|
Isobutylbenzene
Isobutylbenzene is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C10H14. It is used in the industrial manufacture of ibuprofen Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used for treating pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It may also be used to close a patent ductus arte .... Isobutylbenzene is a colorless flammable liquid that is a respiratory irritant. References Alkylbenzenes C4-Benzenes {{Hydrocarbons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used for treating pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It may also be used to close a patent ductus arteriosus in a premature baby. It can be used by mouth or intravenously. It typically begins working within an hour. Common side effects include heartburn and a rash. Compared to other NSAIDs, it may have other side effects such as gastrointestinal bleeding. It increases the risk of heart failure, kidney failure, and liver failure. At low doses, it does not appear to increase the risk of heart attack; however, at higher doses it may. Ibuprofen can also worsen asthma. While whether it is safe in early pregnancy is unclear, it appears to be harmful in later pregnancy, so is not recommended. Like other NSAIDs, it works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins by decreasing the activity of the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX). Ibuprofen is a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-Butylbenzene
''n''-Butylbenzene is the organic compound with the formula C6H5C4H9. Of two isomers of butylbenzene, ''n''-butylbenzene consists of a phenyl group attached to the 1 position of a butyl group. It is a slightly greasy, colorless liquid. The synthesis of ''n''-butylbenzene by the reaction of chlorobenzene and butylmagnesium bromide was one of the first demonstrations of the Kumada coupling using nickel diphosphine Diphosphane, or diphosphine, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula P2H4. This colourless liquid is one of several binary phosphorus hydrides. It is the impurity that typically causes samples of phosphine to ignite in air. Propert ... catalysts. This mild and efficient process contrasted with older methods. See also * C4-Benzenes References {{Hydrocarbons Alkylbenzenes C4-Benzenes Butyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sec-Butylbenzene
''sec''-Butylbenzene is an organic compound classified as an aromatic hydrocarbon. Its structure consists of a benzene ring substituted with a ''sec''-butyl group. It is a flammable colorless liquid which is nearly insoluble in water but miscible with organic solvents. Production ''sec''-Butylbenzene can be produced by the reaction of benzene with either ''n''-butyl alcohol or ''sec''-butyl alcohol in presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride and hydrochloric acid Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol .... References Alkylbenzenes C4-Benzenes {{Hydrocarbons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
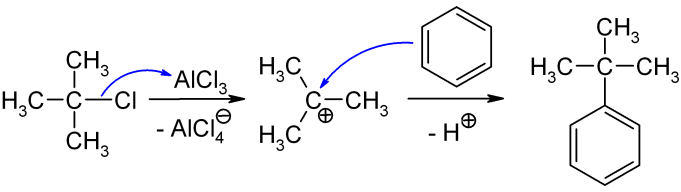
Tert-Butylbenzene
''tert''-Butylbenzene is an organic compound classified as an aromatic hydrocarbon. Its structure consists of a benzene ring substituted with a ''tert''-butyl group. It is a flammable colorless liquid which is nearly insoluble in water but miscible with organic solvents. Production ''tert''-Butylbenzene can be produced by the treatment of benzene with isobutene Isobutylene (or 2-methylpropene) is a hydrocarbon with the chemical formula . It is a four-carbon branched alkene (olefin), one of the four isomers of butylene. It is a colorless flammable gas, and is of considerable industrial value. Productio ... or by the reaction of benzene with ''tert''-butyl chloride in presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride, the latter is depicted below: References Alkylbenzenes C4-Benzenes {{Hydrocarbons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumene
Cumene (isopropylbenzene) is an organic compound that contains a benzene ring with an isopropyl substituent. It is a constituent of crude oil and refined fuels. It is a flammable colorless liquid that has a boiling point of 152 °C. Nearly all the cumene that is produced as a pure compound on an industrial scale is converted to cumene hydroperoxide, which is an intermediate in the synthesis of other industrially important chemicals, primarily phenol and acetone (known as the cumene process). Production Commercial production of cumene is by Friedel–Crafts alkylation of benzene with propylene. Cumene producers account for approximately 20% of the global demand for benzene. The original route for manufacturing of cumene was by alkylation of benzene in the liquid phase using sulfuric acid as a catalyst, but because of the complicated neutralization and recycling steps required, together with corrosion problems, this process has been largely replaced. As an alternative, sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, using the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkylbenzenes
The alkylbenzenes are derivatives of benzene, in which one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl groups of different sizes. They are a subset of the aromatic hydrocarbons. The simplest member is toluene, in which a hydrogen atom of the benzene was replaced by a methyl group In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula . In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many .... Literature * Allinger, Cava, de Jongh, Johnson, Lebel, Stevens: ''Organische Chemie'', 1. Auflage, Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1980, , pp. 367–368, 560–562. * Streitwieser / Heathcock: ''Organische Chemie'', 1. Auflage, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim 1980, , pp. 1051, 1073–1080. * Beyer / Walter: ''Lehrbuch der Organischen Chemie'', 19. Auflage, S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart 1981, , pp. 442–444. * Morrison / Boyd: ''Lehrbuch der Organischen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |