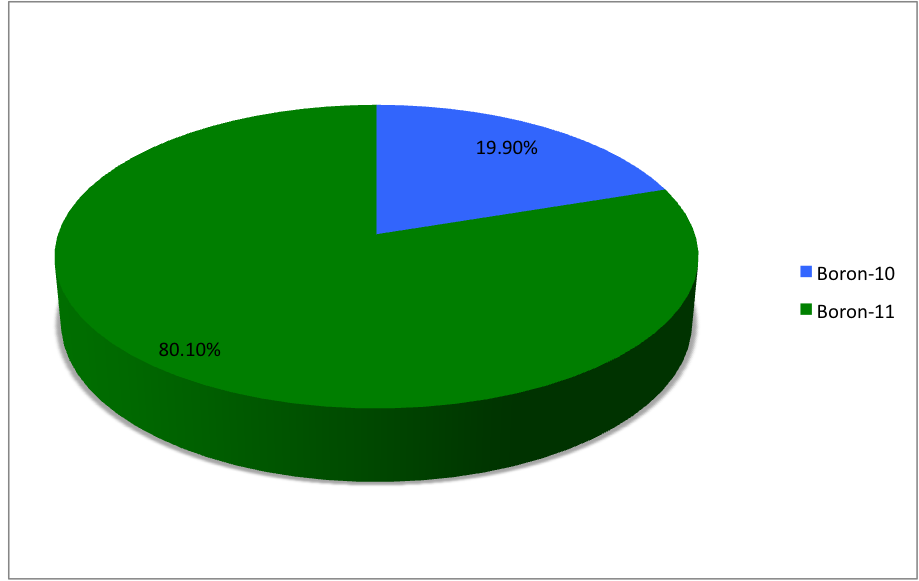
Isotopes Of Boron
Boron (5B) naturally occurs as isotopes and , the latter of which makes up about 80% of natural boron. There are 13 radioisotopes that have been discovered, with mass numbers from 7 to 21, all with short half-lives, the longest being that of , with a half-life of only and with a half-life of . All other isotopes have half-lives shorter than . Those isotopes with mass below 10 decay into helium (via short-lived isotopes of beryllium for and ) while those with mass above 11 mostly become carbon. List of isotopes , - , ?This isotope has not yet been observed; given data is inferred or estimated from periodic trends. , style="text-align:center" , 5 , style="text-align:center" , 1 , , p-unstable , 2p? , ? , 2−# , , , - , , style="text-align:center" , 5 , style="text-align:center" , 2 , , [] , p , Subsequently decays by double proton emission to for a net reaction of → + 3 , (3/2−) , , , - , Has 1 halo nucleus, halo proton , style="text ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the ''boron group'' it has three valence electrons for forming covalent bonds, resulting in many compounds such as boric acid, the mineral borax, sodium borate, and the ultra-hard crystals of boron carbide and boron nitride. Boron is synthesized entirely by cosmic ray spallation and supernovae and not by stellar nucleosynthesis, so it is a low-abundance element in the Solar System and in the Crust (geology), Earth's crust. It constitutes about 0.001 percent by weight of Earth's crust. It is concentrated on Earth by the water-solubility of its more common naturally occurring compounds, the borate minerals. These are mined industrially as evaporites, such as borax and kernite. The largest known deposits are in Turkey, the largest producer of boron minerals. Elemental b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron) is emitted from an atomic nucleus, transforming the original nuclide to an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron transforms it into a proton by the emission of an electron accompanied by an antineutrino; or, conversely a proton is converted into a neutron by the emission of a positron with a neutrino in so-called ''positron emission''. Neither the beta particle nor its associated (anti-)neutrino exist within the nucleus prior to beta decay, but are created in the decay process. By this process, unstable atoms obtain a more stable ratio of protons to neutrons. The probability of a nuclide decaying due to beta and other forms of decay is determined by its nuclear binding energy. The binding energies of all existing nuclides form what is called the nuclear band or valley of stability. For either electron or positron em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Capture Therapy Of Cancer
Neutron capture therapy (NCT) is a type of radiotherapy for treating locally invasive malignant tumors such as primary brain tumors, recurrent cancers of the head and neck region, and cutaneous and extracutaneous melanomas. It is a two-step process: ''first'', the patient is injected with a tumor-localizing drug containing the stable isotope boron-10 (B), which has a high propensity to capture low energy "thermal" neutrons. The neutron cross section of B (3,837 barns) is 1,000 times more than that of other elements, such as nitrogen, hydrogen, or oxygen, that occur in tissue. In the ''second'' step, the patient is radiated with epithermal neutrons, the sources of which in the past have been nuclear reactors and now are accelerators that produce higher energy epithermal neutrons. After losing energy as they penetrate tissue, the resultant low energy "thermal" neutrons are captured by the B atoms. The resulting decay reaction yields high-energy alpha particles that kill the cancer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weakly Interacting Massive Particles
Weakly interacting massive particles (WIMPs) are hypothetical particles that are one of the proposed candidates for dark matter. There exists no formal definition of a WIMP, but broadly, a WIMP is a new elementary particle which interacts via gravity and any other force (or forces), potentially not part of the Standard Model itself, which is as weak as or weaker than the weak nuclear force, but also non-vanishing in its strength. Many WIMP candidates are expected to have been produced thermally in the early Universe, similarly to the particles of the Standard Model according to Big Bang cosmology, and usually will constitute cold dark matter. Obtaining the correct abundance of dark matter today via thermal production requires a self-annihilation cross section of \langle \sigma v \rangle \simeq 3 \times 10^ \mathrm^ \;\mathrm^, which is roughly what is expected for a new particle in the 100 GeV mass range that interacts via the electroweak force. Experimental efforts to dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is a fermion (an elementary particle with spin of ) that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass is so small ('' -ino'') that it was long thought to be zero. The rest mass of the neutrino is much smaller than that of the other known elementary particles excluding massless particles. The weak force has a very short range, the gravitational interaction is extremely weak due to the very small mass of the neutrino, and neutrinos do not participate in the strong interaction. Thus, neutrinos typically pass through normal matter unimpeded and undetected. Weak interactions create neutrinos in one of three leptonic flavors: electron neutrinos muon neutrinos (), or tau neutrinos (), in association with the corresponding charged lepton. Although neutrinos were long believed to be massless, it is now known that there are three discrete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Emission
Neutron emission is a mode of radioactive decay in which one or more neutrons are ejected from a nucleus. It occurs in the most neutron-rich/proton-deficient nuclides, and also from excited states of other nuclides as in photoneutron emission and beta-delayed neutron emission. As only a neutron is lost by this process the number of protons remains unchanged, and an atom does not become an atom of a different element, but a different isotope of the same element. Neutrons are also produced in the spontaneous and induced fission of certain heavy nuclides. Spontaneous neutron emission As a consequence of the Pauli exclusion principle, nuclei with an excess of protons or neutrons have a higher average energy per nucleon. Nuclei with a sufficient excess of neutrons have a greater energy than the combination of a free neutron and a nucleus with one less neutron, and therefore can decay by neutron emission. Nuclei which can decay by this process are described as lying beyond the neutron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Isomer
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy excited state, higher energy levels than in the ground state of the same nucleus. "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have Half-life, half-lives 100 to 1000 times longer than the half-lives of the excited nuclear states that decay with a "prompt" half life (ordinarily on the order of 10−12 seconds). The term "metastable" is usually restricted to isomers with half-lives of 10−9 seconds or longer. Some references recommend 5 × 10−9 seconds to distinguish the metastable half life from the normal "prompt" Induced gamma emission, gamma-emission half-life. Occasionally the half-lives are far longer than this and can last minutes, hours, or years. For example, the Isotopes of tantalum#Tantalum-180m, nuclear isomer survives so long (at least 1015 years) that it has never been observed to decay spontaneously. The half-life of a nuclear isomer can eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Even And Odd Atomic Nuclei
In nuclear physics, properties of a nucleus depend on evenness or oddness of its atomic number (proton number) ''Z'', neutron number ''N'' and, consequently, of their sum, the mass number ''A''. Most importantly, oddness of both ''Z'' and ''N'' tends to lower the nuclear binding energy, making odd nuclei generally less stable. This effect is not only experimentally observed, but is included in the semi-empirical mass formula and explained by some other nuclear models, such as the nuclear shell model. This difference of nuclear binding energy between neighbouring nuclei, especially of odd-''A'' isobars, has important consequences for beta decay. The nuclear spin is zero for even-Z, even N nuclei, integer for all even-''A'' nuclei, and odd half-integer for all odd-''A'' nuclei. The neutron–proton ratio is not the only factor affecting nuclear stability. Adding neutrons to isotopes can vary their nuclear spins and nuclear shapes, causing differences in neutron capture cross s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Decay
Alpha decay or α-decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle (helium nucleus) and thereby transforms or 'decays' into a different atomic nucleus, with a mass number that is reduced by four and an atomic number that is reduced by two. An alpha particle is identical to the nucleus of a helium-4 atom, which consists of two protons and two neutrons. It has a charge of and a mass of . For example, uranium-238 decays to form thorium-234. While alpha particles have a charge , this is not usually shown because a nuclear equation describes a nuclear reaction without considering the electrons – a convention that does not imply that the nuclei necessarily occur in neutral atoms. Alpha decay typically occurs in the heaviest nuclides. Theoretically, it can occur only in nuclei somewhat heavier than nickel (element 28), where the overall binding energy per nucleon is no longer a maximum and the nuclides are therefore unstable toward spontaneou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halo Nucleus
In nuclear physics, an atomic nucleus is called a halo nucleus or is said to have a nuclear halo when it has a core nucleus surrounded by a "halo" of orbiting protons or neutrons, which makes the radius of the nucleus appreciably larger than that predicted by the liquid drop model. Halo nuclei form at the extreme edges of the table of nuclides — the neutron drip line and proton drip line — and have short half-lives, measured in milliseconds. These nuclei are studied shortly after their formation in an ion beam. Typically, an atomic nucleus is a tightly bound group of protons and neutrons. However, in some nuclides, there is an overabundance of one species of nucleon. In some of these cases, a nuclear core and a halo will form. Often, this property may be detected in scattering experiments, which show the nucleus to be much larger than the otherwise expected value. Normally, the cross-section (corresponding to the classical radius) of the nucleus is proportional to the cube roo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have almost the same chemical properties, they have different atomic masses and physical properties. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos ( ἴσος "equal") and topos ( τόπος "place"), meaning "the same place"; thus, the meaning behind the name is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. It was coined by Scottish doctor and writer Margaret Todd in 1913 in a suggestion to the British chemist Frederick Soddy. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called its atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
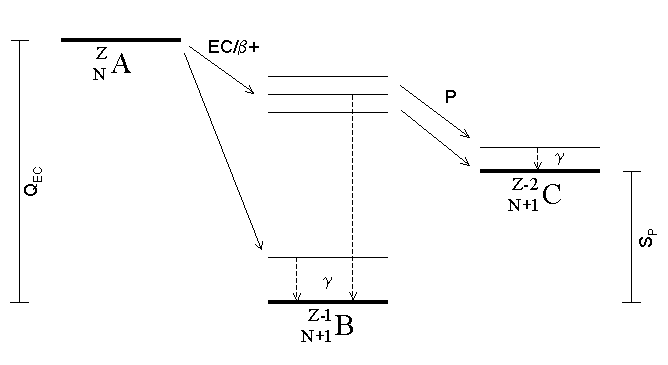
Proton Emission
Proton emission (also known as proton radioactivity) is a rare type of radioactive decay in which a proton is ejected from a nucleus. Proton emission can occur from high-lying excited states in a nucleus following a beta decay, in which case the process is known as beta-delayed proton emission, or can occur from the ground state (or a low-lying isomer) of very proton-rich nuclei, in which case the process is very similar to alpha decay. For a proton to escape a nucleus, the proton separation energy must be negative—the proton is therefore unbound, and tunnels out of the nucleus in a finite time. Proton emission is not seen in naturally occurring isotopes; proton emitters can be produced via nuclear reactions, usually using linear particle accelerators. Although prompt (i.e. not beta-delayed) proton emission was observed from an isomer in cobalt-53 as early as 1969, no other proton-emitting states were found until 1981, when the proton radioactive ground states of lutetium-15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_illustration.jpg)