|
Ion Pillat
Ion Pillat (31 March 1891 – 17 April 1945) was a distinguished Romanian poet. He is best known for his volume ''Pe Argeș în sus'' (''Upstream on the Argeș'') and ''Poeme într-un vers'' (''One-line poems''). His maternal grandfather was Ion Brătianu. He studied at the University of Paris from 1910 to 1914, returning to Bucharest after obtaining a law degree. Biography Childhood Ion Pillat was born on 31 March 1891, in Bucharest. The Pillats were an old family of free farmers, originally from on the Prut river. His father, Ion N. Pillat, was a landowner and parlimenarian. His mother, Maria Brătianu, was the second daughter of the political leader Ion C. Brătianu. His elementary education took place in the town of Pitești. In 1910, he enrolled in a student at the Sorbonne, where he studied mainly literature, history and geography, but he also studied law. Titu Maiorescu published some of his poems in 1911 in Convorbiri literare. In 1912, while on holiday in Buchar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Template:Infobox Writer/doc
Infobox writer may be used to summarize information about a person who is a writer/author (includes screenwriters). If the writer-specific fields here are not needed, consider using the more general ; other infoboxes there can be found in :People and person infobox templates. This template may also be used as a module (or sub-template) of ; see WikiProject Infoboxes/embed for guidance on such usage. Syntax The infobox may be added by pasting the template as shown below into an article. All fields are optional. Any unused parameter names can be left blank or omitted. Parameters Please remove any parameters from an article's infobox that are unlikely to be used. All parameters are optional. Unless otherwise specified, if a parameter has multiple values, they should be comma-separated using the template: : which produces: : , language= If any of the individual values contain commas already, add to use semi-colons as separators: : which produces: : , ps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandru Macedonski
Alexandru Macedonski (; also rendered as Al. A. Macedonski, Macedonschi or Macedonsky; 14 March 1854 – 24 November 1920) was a Romanian poet, novelist, dramatist and literary critic, known especially for having promoted French Symbolism in his native country, and for leading the Romanian Symbolist movement during its early decades. A forerunner of local modernist literature, he is the first local author to have used free verse, and claimed by some to have been the first in modern European literature. Within the framework of Romanian literature, Macedonski is seen by critics as second only to national poet Mihai Eminescu; as leader of a cosmopolitan and aestheticist trend formed around his ''Literatorul'' journal, he was diametrically opposed to the inward-looking traditionalism of Eminescu and his school. Debuting as a Neoromantic in the Wallachian tradition, Macedonski went through the Realist- Naturalist stage deemed "social poetry", while progressively adapting his styl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1891 Births
Events January–March * January 1 ** Paying of old age pensions begins in Germany. ** A strike of 500 Hungarian steel workers occurs; 3,000 men are out of work as a consequence. **Germany takes formal possession of its new African territories. * January 2 – A. L. Drummond of New York is appointed Chief of the Treasury Secret Service. * January 4 – The Earl of Zetland issues a declaration regarding the famine in the western counties of Ireland. * January 5 **The Australian shearers' strike, that leads indirectly to the foundation of the Australian Labor Party, begins. **A fight between the United States and Indians breaks out near Pine Ridge agency. ** Henry B. Brown, of Michigan, is sworn in as an Associate Justice of the Supreme Court. **A fight between railway strikers and police breaks out at Motherwell, Scotland. * January 6 – Encounters continue, between strikers and the authorities at Glasgow. * January 7 ** General Miles' force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corresponding Members Of The Romanian Academy
Correspondence may refer to: *In general usage, non-concurrent, remote communication between people, including letters, email, newsgroups, Internet forums, blogs. Science *Correspondence principle (physics): quantum physics theories must agree with classical physics theories when applied to large quantum numbers *Correspondence principle (sociology), the relationship between social class and available education *Correspondence problem (computer vision), finding depth information in stereography *Regular sound correspondence (linguistics), see Comparative method (linguistics) Mathematics * Binary relation ** 1:1 correspondence, an older name for a bijection ** Multivalued function * Correspondence (algebraic geometry), between two algebraic varieties * Correspondence (category theory), the opposite of a profunctor * Correspondence (von Neumann algebra) or bimodule, a type of Hilbert space * Correspondence analysis, a multivariate statistical technique Philosophy and religio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gândirea
''Gândirea'' ("The Thinking"), known during its early years as ''Gândirea Literară - Artistică - Socială'' ("The Literary - Artistic - Social Thinking"), was a Romanian literary, political and art magazine. Overview Founded by Cezar Petrescu and D. I. Cucu in the city of Cluj, and first issued on May 1, 1921, as a literary supplement for the Cluj-based '' Voința'', it was originally a modernist and expressionist-influenced journal. During its early existence, it attracted criticism from the traditional cultural establishment for allegedly allowing influences from Germanic Europe to permeate Romanian culture. ''Gândirea'' moved to Bucharest in October 1922, and, in 1926, its leadership was joined by the nationalist thinker Nichifor Crainic; he became its director and ideological guide in 1928, gradually moving it toward a mystical Orthodox focus — itself occasionally referred to as ''Gândirism''. With just two interruptions in publication (1925 and 1933–34), ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Writers From Bucharest
A writer is a person who uses written words in different writing styles and techniques to communicate ideas. Writers produce different forms of literary art and creative writing such as novels, short stories, books, poetry, travelogues, plays, screenplays, teleplays, songs, and essays as well as other reports and news articles that may be of interest to the general public. Writers' texts are published across a wide range of media. Skilled writers who are able to use language to express ideas well, often contribute significantly to the cultural content of a society. The term "writer" is also used elsewhere in the arts and music, such as songwriter or a screenwriter, but also a stand-alone "writer" typically refers to the creation of written language. Some writers work from an oral tradition. Writers can produce material across a number of genres, fictional or non-fictional. Other writers use multiple media such as graphics or illustration to enhance the communication of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Paris Alumni
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian Male Poets
Romanian may refer to: *anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Romania **Romanians, an ethnic group **Romanian language, a Romance language *** Romanian dialects, variants of the Romanian language ** Romanian cuisine, traditional foods **Romanian folklore The folklore of Romania is the collection of traditions of the Romanians. A feature of Romanian culture is the special relationship between folklore and the learned culture, determined by two factors. First, the rural character of the Romanian ... * Romanian (stage), a stage in the Paratethys stratigraphy of Central and Eastern Europe *'' The Romanian'' newspaper *'' The Romanian: Story of an Obsession'', a 2004 novel by Bruce Benderson * * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Gothic
High Gothic is a particularly refined and imposing style of Gothic architecture that appeared in northern France from about 1195 until 1250. Notable examples include Chartres Cathedral, Reims Cathedral, Amiens Cathedral, Beauvais Cathedral, and Bourges Cathedral. It is characterized by great height, harmony, subtle and refined tracery and realistic sculpture, and by large stained glass windows, particularly rose windows and larger windows on the upper levels, which filled the interiors with light. It followed Early Gothic architecture and was succeeded by the Rayonnant style. It is often described as the high point of the Gothic style. Origins The new style illustrated the ambitions of the French kings of the Capetian dynasty, and particularly Philip II of France, who reigned from 1180 until 1223. He gradually extended his power beyond the Ile-de-France to assume dominance over Normandy, Burgundy, and Brittany. He defeated a coalition of English, German, and Flemish forces at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chartres Cathedral
Chartres Cathedral, also known as the Cathedral of Our Lady of Chartres (french: Cathédrale Notre-Dame de Chartres), is a Roman Catholic church in Chartres, France, about southwest of Paris, and is the seat of the Bishop of Chartres. Mostly constructed between 1194 and 1220, it stands on the site of at least five cathedrals that have occupied the site since the Diocese of Chartres was formed as an episcopal see in the 4th century. It is in the High Gothic and Romanesque styles, with a Flamboyant north spire. The cathedral was designated a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1979, which called it "the high point of French Gothic art" and a "masterpiece". The cathedral is well-preserved and well-restored: the majority of the original stained glass windows survive intact, while the architecture has seen only minor changes since the early 13th century. The building's exterior is dominated by heavy flying buttresses which allowed the architects to increase the window size significan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
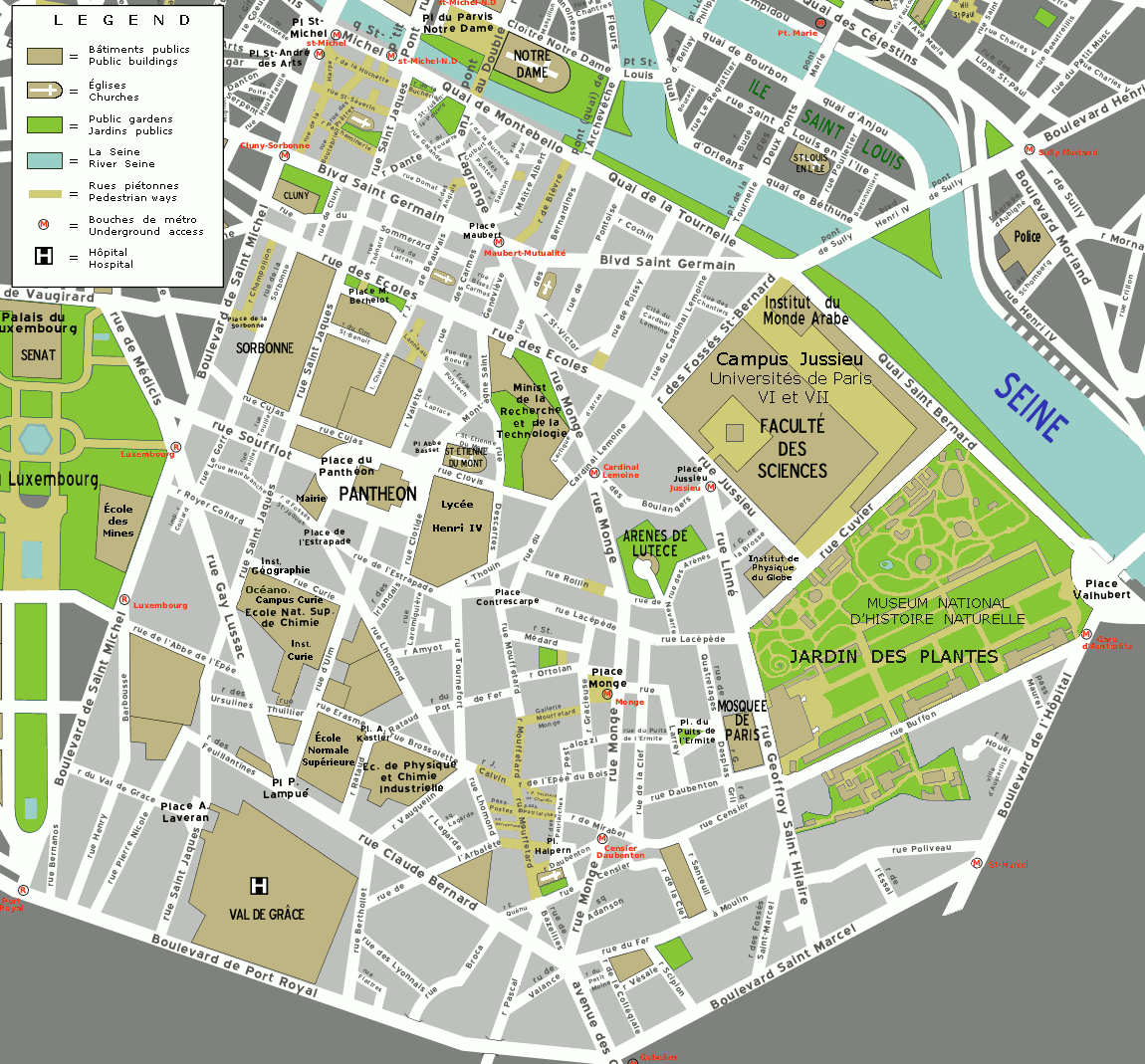
Boulevard Saint-Michel
Boulevard Saint-Michel () is one of the two major streets in the Latin Quarter of Paris, the other being Boulevard Saint-Germain. It is a tree-lined boulevard which runs south from the Pont Saint-Michel on the Seine and Place Saint-Michel, crosses Boulevard Saint-Germain and continues alongside the Sorbonne and the Jardin du Luxembourg, ending at the Place Camille Jullian just before the Port-Royal RER station and the Avenue de l'Observatoire. It was created by Baron Haussmann to run parallel to Rue Saint-Jacques which marks the historical north-south axis of Paris. It is known colloquially as ''Boul'Mich'' in French. The boulevard serves as a boundary between the 5th and 6th arrondissements of Paris; odd-numbered buildings on the eastern side are in the 5th arrondissement and even numbers on the western side are in the 6th. It has a length of 1,380 m (4,530 ft), an average width of 30 m (98 ft) and takes its name from the Pont Saint-Michel. As the centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycée Henri-IV
The Lycée Henri-IV is a public secondary school located in Paris. Along with the Lycée Louis-le-Grand, it is widely regarded as one of the most prestigious and demanding sixth-form colleges (''lycées'') in France. The school educates more than 2,500 students from ''collège'' (the first four years of secondary education in France) to '' classes préparatoires'' (preparatory classes to prepare students for entry to the elite grandes écoles such as École normale supérieure, École polytechnique, Centrale Paris, Mines ParisTech, ISAE-SUPAERO, HEC Paris, ESSEC Business School, and ESCP Europe, among others). Its motto is ''"Domus Omnibus Una"'' ("A Home For All"). __TOC__ Buildings and history Lycée Henri-IV is located in the former royal Abbey of St Genevieve, in the heart of the Latin Quarter on the left bank of the river Seine, near the Panthéon, the church Saint-Étienne-du-Mont, and the rue Mouffetard. Rich in history, architecture and culture, the Latin Quarter con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |