|
Ipubi
Ipubi is a city in the state of Pernambuco, Brazil. The population in 2020, according with IBGE was 31,187 inhabitants and the total area is 693.91 km². Geography * State - Pernambuco * Region - Sertão Pernambucano * Boundaries - Ceará state (N); Ouricuri (S); Bodocó (E); Araripina and Trindade (W). * Area - 665.62 km² * Elevation - 535 m * Hydrography - Brigida River * Vegetation - Caatinga * Climate - semi arid - (Sertão) hot * Annual average temperature - 24.8 c * Distance to Recife - 665.8 km Economy The main economic activities in Ipubi are based in industry and agribusiness, especially creation of cattle, sheep, pigss, goats, horses, chickens; and plantations of manioc ''Manihot esculenta'', commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated ... (over 35,000 tons). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ouricuri
Ouricuri is a city in the state of Pernambuco, Brazil. It is located in the mesoregion of ''Sertão Pernambucano''. Ouricuri has a total area of 2,423 square kilometers and had an estimated population of 66,978 inhabitants in 2009 according to the IBGE. Geography * State - Pernambuco * Region - Sertão Pernambucano * Boundaries - Araripina, Trindade and Ipubi (N), Santa Cruz and Santa Filomena (S), Parnamirim and Bodocó (E), Piaui state (W) * Area - 2,423 km2 * Elevation - 451 m * Hydrography - Brigida River * Vegetation - Caatinga * Climate - Semi-arid ( Sertao) hot and dry * Annual average temperature - 25.5 c * Main road - BR 232 and BR 316 * Distance to Recife - 621 km Economy The main economic activities in Ouricuri are based in extraction of gypsum and no metallic minerals, and primary sector especially creation of goats, donkeys, pigs and farms with beans, manioc and corn. Ouricuri is located in the micro region of Araripina which contains 95% of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bodocó
Bodocó is a municipality in the state of Pernambuco, Brazil. Its population in 2020, according to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE), was an estimated 38,378 and its area is 1621.79 km². Bodocó was established in 1909 from territory of the municipality of Granito. Its current mayor () is Otávio Augusto Tavares Pedrosa Cavalcante of the Brazilian Socialist Party, elected in 2020. Geography * Region – Sertão of Pernambuco * Boundaries – state of Ceará (N); Parnamirim (S); Exu and Granito (E); Ouricuri and Ipubi (W) * Area – 1553.85 km² * Elevation – 443 m * Drainage basin – Brigida River * Vegetation – Caatinga (shrubland) * Climate – semi-arid, hot and dry, Köppen: BSh * Annual average temperature – 25.6°C * Distance to Recife – 642.6 km Economy The main economic activities in Bodocó are based in commerce and agribusiness, especially the farming of goats, cattle, sheep, horses, donkeys, pigs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Araripina
Araripina is a Brazilian municipality in the state of Pernambuco. Has an estimated population in 2020 of 84,864 inhabitants according with IBGE. Total area of 1.847,5 km and is located in the state mesoregion of Sertão, at 622 meters above the sea level and 683 km West from the state capital, Recife. The exploration of gypsum (95% of the Brazilian reserves) and calcarium is the base of the local economy and at the homonymous microregion. Geography * State - Pernambuco * Region - Sertao Pernambucano * Boundaries - Ceará (N); Ouricuri (S); Ipubi and Trindade (E); Piaui (W) * Area - 1847.5 km2 * Elevation - 622 m * Hydrography - Brigida River * Vegetation - Caatinga * Climate - Semi desertic ( Sertao)- hot and dry * Annual average temperature - 22.4 c * Main road - BR 232 and BR 316 * Distance to Recife - 683 km Economy The main economic activities in Araripina are based in extraction of gypsum and no metallic minerals; and primary sect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trindade, Pernambuco
Trindade is a municipality in the state of Pernambuco, Brazil. The estimated population in 2021, according to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE) was 31,103 inhabitants and the total area is 295.77 km². Geography * State - Pernambuco * Region - Sertão Pernambucano * Boundaries - Araripina (N and W); Ouricuri (S); Ouricuri and Ipubi (E). * Area - 229.57 km² * Elevation - 518 m * Hydrography - Brigida River * Vegetation - Caatinga hiperxerófila * Climate - semi arid - ( Sertão) hot * Annual average temperature - 24.9 c * Distance to Recife - 645 km *Population at last census (2010) - 26,116 Economy The main economic activities in Trindade are based in no metallic ( gypsum) industry, commerce and agribusiness, especially creation of cattle, goats, sheep, pigs, chickens; and plantations of manioc. Trindade is located in the micro region of Araripina Araripina is a Brazilian municipality in the state of Pernambu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pernambuco
Pernambuco () is a state of Brazil, located in the Northeast region of the country. With an estimated population of 9.6 million people as of 2020, making it seventh-most populous state of Brazil and with around 98,148 km², being the 19th-largest in area among federative units of the country, it is the sixth-most densely populated with around 89 people per km². Its capital and largest city, Recife, is one of the most important economic and urban hubs in the country. Based on 2019 estimates, the Recife Metropolitan Region is seventh-most populous in the country, and the second-largest in northeastern Brazil. In 2015, the state had 4.6% of the national population and produced 2.8% of the national gross domestic product (GDP). The contemporary state inherits its name from the Captaincy of Pernambuco, established in 1534. The region was originally inhabited by Tupi-Guarani-speaking peoples. European colonization began in the 16th century, under mostly Portuguese rule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
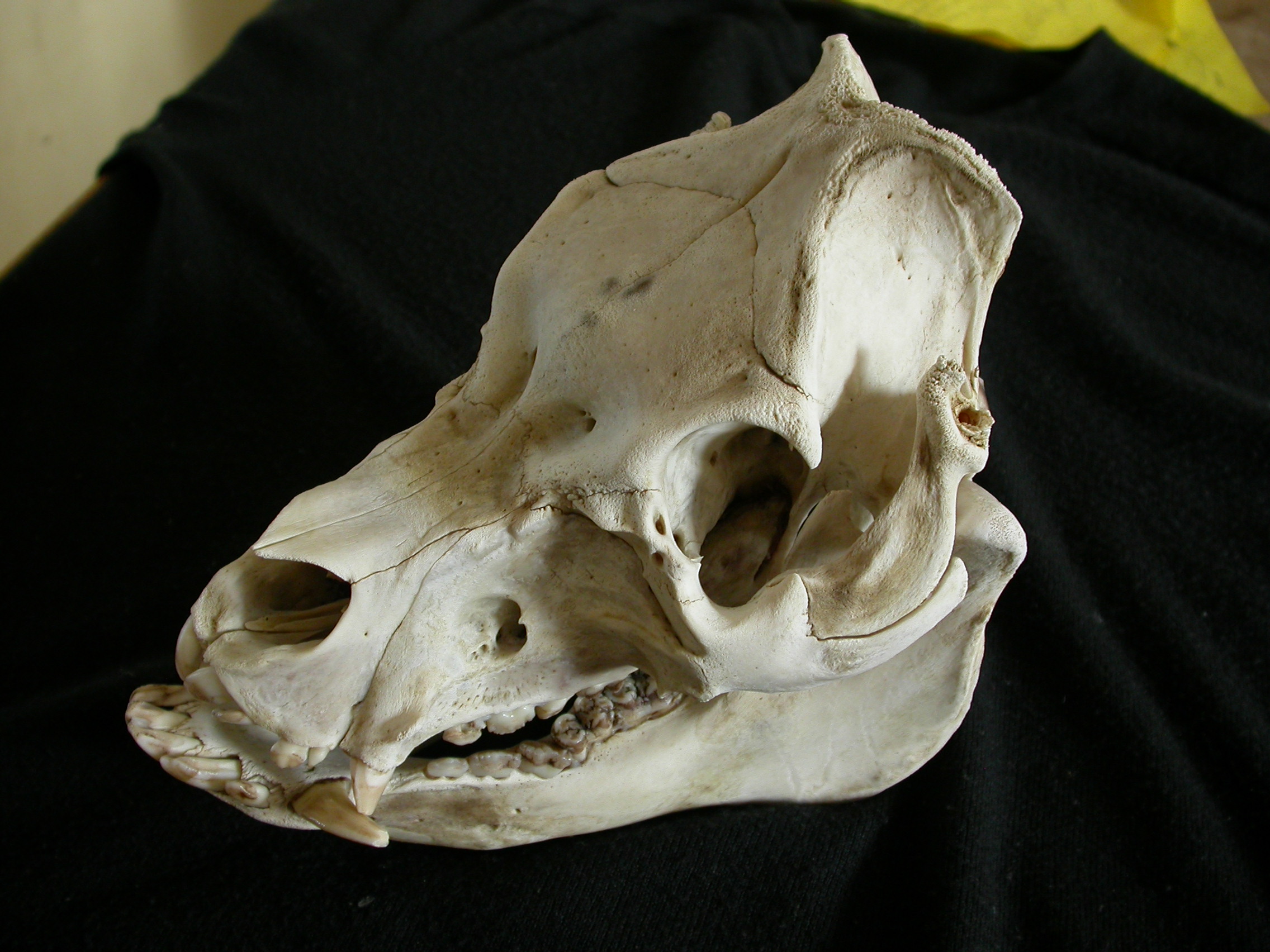
Pigs
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), often called swine, hog, or domestic pig when distinguishing from other members of the genus ''Sus'', is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is variously considered a subspecies of ''Sus scrofa'' (the wild boar or Eurasian boar) or a distinct species. The pig's head-plus-body length ranges from , and adult pigs typically weigh between , with well-fed individuals even exceeding this range. The size and weight of hogs largely depends on their breed. Compared to other artiodactyls, a pig's head is relatively long and pointed. Most even-toed ungulates are herbivorous, but pigs are omnivores, like their wild relative. Pigs grunt and make snorting sounds. When used as livestock, pigs are farmed primarily for the production of meat, called pork. A group of pigs is called a ''passel'', a ''team'', or a ''sounder''. The animal's bones, hide, and bristles are also used in products. Pigs, especially miniature breeds, are kept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Service Sector
The tertiary sector of the economy, generally known as the service sector, is the third of the three economic sectors in the three-sector model (also known as the economic cycle). The others are the primary sector ( raw materials) and the secondary sector (manufacturing). The tertiary sector consists of the provision of services instead of end products. Services (also known as "intangible goods") include attention, advice, access, experience and affective labor. The production of information has been long regarded as a service, but some economists now attribute it to a fourth sector, called the quaternary sector. The tertiary sector involves the provision of services to other businesses as well as to final consumers. Services may involve the transport, distribution and sale of goods from a producer to a consumer, as may happen in wholesaling and retailing, pest control or entertainment. The goods may be transformed in the process of providing the service, as happens i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Sector
In macroeconomics, the secondary sector of the economy is an economic sector in the three-sector theory that describes the role of manufacturing. It encompasses industries that produce a finished, usable product or are involved in construction. This sector generally takes the output of the primary sector (i.e. raw materials) and creates finished goods suitable for sale to domestic businesses or consumers and for export (via distribution through the tertiary sector). Many of these industries consume large quantities of energy, require factories and use machinery; they are often classified as light or heavy based on such quantities. This also produces waste materials and waste heat that may cause environmental problems or pollution (see negative externalities). Examples include textile production, car manufacturing, and handicraft. Manufacturing is an important activity in promoting economic growth and development. Nations that export manufactured products tend to gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Sector
The primary sector of the economy includes any industry involved in the extraction and production of raw materials, such as farming, logging, fishing, forestry and mining. The primary sector tends to make up a larger portion of the economy in developing countries than it does in developed countries. For example, in 2018, agriculture, forestry, and fishing comprised more than 15% of GDP in sub-Saharan Africa but less than 1% of GDP in North America. In developed countries the primary sector has become more technologically advanced, enabling for example the mechanization of farming, as compared with lower-tech methods in poorer countries. More developed economies may invest additional capital in primary means of production: for example, in the United States corn belt, combine harvesters pick the corn, and sprayers spray large amounts of insecticides, herbicides and fungicides, producing a higher yield than is possible using less capital-intensive techniques. These technol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GDP Per Capita
Lists of countries by GDP per capita list the countries in the world by their gross domestic product (GDP) per capita. The lists may be based on nominal or purchasing power parity Purchasing power parity (PPP) is the measurement of prices in different countries that uses the prices of specific goods to compare the absolute purchasing power of the countries' currencies. PPP is effectively the ratio of the price of a baske ... GDP. Gross national income (GNI) per capita accounts for inflows and outflows of foreign capital. Income inequality metrics measure the distribution of income between rich and poor. Lists *GDP ** List of countries by GDP (nominal) per capita ** List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita *GNI ** List of countries by GNI (nominal) per capita ** List of countries by GNI (PPP) per capita {{DEFAULTSORT:GDP per capita Lists of countries by GDP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manioc
''Manihot esculenta'', commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated as an annual crop in tropical and subtropical regions for its edible starchy tuberous root, a major source of carbohydrates. Though it is often called ''yuca'' in parts of Spanish America and in the United States, it is not related to yucca, a shrub in the family Asparagaceae. Cassava is predominantly consumed in boiled form, but substantial quantities are used to extract cassava starch, called tapioca, which is used for food, animal feed, and industrial purposes. The Brazilian farinha, and the related '' garri'' of West Africa, is an edible coarse flour obtained by grating cassava roots, pressing moisture off the obtained grated pulp, and finally drying it (and roasting both in the case of farinha and garri). Cassava is the third-l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chickens
The chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') is a domestication, domesticated junglefowl species, with attributes of wild species such as the grey junglefowl, grey and the Ceylon junglefowl that are originally from Southeastern Asia. Rooster or cock is a term for an adult male bird, and a younger male may be called a cockerel. A male that has been castrated is a capon. An adult female bird is called a hen and a sexually immature female is called a pullet. Humans now keep chickens primarily as a source of food (consuming both their Chicken as food, meat and egg as food, eggs) and as pets. Traditionally they were also bred for cockfighting, which is still practiced in some places. Chickens are one of the most common and widespread domestic animals, with a total population of 23.7 billion , up from more than 19 billion in 2011. There are more chickens in the world than any other bird. There are numerous cultural references to chickens – in myth, folklore and religion, and in la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |