|
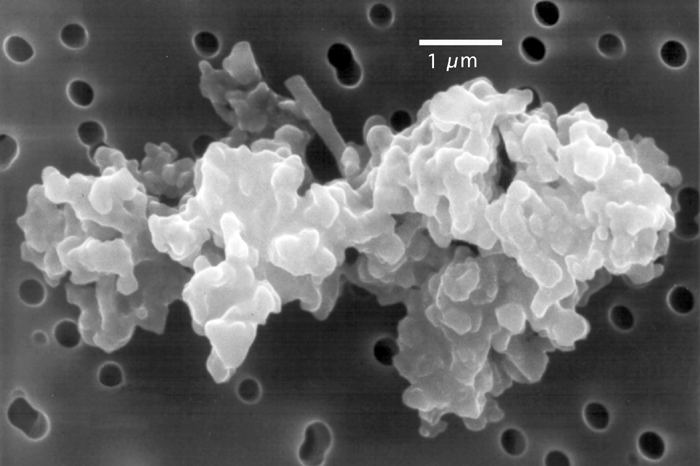
Intergalactic Dust
Intergalactic dust is cosmic dust in between galaxies in intergalactic space. Evidence for intergalactic dust has been suggested as early as 1949, and study of it grew throughout the late 20th century. There are large variations in the distribution of intergalactic dust. The dust may affect intergalactic distance measurements, such as to supernovae and quasars in other galaxies. Intergalactic dust can form intergalactic dust clouds, known since the 1960s to exist around some galaxies. By the 1980s, at least four intergalactic dust clouds had been discovered within several megaparsecs of the Milky Way galaxy, exemplified by the Okroy Cloud. See also * Astrochemistry * Atomic and molecular astrophysics * Cosmochemistry * Extragalactic astronomy * Extraterrestrial materials * Hypervelocity star * Intergalactic medium * Intergalactic space * Intergalactic star * Interstellar medium * List of interstellar and circumstellar molecules * Warm–hot intergalactic medium The warm–hot i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Dust
Cosmic dust, also called extraterrestrial dust, star dust or space dust, is dust which exists in outer space, or has fallen on Earth. Most cosmic dust particles measure between a few molecules and 0.1 mm (100 micrometers). Larger particles are called meteoroids. Cosmic dust can be further distinguished by its astronomical location: intergalactic dust, interstellar dust, interplanetary dust (such as in the zodiacal cloud) and circumplanetary dust (such as in a planetary ring). There are several methods to obtain space dust measurement. In the Solar System, interplanetary dust causes the zodiacal light. Solar System dust includes comet dust, asteroidal dust, dust from the Kuiper belt, and interstellar dust passing through the Solar System. Thousands of tons of cosmic dust are estimated to reach the Earth's surface every year, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warm–hot Intergalactic Medium
The warm–hot intergalactic medium (WHIM) is the sparse, warm-to-hot (105 to 107 K) plasma that cosmologists believe to exist in the spaces between galaxies and to contain 40–50% of the baryonic 'normal matter' in the universe at the current epoch. The WHIM can be described as a web of hot, diffuse gas stretching between galaxies, and consists of plasma, as well as atoms and molecules, in contrast to dark matter. The WHIM is a proposed solution to the missing baryon problem, where the observed amount of baryonic matter does not match theoretical predictions from cosmology. Much of what is known about the warmhot intergalactic medium comes from computer simulations of the cosmos. The WHIM is expected to form a filamentary structure of tenuous, highly ionized baryons with a density of 1−10 particles per cubic meter. Within the WHIM, gas shocks are created as a result of active galactic nuclei, along with the gravitationally-driven processes of merging and accretion. Part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Interstellar And Circumstellar Molecules
This is a list of molecules that have been detected in the interstellar medium and circumstellar envelopes, grouped by the number of component atoms. The chemical formula is listed for each detected compound, along with any ionized form that has also been observed. Background The molecules listed below were detected through astronomical spectroscopy. Their spectral features arise because molecules either absorb or emit a photon of light when they transition between two molecular energy levels. The energy (and thus the wavelength) of the photon matches the energy difference between the levels involved. Molecular electronic transitions occur when one of the molecule's electrons moves between molecular orbitals, producing a spectral line in the ultraviolet, optical or near-infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. Alternatively, a vibrational transition transfers quanta of energy to (or from) vibrations of molecular bonds, producing signatures in the mid- or far-infrared. Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstellar Medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter and radiation that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstellar space and blends smoothly into the surrounding intergalactic space. The energy that occupies the same volume, in the form of electromagnetic radiation, is the interstellar radiation field. The interstellar medium is composed of multiple phases distinguished by whether matter is ionic, atomic, or molecular, and the temperature and density of the matter. The interstellar medium is composed, primarily, of hydrogen, followed by helium with trace amounts of carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen. The thermal pressures of these phases are in rough equilibrium with one another. Magnetic fields and turbulent motions also provide pressure in the ISM, and are typically more important, dynamically, than the thermal pressure is. In the interstellar medium, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intergalactic Star
An intergalactic star, also known as an intracluster star or a rogue star, is a star not gravitationally bound to any galaxy. Although a source of much discussion in the scientific community during the late 1990s, intergalactic stars are now generally thought to have originated in galaxies, like other stars, before being expelled as the result of either galaxies colliding or of a multiple-star system traveling too close to a supermassive black hole, which are found at the center of many galaxies. Collectively, intergalactic stars are referred to as the intracluster stellar population, or IC population for short, in the scientific literature. Discovery The hypothesis that stars exist only in galaxies was disproven in 1997 with the discovery of intergalactic stars. The first to be discovered were in the Virgo cluster of galaxies, where some one trillion are now surmised to exist. Formation The way these stars arise is still a mystery, but several scientifically credible hypothesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intergalactic Space
Outer space, commonly shortened to space, is the expanse that exists beyond Earth and its atmosphere and between celestial bodies. Outer space is not completely empty—it is a near-perfect vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium, as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust, and cosmic rays. The baseline temperature of outer space, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is . The plasma between galaxies is thought to account for about half of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in the universe, having a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a kinetic temperature of millions of kelvins. Local concentrations of matter have condensed into stars and galaxies. Studies indicate that 90% of the mass in most galaxies is in an unknown form, called dark matter, which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. Observations sugges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intergalactic Medium
{{disambiguation ...
Intergalactic may refer to: * "Intergalactic" (song), a song by the Beastie Boys * ''Intergalactic'' (TV series), a 2021 UK science fiction TV series * Intergalactic space * Intergalactic travel, travel between galaxies in science fiction and speculation See also * *Interstellar (other) *Interplanetary (other) *Entergalactic (other) Entergalactic may refer to: * ''Entergalactic'' (album), a 2022 album by Kid Cudi * ''Entergalactic'' (TV special), a TV special on Netflix ** ''Entergalactic (Original Score)'', a film score composed by Dot da Genius and Plain Pat * "Enter Gala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypervelocity Star
In astronomy, stellar kinematics is the observational study or measurement of the kinematics or motions of stars through space. Stellar kinematics encompasses the measurement of stellar velocities in the Milky Way and its satellites as well as the internal kinematics of more distant galaxies. Measurement of the kinematics of stars in different subcomponents of the Milky Way including the thin disk, the thick disk, the bulge, and the stellar halo provides important information about the formation and evolutionary history of our Galaxy. Kinematic measurements can also identify exotic phenomena such as hypervelocity stars escaping from the Milky Way, which are interpreted as the result of gravitational encounters of binary stars with the supermassive black hole at the Galactic Center. Stellar kinematics is related to but distinct from the subject of stellar dynamics, which involves the theoretical study or modeling of the motions of stars under the influence of gravity. Stella ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extragalactic Astronomy
Extragalactic astronomy is the branch of astronomy concerned with objects outside the Milky Way galaxy. In other words, it is the study of all astronomical objects which are not covered by galactic astronomy. The closest objects in extragalactic astronomy include the galaxies of the Local Group, which are close enough to allow very detailed analyses of their contents (e.g. supernova remnants, stellar associations). As instrumentation has improved, distant objects can now be examined in more detail and so extragalactic astronomy includes objects at nearly the edge of the observable universe. Research into distant galaxies (outside of our local group) is valuable for studying aspects of the universe such as galaxy evolution and Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) which give insight into physical phenomena (e.g. super massive black hole accretion and the presence of dark matter). It is through extragalactic astronomy that astronomers and physicists are able to study the effects of General ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. Galaxies, averaging an estimated 100 million stars, range in size from dwarfs with less than a hundred million stars, to the largest galaxies known – supergiants with one hundred trillion stars, each orbiting its galaxy's center of mass. Most of the mass in a typical galaxy is in the form of dark matter, with only a few percent of that mass visible in the form of stars and nebulae. Supermassive black holes are a common feature at the centres of galaxies. Galaxies are categorized according to their visual morphology as elliptical, spiral, or irregular. Many are thought to have supermassive black holes at their centers. The Milky Way's central black hole, known as Sagittarius A*, has a mass four million times greater than the Sun. As o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmochemistry
Cosmochemistry (from Greek κόσμος ''kósmos'', "universe" and χημεία ''khemeía'') or chemical cosmology is the study of the chemical composition of matter in the universe and the processes that led to those compositions. This is done primarily through the study of the chemical composition of meteorites and other physical samples. Given that the asteroid parent bodies of meteorites were some of the first solid material to condense from the early solar nebula, cosmochemists are generally, but not exclusively, concerned with the objects contained within the Solar System. History In 1938, Swiss mineralogist Victor Goldschmidt and his colleagues compiled a list of what they called "cosmic abundances" based on their analysis of several terrestrial and meteorite samples. Goldschmidt justified the inclusion of meteorite composition data into his table by claiming that terrestrial rocks were subjected to a significant amount of chemical change due to the inherent processes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |