|
International Financial Control
The International Financial Control ( el, Διεθνής Οικονομικός Έλεγχος) was the supervision of the public finances of Greece which was imposed by European powers, who had lent Greece in autumn of 1897 when the country bankrupted four years earlier. The goal was the payment of the country's debts to its creditors. The control was exercised by a six-person commission, the ''International Financial Commission'' (official name, in french: Commission Internationale Financière de la Grèce). Background and precedent international practice Between 1857 and 1859, UK, France and Russia created the International Financial Commission of Inquiry, a commission whose goal was reporting Greece's capability of repaying the debt of 1833. This commission, by the intervention of Russia, did not have the role of controlling the economy and ensuring payments; it was restricted to an advisory role. The result from the work of this commission was the payment of an instalment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Greece
The Kingdom of Greece ( grc, label=Greek, Βασίλειον τῆς Ἑλλάδος ) was established in 1832 and was the successor state to the First Hellenic Republic. It was internationally recognised by the Treaty of Constantinople, where Greece also secured its full independence from the Ottoman Empire after nearly four centuries. The Kingdom of Greece was dissolved in 1924 and the Second Hellenic Republic was established following Greece's defeat by Turkey in the Asia Minor Campaign. A military ''coup d'état'' restored the monarchy in 1935 and Greece became a Kingdom again until 1973. The Kingdom was finally dissolved in the aftermath of a seven-year military dictatorship (1967–1974) and the Third Hellenic Republic was established following a referendum held in 1974. Background The Greek-speaking Eastern Roman Empire, also known as Byzantine Empire, which ruled most of the Eastern Mediterranean region for over 1100 years, had been fatally weakened since the sackin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War and was dissolved shortly after its defeat in the First World War. Austria-Hungary was ruled by the House of Habsburg and constituted the last phase in the constitutional evolution of the Habsburg monarchy. It was a multinational state and one of Europe's major powers at the time. Austria-Hungary was geographically the second-largest country in Europe after the Russian Empire, at and the third-most populous (after Russia and the German Empire). The Empire built up the fourth-largest machine building industry in the world, after the United States, Germany and the United Kingdom. Austria-Hungary also became the world's third-largest manufacturer and exporter of electric home appliances, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
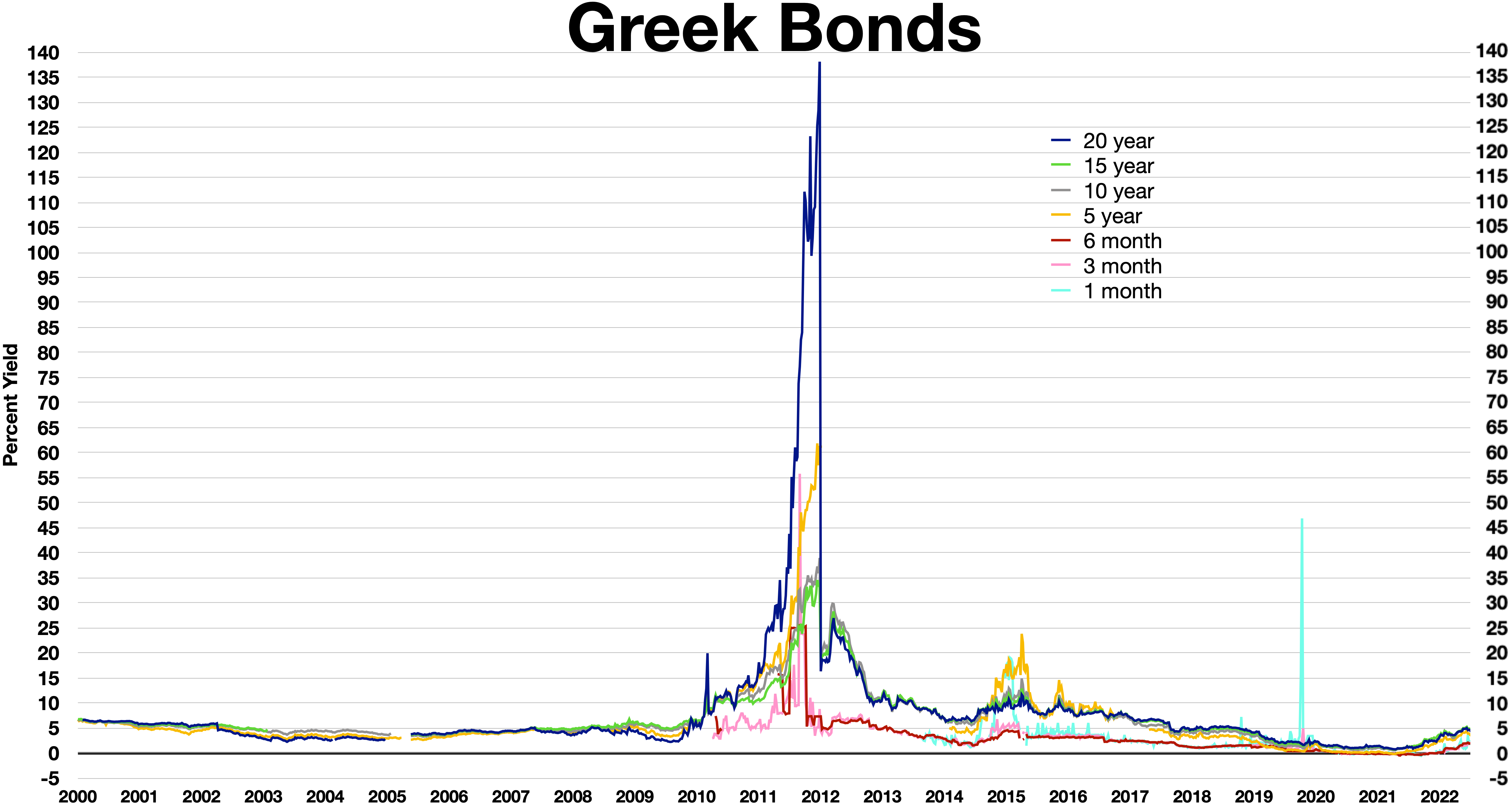
Economic History Of Greece
The economic history of the Greek World spans several millennia and encompasses many modern-day nation states. Since the focal point of the center of the Greek World often changed it is necessary to enlarge upon all these areas as relevant to the time. The economic history of Greece refers to the economic history of the Greek nation state since 1829. Earliest Greek civilizations Cycladic civilization Cycladic civilization is the earliest trading center of goods. It was extensively distributed throughout the Aegean region. Minoan civilization The Minoan civilization emerged on Crete around the time the early Bronze Age, it had a wide range of economic interests and was something of a trade hub, exporting many items to mainland Greece as well as the Egyptian Empire of the period. The Minoans were also innovators, developing (or adopting) a system of lead weights to facilitate economic transactions. Despite this Minoan civilization remained, for the most part, an agriculturally d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleftherotypia
''Eleftherotypia'' ( el, Ελευθεροτυπία, lit=freedom of the press) was a daily national newspaper published in Athens, Greece. Published since 21 July 1975, it was the first newspaper to appear after the fall of the Regime of the Colonels, and for most of its period had been one of the two most widely circulated newspapers in the country. Generally taking a center-left, socialist stance, it was highly respected for its independence and impartiality. Following the economic downturn in Greece, the newspaper had to file for bankruptcy in 2011. Briefly taken over by a new publisher, lawyer Harris Oikonomopoulos, it was finally shut down in November 2014. Profile From the beginning, ''Eleftherotypia'' had been an opposition voice against the governments of the conservative Nea Demokratia party. Editors often adopted a social-democratic stance on a number of issues, but more radical viewpoints are also frequently represented in the paper, to a notably greater extent than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rizospastis
''Rizospastis'' ( el, Ριζοσπάστης, "The Radical") is the official newspaper of the Communist Party of Greece. It has been published daily since its first issue in 1916. Liana Kanelli is currently one of the senior editors of the newspaper. Motto "Organ of the Communist Party's Central Committee" and "Proletarians of all countries unite!" See also *Nikos Boyiopoulos References External links * Publications established in 1916 1916 establishments in Greece Greek-language newspapers Newspapers published in Athens Communist newspapers Communist Party of Greece Daily newspapers published in Greece {{Greece-newspaper-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultanate Of Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to the east, and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to the south. Mauritania lies to the south of Western Sahara. Morocco also claims the Spanish exclaves of Ceuta, Melilla and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, and several small Spanish-controlled islands off its coast. It spans an area of or , with a population of roughly 37 million. Its official and predominant religion is Islam, and the official languages are Arabic and Berber; the Moroccan dialect of Arabic and French are also widely spoken. Moroccan identity and culture is a mix of Arab, Berber, and European cultures. Its capital is Rabat, while its largest city is Casablanca. In a region inhabited since the Paleolithic Era over 300,000 years ago, the first Moroccan state was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moroccan Debt Administration
The Moroccan Debt Administration (french: administration de la dette marocaine), formally known as the ''Contrôle de la dette'' from 1904 to 1910 and after that as the ''Administration du Contrôle de la dette publique mahghzénienne'' (referring to the Moroccan monarchy as the Makhzen), was an entity set up by the French government in 1904 to administer the sovereign debt of the Moroccan Monarchy. History The Moroccan Debt Administration originated in 1904, as Morocco's sovereign debt, which had increased significantly following the Hispano-Moroccan War (1859–1860) and the First Melillan campaign of 1894, was restructured by the Banque de Paris et des Pays-Bas (BPPB) in coordination with the French government. as a consequence, France became the only creditor of the Moroccan government. The loan contract was signed on by Moroccan Foreign Minister Si Abdelkrim Ben Slimane, Moroccan Finance Minister Si Mohammed Tazi, and the BPPB's representative Georges Zangarussiano. The loa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khedivate Of Egypt
The Khedivate of Egypt ( or , ; ota, خدیویت مصر ') was an autonomous tributary state of the Ottoman Empire, established and ruled by the Muhammad Ali Dynasty following the defeat and expulsion of Napoleon Bonaparte's forces which brought an end to the short-lived French occupation of Lower Egypt. The Khedivate of Egypt had also expanded to control present-day Sudan, South Sudan, Eritrea, Djibouti, north western Somalia, north Eastern Ethiopia, Israel, Lebanon, Jordan, Syria, Greece, Cyprus, southern and central Turkey, in addition to parts from Libya, Chad, Central African Republic, and Democratic Republic of Congo, as well as northwestern Saudi Arabia, parts of Yemen and the Kingdom of Hejaz. The United Kingdom invaded and took control in 1882. In 1914 the Ottoman Empire connection was ended and Britain established a protectorate called the Sultanate of Egypt. History Rise of Muhammad Ali Upon the conquest of the Sultanate of Egypt by the Ottoman Empire in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caisse De La Dette
The Caisse de la Dette Publique ("Public Debt Commission") was an international commission established by a decree issued by Khedive Ismail of Egypt on 2 May 1876 to supervise the payment by the Egyptian government of the loans to the European governments following the construction of the Suez Canal. It was initially led by a secretary and three commissioners representing the governments of Austria-Hungary, France and Italy; from 1877 the United Kingdom and from 1885 Russia and Germany. One of the Commissioners would serve as the President, or Chairman, of the Commission. "This system was under the control of two main countries, France and Britain. This system of 'dual control' represented Europeans direct intervention in Egypt's financial affairs." The Public Debt Commission was abolished by a bilateral agreement between the British and the Egyptian governments, signed on 17 July 1940,Text in ''League of Nations Treaty Series'', vol. 202, pp. 98-105. due to Allied interest in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Of Piraeus
The Port of Piraeus ( el, Λιμάνι του Πειραιά) is the chief sea port of Athens, Greece, located on the Saronic Gulf on the western coasts of the Aegean Sea, the largest port in Greece and List of busiest ports in Europe, one of the largest in Europe. The Chinese state-owned COSCO Shipping owns the port. History The Port of Piraeus served as the port of Athens since Ancient Greece, ancient times. Early Antiquity Until the 3rd millennium BC, Piraeus was a rocky island connected to the mainland by a low-lying stretch of land that was flooded with sea water most of the year. It was then that the area was increasingly silted and flooding ceased, thus permanently connecting Piraeus to Attica and forming its ports, the main port of Cantharus and the two smaller of Zea and Munichia. In 493 BC, Themistocles initiated the fortifications of Piraeus and later advised the Athenians to take advantage of its natural harbours' strategic potential. In 483 BC, the Athenian navy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naxos Emery
Naxos (; el, Νάξος, ) is a Greek island and the largest of the Cyclades. It was the centre of archaic Cycladic culture. The island is famous as a source of emery, a rock rich in corundum, which until modern times was one of the best abrasives available. The largest town and capital of the island is Chora or Naxos City, with 7,374 inhabitants (2011 census). The main villages are Filoti, Apiranthos, Vivlos, Agios Arsenios, Koronos and Glynado. Geography Climate Naxos experiences a Mediterranean climate, with relatively mild winters and warm summers. The Köppen Climate Classification subtype for this climate is "Csa". (Mediterranean Climate). Inland areas of the island are much wetter and cooler in winter. Mythic Naxos According to Greek mythology, the young Zeus was raised in a cave on Mt. Zas ("''Zas''" meaning "''Zeus''"). Homer mentions " Dia"; literally the sacred island "of the Goddess". Károly Kerényi explains: One legend has it that in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kathimerini
''Kathimerini'' (Greek: Η Καθημερινή, pronounced kaθimeriˈni meaning ''The Daily'') is a daily, political and financial morning newspaper published in Athens. Its first edition was printed on September 15, 1919. and it is considered the leading newspaper in Greece, with both the highest circulation and a strong digital presence. It is published in Greek and there is also an English edition, both print and digital. ''Kathimerini English Edition'' is published in Greece and Cyprus along with the ''New York Times International''. ''Kathimerini'' also produces a wide range of leading magazines, including ''Vogue Greece'' with ''Conde Nast International'', as well as publications for The Walt Disney Company Greece. Considered Greece's paper of record, ''Kathimerini'' traditionally identifies with a broad range of the political spectrum, from the liberal center to the moderate right, while covering the positions and hosting analyses from all the main political parties an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |