|
Irminger Rings
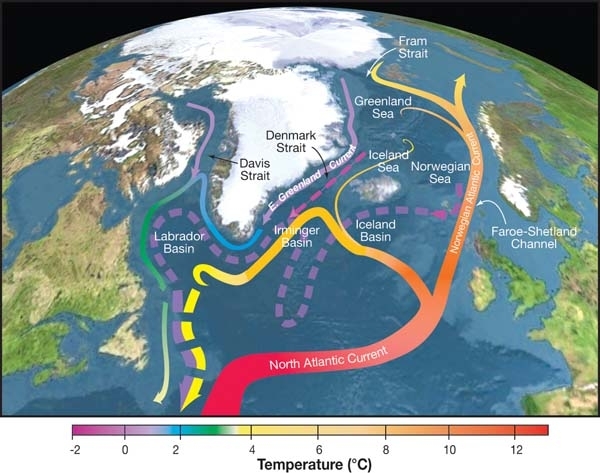
Irminger Rings (IRs) are mesoscale (15-50 kilometers) ocean eddies that are formed off the West coast of Greenland and travel southwestwards through the Labrador Sea. Most IRs are anti-cyclonic (clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere). There is considerable interest in researching IRs, because they have been hypothesized to influence deep convection in the Labrador sea, and therefore the formation of deep water. Basin overview The Irminger Current (IC) is a branch of the North Atlantic Drift (NAD) that flows westward from Iceland. Because of its Atlantic origins, IC waters are relatively warm and saline compared to the cold, fresh water of the East Greenland Current (EGC) originating from the Greenland Sea. Off the East coast of Greenland, the IC and the EGC meet and "combine" after rounding Cape Farewell to form the heavily stratified current system known as the West Greenland Current (WGC). The top layer of the WGC is 200 meters deep and consists of fresh EGC water. The laye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eddy (fluid Dynamics)
In fluid dynamics, an eddy is the swirling of a fluid and the reverse current created when the fluid is in a turbulent flow regime. The moving fluid creates a space devoid of downstream-flowing fluid on the downstream side of the object. Fluid behind the obstacle flows into the void creating a swirl of fluid on each edge of the obstacle, followed by a short reverse flow of fluid behind the obstacle flowing upstream, toward the back of the obstacle. This phenomenon is naturally observed behind large emergent rocks in swift-flowing rivers. An eddy is a movement of fluid that deviates from the general flow of the fluid. An example for an eddy is a vortex which produces such deviation. However, there are other types of eddies that are not simple vortices. For example, a Rossby wave is an eddy which is an undulation that is a deviation from mean flow, but doesn't have the local closed streamlines of a vortex. Swirl and eddies in engineering The propensity of a fluid to swirl is used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barotropic Fluid
In fluid dynamics, a barotropic fluid is a fluid whose density is a function of pressure only. The barotropic fluid is a useful model of fluid behavior in a wide variety of scientific fields, from meteorology to astrophysics. The density of most liquids is nearly constant (isopycnic), so it can be stated that their densities vary only weakly with pressure and temperature. Water, which varies only a few percent with temperature and salinity, may be approximated as barotropic. In general, air is not barotropic, as it is a function of temperature and pressure; but, under certain circumstances, the barotropic assumption can be useful. In astrophysics, barotropic fluids are important in the study of stellar interiors or of the interstellar medium. One common class of barotropic model used in astrophysics is a polytropic fluid. Typically, the barotropic assumption is not very realistic. In meteorology, a barotropic atmosphere is one that for which the density of the air depends on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation
The Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) is part of a global thermohaline circulation in the oceans and is the zonally integrated component of surface and deep currents in the Atlantic Ocean. It is characterized by a northward flow of warm, salty water in the upper layers of the Atlantic, and a southward flow of colder, deep waters. These "limbs" are linked by regions of overturning in the Nordic and Labrador Seas and the Southern Ocean, although the extent of overturning in the Labrador Sea is disputed. The AMOC is an important component of the Earth's climate system, and is a result of both atmospheric and thermohaline drivers. Climate change has the potential to weaken the AMOC through increases in ocean heat content and elevated freshwater flows from the melting ice sheets. Oceanographic reconstructions generally suggest that the AMOC is already weaker than it was before the Industrial Revolution, although there is a robust debate over the role of climate cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Atlantic Deep Water
North Atlantic Deep Water (NADW) is a deep water mass formed in the North Atlantic Ocean. Thermohaline circulation (properly described as meridional overturning circulation) of the world's oceans involves the flow of warm surface waters from the southern hemisphere into the North Atlantic. Water flowing northward becomes modified through evaporation and mixing with other water masses, leading to increased salinity. When this water reaches the North Atlantic it cools and sinks through convection, due to its decreased temperature and increased salinity resulting in increased density. NADW is the outflow of this thick deep layer, which can be detected by its high salinity, high oxygen content, nutrient minima, high 14C/12C, and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). CFCs are anthropogenic substances that enter the surface of the ocean from gas exchange with the atmosphere. This distinct composition allows its path to be traced as it mixes with Circumpolar Deep Water (CDW), which in turn fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labrador Sea Water
Labrador Sea Water is an intermediate water mass characterized by cold water, relatively low salinity compared to other intermediate water masses, and high concentrations of both oxygen and anthropogenic tracers.Pickart, Robert S., et al. "Is Labrador Sea Water formed in the Irminger basin?" Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers 50.1 (2003): 23-52 It is formed by convective processes in the Labrador SeaYashayaev, I.M., et al. "Recent Decline of the Labrador Sea Water." Bedford Institute of Oceanography, 2000 located between Greenland and the northeast coast of the Labrador Peninsula. Deep convection in the Labrador Sea allows colder water to sink forming this water mass, which is a contributor to the upper layer of North Atlantic Deep Water. North Atlantic Deep Water flowing southward is integral to the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation. The Labrador Sea experiences a net heat loss to the atmosphere annually. Formation Convection in the Labrador Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixed Layer
The oceanic or limnological mixed layer is a layer in which active turbulence has homogenized some range of depths. The surface mixed layer is a layer where this turbulence is generated by winds, surface heat fluxes, or processes such as evaporation or sea ice formation which result in an increase in salinity. The atmospheric mixed layer is a zone having nearly constant potential temperature and specific humidity with height. The depth of the atmospheric mixed layer is known as the mixing height. Turbulence typically plays a role in the formation of fluid mixed layers. Oceanic mixed layer Importance of the mixed layer The mixed layer plays an important role in the physical climate. Because the specific heat of ocean water is much larger than that of air, the top 2.5 m of the ocean holds as much heat as the entire atmosphere above it. Thus the heat required to change a mixed layer of 2.5 m by 1 °C would be sufficient to raise the temperature of the atmosphere by 1&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Oscillation
The Arctic oscillation (AO) or Northern Annular Mode/Northern Hemisphere Annular Mode (NAM) is a weather phenomenon at the Arctic pole north of 20 degrees latitude. It is an important mode of climate variability for the Northern Hemisphere. The southern hemisphere analogue is called the Antarctic oscillation or Southern Annular Mode (SAM). The index varies over time with no particular periodicity, and is characterized by non-seasonal sea-level pressure anomalies of one sign in the Arctic, balanced by anomalies of opposite sign centered at about 37–45° N. The North Atlantic oscillation (NAO) is a close relative of the Arctic oscillation. There is debate over whether one or the other is more fundamentally representative of the atmosphere's dynamics. The NAO may be identified in a more physically meaningful way, which may carry more impact on measurable effects of changes in the atmosphere. Description The Arctic oscillation appears as a ringlike (or "annular") pattern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boundary Current
Boundary currents are ocean currents with dynamics determined by the presence of a coastline, and fall into two distinct categories: western boundary currents and eastern boundary currents. Eastern boundary currents Eastern boundary currents are relatively shallow, broad and slow-flowing. They are found on the eastern side of oceanic basins (adjacent to the western coasts of continents). Subtropical eastern boundary currents flow equatorward, transporting cold water from higher latitudes to lower latitudes; examples include the Benguela Current, the Canary Current, the Humboldt (Peru) Current, and the California Current. Coastal upwelling often brings nutrient-rich water into eastern boundary current regions, making them productive areas of the ocean. Western boundary currents Western boundary currents may themselves be divided into sub-tropical or low-latitude western boundary currents. Sub-tropical western boundary currents are warm, deep, narrow, and fast-flowing currents t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isobath
Bathymetry (; ) is the study of underwater depth of ocean floors (''seabed topography''), lake floors, or river floors. In other words, bathymetry is the underwater equivalent to hypsometry or topography. The first recorded evidence of water depth measurements are from Ancient Egypt over 3000 years ago. Bathymetric (or hydrographic) charts are typically produced to support safety of surface or sub-surface navigation, and usually show seafloor relief or terrain as contour lines (called depth contours or isobaths) and selected depths ('' soundings''), and typically also provide surface navigational information. Bathymetric maps (a more general term where navigational safety is not a concern) may also use a Digital Terrain Model and artificial illumination techniques to illustrate the depths being portrayed. The global bathymetry is sometimes combined with topography data to yield a global relief model. Paleobathymetry is the study of past underwater depths. Seabed topography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
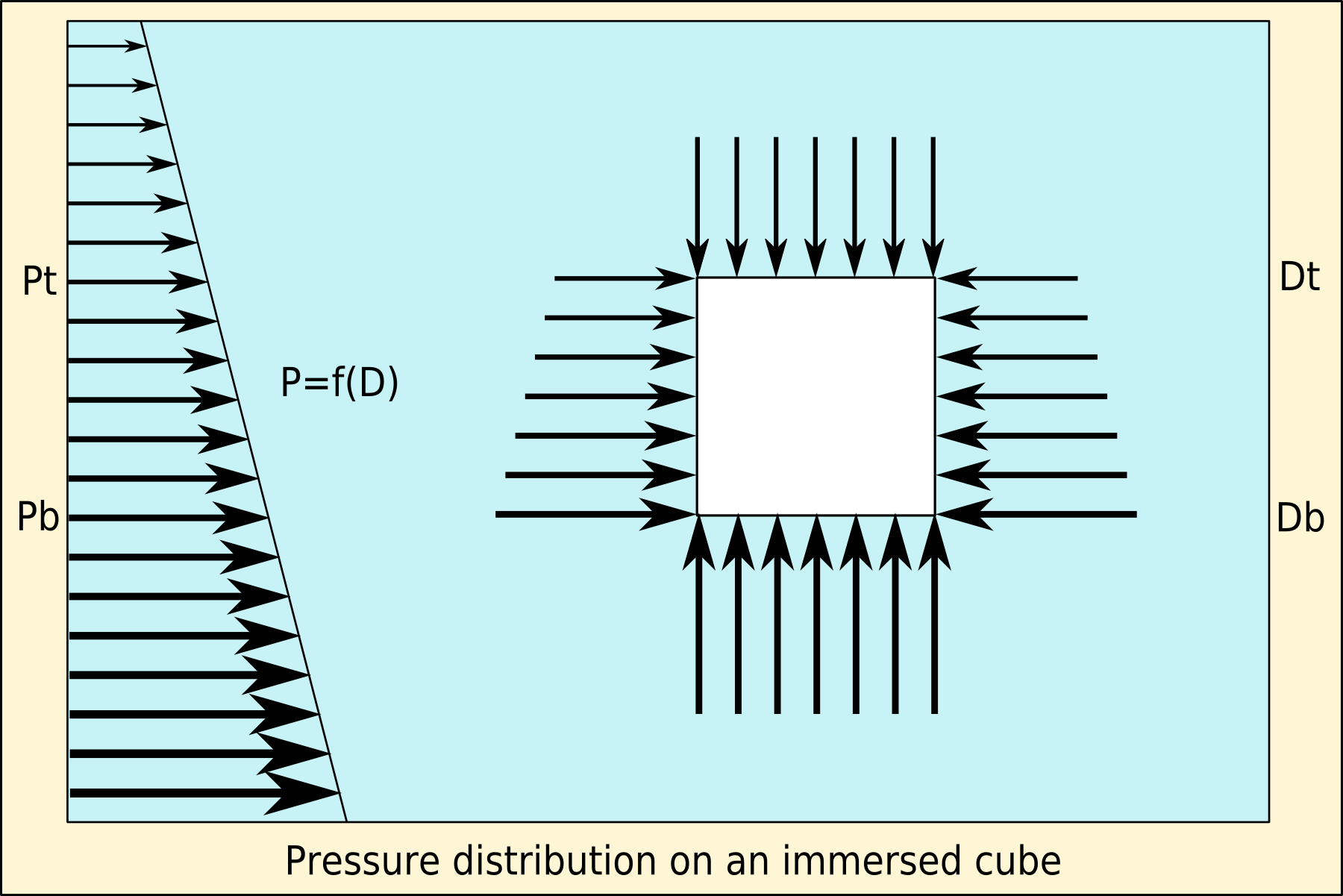
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid. For this reason, an object whose average density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is less dense than the liquid, the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopycnal
Isopycnals are layers within the ocean that are stratified based on their densities and can be shown as a line connecting points of a specific density or potential density on a graph. Isopycnals are often displayed graphically to help visualize "layers" of the water in the ocean or gases in the atmosphere in a similar manner to how contour lines are used in topographic maps to help visualize topography. Types Oceanography Water masses in the ocean are characterized by their properties. Factors such as density, temperature, and salinity can all be used to identify these masses and their origins as well as where they are in the water column. Density plays a large role in stratifying the ocean into layers. In a body of water, as the depth increases, so does the density; water masses with the highest density are at the bottom and the lowest densities are at the top. Typically, warm freshwater is less dense than cold salty water, thus the colder water will sink below the warmer wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rossby Number
The Rossby number (Ro), named for Carl-Gustav Arvid Rossby, is a dimensionless number used in describing fluid flow. The Rossby number is the ratio of inertial force to Coriolis force, terms , \mathbf \cdot \nabla \mathbf, \sim U^2 / L and \Omega \times \mathbf \sim U\Omega in the Navier–Stokes equations respectively. It is commonly used in geophysical phenomena in the oceans and atmosphere, where it characterizes the importance of Coriolis accelerations arising from planetary rotation. It is also known as the Kibel number. The Rossby number (Ro, not Ro) is defined as : \text = \frac, where ''U'' and ''L'' are respectively characteristic velocity and length scales of the phenomenon, and f = 2\Omega \sin \phi is the Coriolis frequency, with \Omega being the angular frequency of planetary rotation, and \phi the latitude. A small Rossby number signifies a system strongly affected by Coriolis forces, and a large Rossby number signifies a system in which inertial and centrifugal f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |