|
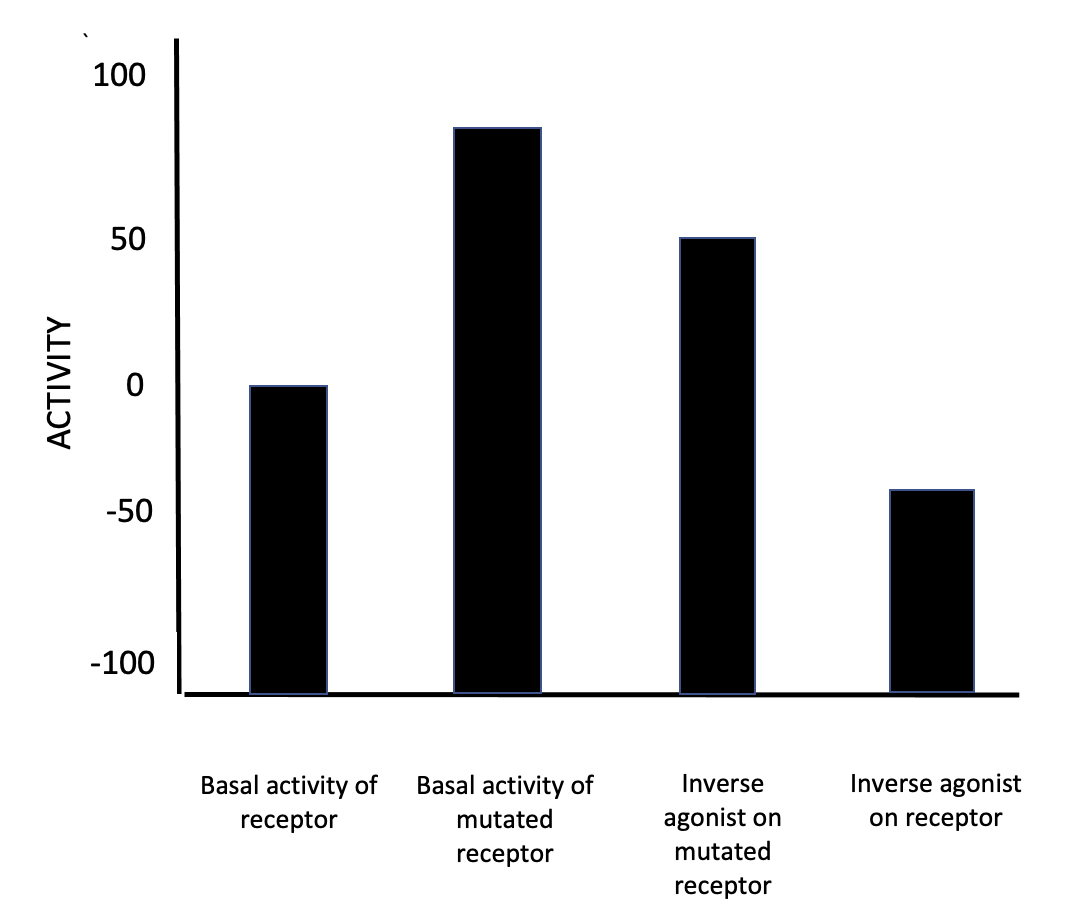
Inverse Agonist
In pharmacology, an inverse agonist is a drug that binds to the same receptor as an agonist but induces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist. A neutral antagonist has no activity in the absence of an agonist or inverse agonist but can block the activity of either. Inverse agonists have opposite actions to those of agonists but the effects of both of these can be blocked by antagonists. A prerequisite for an inverse agonist response is that the receptor must have a constitutive (also known as intrinsic or basal) level of activity in the absence of any ligand. An agonist increases the activity of a receptor above its basal level, whereas an inverse agonist decreases the activity below the basal level. The efficacy of a full agonist is by definition 100%, a neutral antagonist has 0% efficacy, and an inverse agonist has < 0% (i.e., negative) efficacy. Examples Receptors for which inverse agonists have been identified include the[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverse Agonist 3
Inverse or invert may refer to: Science and mathematics * Inverse (logic), a type of conditional sentence which is an immediate inference made from another conditional sentence * Additive inverse (negation), the inverse of a number that, when added to the original number, yields zero * Compositional inverse, a function that "reverses" another function * Inverse element * Inverse function, a function that "reverses" another function **Generalized inverse, a matrix that has some properties of the inverse matrix but not necessarily all of them * Multiplicative inverse (reciprocal), a number which when multiplied by a given number yields the multiplicative identity, 1 ** Inverse matrix of an Invertible matrix Other uses * Invert level, the base interior level of a pipe, trench or tunnel * ''Inverse'' (website), an online magazine * An outdated term for an LGBT person; see Sexual inversion (sexology) See also * Inversion (other) * Inverter (other) * Opposite (di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscimol
Muscimol (also known as agarin or pantherine) is one of the principal psychoactive constituents of ''Amanita muscaria'' and related species of mushroom. Muscimol is a potent and selective orthosteric agonist for the GABAA receptors and displays sedative-hypnotic, depressant and hallucinogenic psychoactivity. This colorless or white solid is classified as an isoxazole. Muscimol went under clinical trial phase I for epilepsy, but the trial was discontinued. Biochemistry Muscimol is one of the psychoactive compounds responsible for the effects of ''Amanita muscaria'' intoxication. Ibotenic acid, a neurotoxic secondary metabolite of ''Amanita muscaria'', serves as a prodrug to muscimol when the mushroom is ingested or dried, converting to muscimol via decarboxylation. Muscimol is produced in the mushrooms ''Amanita muscaria'' (fly agaric) and ''Amanita pantherina'', along with muscarine (which is present in trace amounts and it is not active), muscazone, and ibotenic acid. ''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
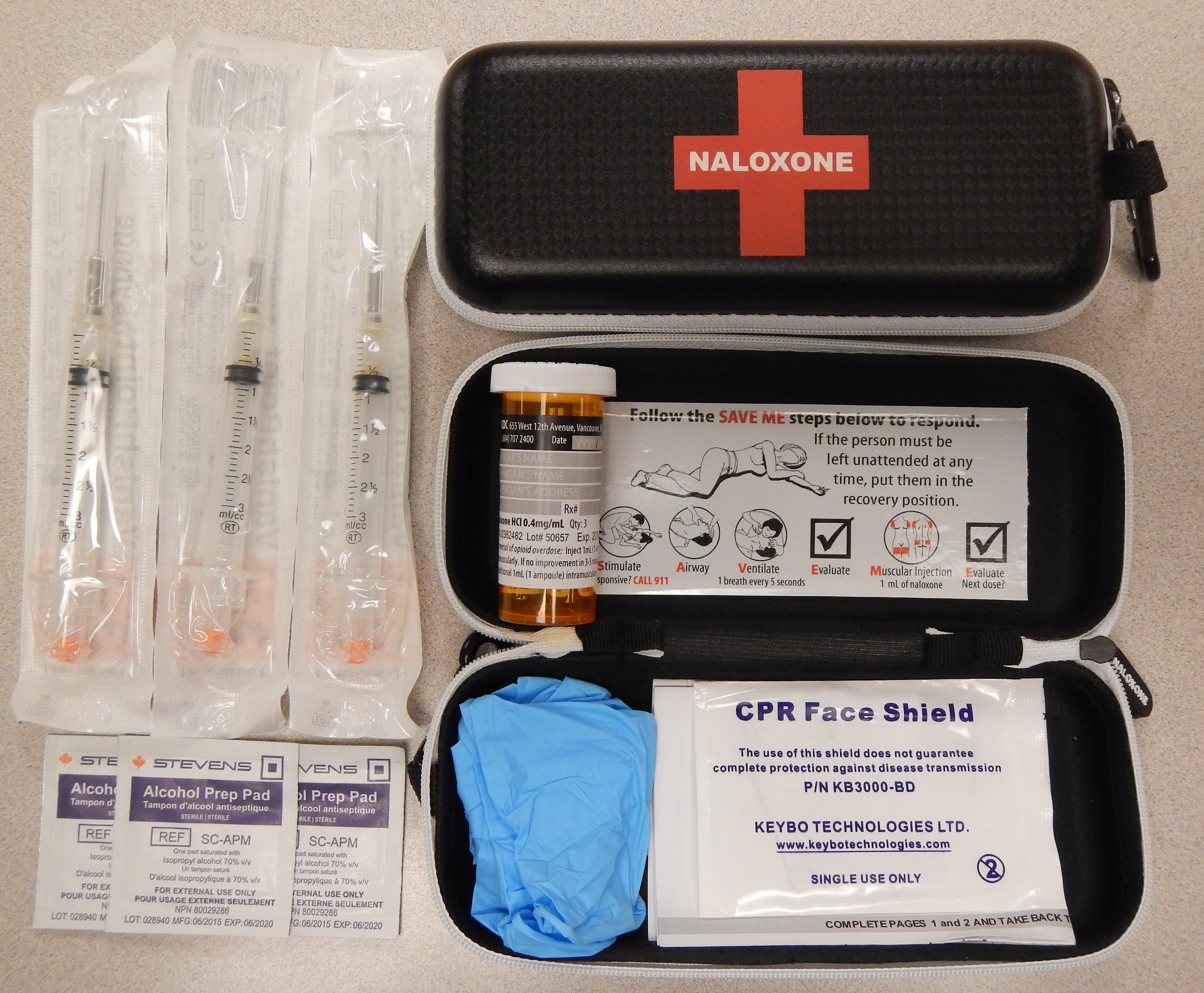
Naloxone
Naloxone, sold under the brand names Narcan (4 mg) and Kloxxado (8 mg) among others, is a medication used to reverse or reduce the effects of opioids. It is commonly used to counter decreased breathing in opioid overdose. Effects begin within two minutes when given intravenously, and within five minutes when injected into a muscle. The medicine can also be administered by spraying it into a person's nose. Naloxone commonly blocks the effects of opioids for 30 to 90 minutes. Multiple doses may be required, as the duration of action of some opioids is greater than that of naloxone. Administration to opioid-dependent individuals may cause symptoms of opioid withdrawal, including restlessness, agitation, nausea, vomiting, a fast heart rate, and sweating. To prevent this, small doses every few minutes can be given until the desired effect is reached. In those with previous heart disease or taking medications that negatively affect the heart, further heart problems have occurred. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opioid Antagonist
An opioid antagonist, or opioid receptor antagonist, is a receptor antagonist that acts on one or more of the opioid receptors. Naloxone and naltrexone are commonly used opioid antagonist drugs which are competitive antagonists that bind to the opioid receptors with higher affinity than agonists but do not activate the receptors. This effectively blocks the receptor, preventing the body from responding to opioids and endorphins. Some opioid antagonists are not pure antagonists but do produce some weak opioid partial agonist effects, and can produce analgesic effects when administered in high doses to opioid-naive individuals. Examples of such compounds include nalorphine and levallorphan. However, the analgesic effects from these specific drugs are limited and tend to be accompanied by dysphoria, most likely due to additional agonist action at the κ-opioid receptor. As they induce opioid withdrawal effects in people who are taking, or have recently used, opioid full agonists, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanocortin 1 Receptor
The melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R), also known as melanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor (MSHR), melanin-activating peptide receptor, or melanotropin receptor, is a G protein–coupled receptor that binds to a class of pituitary peptide hormones known as the melanocortins, which include adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and the different forms of melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). It is coupled to Gαs and upregulates levels of cAMP by activating adenylyl cyclase in cells expressing this receptor. It is normally expressed in skin and melanocytes, and to a lesser degree in periaqueductal gray matter, astrocytes and leukocytes. In skin cancer, MC1R is highly expressed in melanomas but not carcinomas. MC1R is one of the key proteins involved in regulating mammalian skin color and hair color. It is located on the plasma membrane of specialized cells known as melanocytes, which produce the pigment melanin through the process of melanogenesis. It works by controlling the type of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanocortin 4 Receptor
Melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R) is a melanocortin receptor that in humans is encoded by the gene. It encodes the MC4R protein, a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that binds α-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH). In mouse models, MC4 receptors have been found to be involved in feeding behaviour, the regulation of metabolism, sexual behaviour, and male erectile function. Clinical significance In 2009, two very large genome-wide association studies of body mass index (BMI) confirmed the association of variants about 150 kilobases downstream of the ''MC4R'' gene with insulin resistance, obesity, and other anthropometric traits. ''MC4R'' may also have clinical utility as a biomarker for predicting individual susceptibility to drug-induced adverse effects causing weight gain and related metabolic abnormalities. Another GWAS performed in 2012 identified twenty SNPs located ~190 Kb downstream of ''MC4R'' in association with severe antipsychotic-induced weight gain. This ''locus'' o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanocortin Receptors
Melanocortin receptors are members of the rhodopsin family of 7-transmembrane G protein-coupled receptors. There are five known members of the melanocortin receptor system each with differing specificities for melanocortins: * . MC1R is associated with pigmentation genetics. * . MC2R is also known as the ACTH receptor or corticotropin receptor because it is specific for ACTH alone. * . MC3R is associated with childhood growth, accrual of lean mass and onset of puberty. * . Defects in MC4R are a cause of autosomal dominant obesity, accounting for 6% of all cases of early-onset obesity. * . MC5R These receptors are inhibited by endogenous inverse agonists agouti signalling peptide and agouti-related peptide, and activated by synthetic (i.e. afamelanotide) and endogenous agonist melanocyte-stimulating hormones. Selective ligands Several selective ligands for the melanocortin receptors are known, and some synthetic compounds have been investigated as potential tanning, anti-obesity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agouti Signalling Peptide
Agouti-signaling protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ASIP gene. It is responsible for the distribution of melanin pigment in mammals. Agouti interacts with the melanocortin 1 receptor to determine whether the melanocyte (pigment cell) produces phaeomelanin (a red to yellow pigment), or eumelanin (a brown to black pigment). This interaction is responsible for making distinct light and dark bands in the hairs of animals such as the agouti, which the gene is named after. In other species such as horses, agouti signalling is responsible for determining which parts of the body will be red or black. Mice with wildtype agouti will be grey, with each hair being partly yellow and partly black. Loss of function mutations in mice and other species cause black fur coloration, while mutations causing expression throughout the whole body in mice cause yellow fur and obesity. The agouti-signaling protein (ASIP) is a competitive antagonist with alpha-Melanocyte-stimulating hormon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agouti-related Peptide
Agouti-related protein (AgRP), also called agouti-related peptide, is a neuropeptide produced in the brain by the AgRP/NPY neuron. It is synthesized in neuropeptide Y (NPY)-containing cell bodies located in the ventromedial part of the arcuate nucleus in the hypothalamus. AgRP is co-expressed with NPY and acts to increase appetite and decrease metabolism and energy expenditure. It is one of the most potent and long-lasting of appetite stimulators. In humans, the agouti-related peptide is encoded by the ''AGRP'' gene. Structure AgRP is a paracrine signaling molecule made of 112 amino acids (the gene product of 132 amino acids is processed by removal of the N-terminal 20-residue signal peptide domain). It was independently identified by two teams in 1997 based on its sequence similarity with agouti signalling peptide (ASIP), a protein synthesized in the skin controlling coat colour. AgRP is approximately 25% identical to ASIP. The murine homologue of AgRP consists of 111 amino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-carboline
β-Carboline (9''H''- pyrido ,4-''b'' ndole) represents the basic chemical structure for more than one hundred alkaloids and synthetic compounds. The effects of these substances depend on their respective substituent. Natural β-carbolines primarily influence brain functions but can also exhibit antioxidant effects. Synthetically designed β-carboline derivatives have recently been shown to have neuroprotective, cognitive enhancing and anti-cancer properties. Pharmacology The pharmacological effects of specific β-carbolines are dependent on their substituents. For example, the natural β-carboline harmine has substituents on position 7 and 1. Thereby, it acts as a selective inhibitor of the DYRK1A protein kinase, a molecule necessary for neurodevelopment. It also exhibits various antidepressant-like effects in rats by interacting with serotonin receptor 2A. Furthermore, it increases levels of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in rat hippocampus. A decreased BDNF le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiogenic
An anxiogenic or panicogenic substance is one that causes anxiety. This effect is in contrast to anxiolytic agents, which inhibits anxiety. Together these categories of psychoactive compounds may be referred to as anxiotropic compounds. Anxiogenic effects can be measured by, for example, the hole-board test in rats and mice. A number of agents are used to provoke anxiety (anxiogens) or panic (panicogens) in experimental models. Some of the most common substances are: carbon dioxide (as carbogen), sodium lactate, cocaine, substituted amphetamines, caffeine, L-DOPA, methylphenidate, modafinil, GABA antagonists such as DMCM, FG-7142 and ZK-93426, serotonergic agents such as mCPP and LY-293,284, adrenergic agents such as yohimbine, psychoactive agents such as THC and LSD in susceptible individuals, antipsychotics/dopamine antagonists such as ecopipam and reserpine, and cholecystokinin (CCK) (especially the tetrapeptide and octapeptide fragments CCK-4 and CCK-8). Sodium lactate g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convulsive
A convulsion is a medical condition where the body muscles contract and relax rapidly and repeatedly, resulting in uncontrolled shaking. Because epileptic seizures typically include convulsions, the term ''convulsion'' is sometimes used as a synonym for ''seizure''. However, not all epileptic seizures lead to convulsions, and not all convulsions are caused by epileptic seizures. Convulsions are also consistent with an electric shock and improper enriched air scuba diving. Non-epileptic convulsions have no relation with epilepsy, and are caused by non-epileptic seizures. Convulsion is a common term generally describing uncontrollable muscle contractions. The term convulsion has been used interchangeably with the word "seizure". Seizures may cause a person to have convulsions, but this is not always the case. Convulsion is a type of seizure that involves bursts of electrical activity in the brain. Occasionally the reason for a convulsion is unfamiliar. A convulsion may be caused ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |