|
Interleukin-28 Receptor
Interleukin-28 receptor is a type II cytokine receptor found largely in epithelial cells. It binds type 3 interferons, interleukin-28 A (Interferon lambda 1), Interleukin-28B (Interferon lambda 2), interleukin 29 (Interferon lambda 3) and interferon lambda 4. It consists of an α chain and shares a common β subunit with the interleukin-10 receptor. Binding to the interleukin-28 receptor, which is restricted to select cell types, is important for fighting infection. Binding of the type 3 interferons to the receptor results in activation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Structure The interleukin 28 receptor consists of an interleukin-28R alpha chain (IL-28RA) and another receptor, the beta subunit of the Interleukin-10 receptor ( IL-10R2). IL-10R2 is part of the receptor for other cytokines such as IL-10, IL-22, IL-26, and IL-20. The IL-28Ra chain is a part of the cytokine receptor family 2. The IL-28Ra chain is important for recognition and ligand specificity, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 28 Receptor, Alpha Subunit
Interleukin 28 receptor, alpha subunit is a subunit for the interleukin-28 receptor. IL28RA is its human gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba .... The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the class II cytokine receptor family. This protein forms a receptor complex with interleukin 10 receptor, beta (IL10RB). The receptor complex has been shown to interact with three closely related cytokines, including interleukin 28A (IL28A), interleukin 28B (IL28B), and interleukin 29 (IL29). The expression of all three cytokines can be induced by viral infection. The cells overexpressing this protein have been found to have enhanced responses to IL28A and IL29, but decreased response to IL28B. Three alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer (stratum basale) composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. The human epidermis is a familiar example of epithelium, particularly a stratified squamous epithelium. The word epidermis is derived through Latin , itself and . Something related to or part of the epidermis is termed epidermal. Structure Cellular components The epidermis primarily consists of keratinocytes ( proliferating basal and differentiated suprabasal), which comprise 90% of its cells, but also contains melanocytes, Langerhans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STAT3
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is a transcription factor which in humans is encoded by the ''STAT3'' gene. It is a member of the STAT protein family. Function STAT3 is a member of the STAT protein family. In response to cytokines and growth factors, STAT3 is phosphorylated by receptor-associated Janus kinases (JAK), forms homo- or heterodimers, and translocates to the cell nucleus where it acts as a transcription activator. Specifically, STAT3 becomes activated after phosphorylation of tyrosine 705 in response to such ligands as interferons, epidermal growth factor (EGF), Interleukin (IL-)5 and IL-6. Additionally, activation of STAT3 may occur via phosphorylation of serine 727 by Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) and through c-src non-receptor tyrosine kinase. STAT3 mediates the expression of a variety of genes in response to cell stimuli, and thus plays a key role in many cellular processes such as cell growth and apoptosis. STAT3-deficien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IRF9
Interferon regulatory factor 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IRF9'' gene, previously known as ISGF3G. Interactions IRF9 has been shown to interact with STAT2 and STAT1 Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) is a transcription factor which in humans is encoded by the ''STAT1'' gene. It is a member of the STAT protein family. Function All STAT molecules are phosphorylated by receptor associa .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * * * Transcription factors {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are expressed in the desired cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are up to 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STAT2
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''STAT2'' gene. It is a member of the STAT protein family. This protein is critical to the biological response of type I interferons (IFNs). STAT2 sequence identity between mouse and human is only 68%. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the STAT protein family. In response to cytokines and growth factors, STAT family members are phosphorylated by the receptor associated kinases, and then form homo- or heterodimers that translocate to the cell nucleus where they act as transcription activators. In response to IFN, this protein forms a complex with STAT1 and IFN regulatory factor family protein p48 (IRF9) and form ISGF-3 (IFN-stimulated gene factor-3), in which this protein acts as a transactivator, but lacks the ability to bind DNA directly. ISGF-3 proceeds the activation of genes via the IFN-stimulated response element (ISRE). ISRE-driven genes include Ly-6C, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STAT1
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) is a transcription factor which in humans is encoded by the ''STAT1'' gene. It is a member of the STAT protein family. Function All STAT molecules are phosphorylated by receptor associated kinases, that causes activation, dimerization by forming homo- or heterodimers and finally translocate to nucleus to work as transcription factors. Specifically STAT1 can be activated by several ligands such as Interferon alpha (IFNα), Interferon gamma (IFNγ), Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF), Platelet Derived Growth Factor (PDGF), Interleukin 6 (IL-6), or IL-27. Type I interferons (IFN-α, IFN-ß) bind to receptors, cause signaling via kinases, phosphorylate and activate the Jak kinases TYK2 and JAK1 and also STAT1 and STAT2. STAT molecules form dimers and bind to ISGF3G/IRF-9, which is Interferon stimulated gene factor 3 complex with Interferon regulatory Factor 9. This allows STAT1 to enter the nucleus. STAT1 has a key role in many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
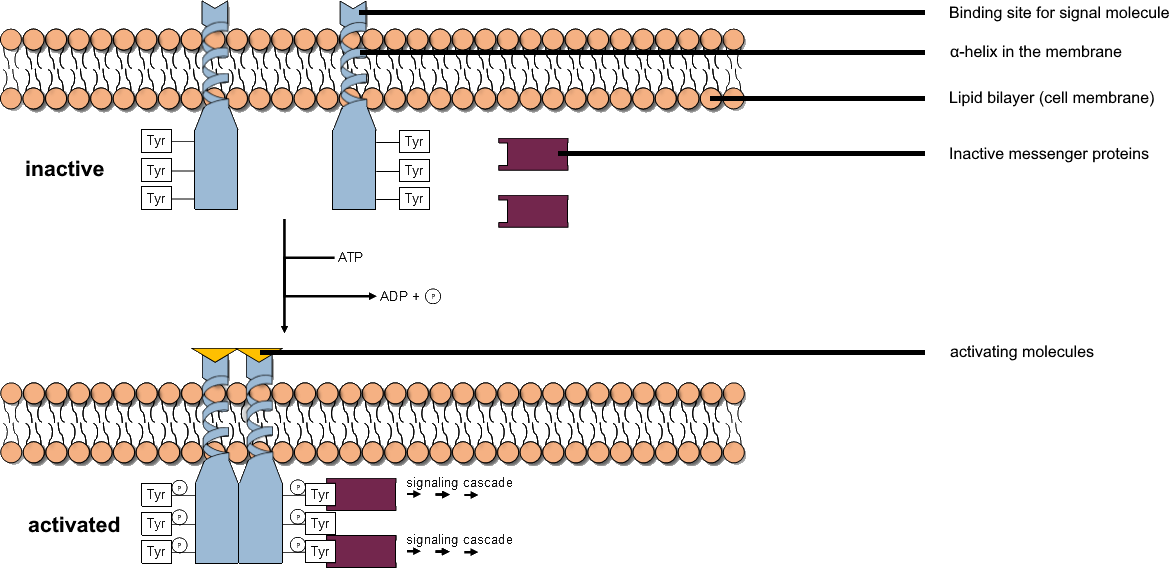
Tyrosine Kinase 2
Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''TYK2'' gene. Tyk2 was the first member of the JAK family that was described (the other members are JAK1, JAK2, and JAK3). It has been implicated in IFN-α, IL-6, IL-10 and IL-12 signaling. Function This gene encodes a member of the tyrosine kinase and, to be more specific, the Janus kinases (JAKs) protein families. This protein associates with the cytoplasmic domain of type I and type II cytokine receptors and promulgate cytokine signals by phosphorylating receptor subunits. It is also component of both the type I and type III interferon signaling pathways. As such, it may play a role in anti-viral immunity. Cytokines play pivotal roles in immunity and inflammation by regulating the survival, proliferation, differentiation, and function of immune cells, as well as cells from other organ systems. Hence, targeting cytokines and their receptors is an effective means of treating such diso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janus Kinase 1
JAK1 is a human tyrosine kinase protein essential for signaling for certain type I and type II cytokines. It interacts with the common gamma chain (γc) of type I cytokine receptors, to elicit signals from the IL-2 receptor family (e.g. IL-2R, IL-7R, IL-9R and IL-15R), the IL-4 receptor family (e.g. IL-4R and IL-13R), the gp130 receptor family (e.g. IL-6R, IL-11R, LIF-R, OSM-R, cardiotrophin-1 receptor (CT-1R), ciliary neurotrophic factor receptor (CNTF-R), neurotrophin-1 receptor (NNT-1R) and Leptin-R). It is also important for transducing a signal by type I (IFN-α/β) and type II (IFN-γ) interferons, and members of the IL-10 family via type II cytokine receptors. Jak1 plays a critical role in initiating responses to multiple major cytokine receptor families. Loss of Jak1 is lethal in neonatal mice, possibly due to difficulties suckling. Expression of JAK1 in cancer cells enables individual cells to contract, potentially allowing them to escape their tumor and metas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine Kinase
A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the tyrosine residues of specific proteins inside a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions. Tyrosine kinases belong to a larger class of enzymes known as protein kinases which also attach phosphates to other amino acids such as serine and threonine. Phosphorylation of proteins by kinases is an important mechanism for communicating signals within a cell (signal transduction) and regulating cellular activity, such as cell division. Protein kinases can become mutated, stuck in the "on" position, and cause unregulated growth of the cell, which is a necessary step for the development of cancer. Therefore, kinase inhibitors, such as imatinib and osimertinib, are often effective cancer treatments. Most tyrosine kinases have an associated protein tyrosine phosphatase, which removes the phosphate group. Reaction Protein kinases are a group of enzymes that possess a catal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
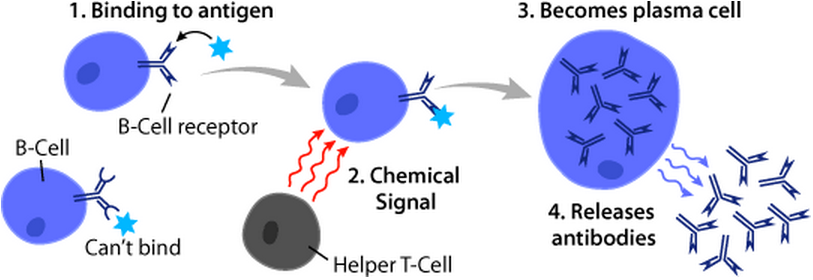
B Cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed. B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cells and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins CD8 or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |