|
Integral Windup
Integral windup, also known as integrator windup or reset windup, refers to the situation in a PID feedback controller where a large change in setpoint occurs (say a positive change) and the integral term accumulates a significant error during the rise (windup), thus overshooting and continuing to increase as this accumulated error is unwound (offset by errors in the other direction). The specific problem is the excess overshooting. Solutions This problem can be addressed by * Initializing the controller integral to a desired value, for instance to the value before the problem * Increasing the setpoint in a suitable ramp * "Conditional Integration"--disabling the integral function until the to-be-controlled process variable (PV) has entered the controllable region * Preventing the integral term from accumulating above or below pre-determined bounds * Back-calculating the integral term to constrain the process output within feasible bounds. * Zeroing the integral value every time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PID Feedback Controller
PID or Pid may refer to: Medicine * Pelvic inflammatory disease or pelvic inflammatory disorder, an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system * Primary immune deficiency, disorders in which part of the body's immune system is missing or does not function properly * Prolapsed intervertebral disc, commonly called a herniated disc Science, technology and engineering * BBC Programme Identifier, a unique identifier for a BBC television or radio programme brand, a season or series, or an individual episode * OBD-II PIDs (on-board diagnostics parameter IDs), requests for data through an OBD connector in automotive repair * Packet Identifier, a field in a MPEG transport stream packet * Passive infrared detector, a passive infrared sensor * Persistent identifier, a long-lasting reference to a document, file, web page, or other object * Phosphotyrosine-interacting domain, also known as phosphotyrosine-binding domain, a protein domain which bind to phosphotyrosine * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
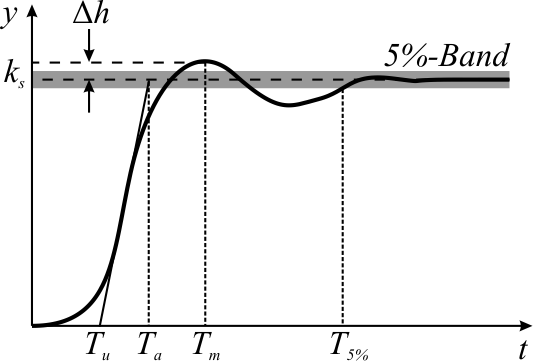
Overshoot (signal)
In signal processing, control theory, electronics, and mathematics, overshoot is the occurrence of a signal or function exceeding its target. Undershoot is the same phenomenon in the opposite direction. It arises especially in the step response of bandlimited systems such as low-pass filters. It is often followed by ringing, and at times conflated with the latter. Definition Maximum overshoot is defined in Katsuhiko Ogata's ''Discrete-time control systems'' as "the maximum peak value of the response curve measured from the desired response of the system." Control theory In control theory, overshoot refers to an output exceeding its final, steady-state value. For a step input, the ''percentage overshoot'' (PO) is the maximum value minus the step value divided by the step value. In the case of the unit step, the ''overshoot'' is just the maximum value of the step response minus one. Also see the definition of ''overshoot'' in an electronics context. For second-order sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Process Variable
In control theory, a process variable (PV; also process value or process parameter) is the current measured value of a particular part of a process which is being monitored or controlled. An example of this would be the temperature of a furnace. The current temperature is the process variable, while the desired temperature is known as the set-point (SP). Control system use Measurement of process variables is essential in control systems to controlling a process. The value of the process variable is continuously monitored so that control may be exerted. Four commonly measured variables that affect chemical and physical processes are: pressure, temperature, level and flow. but there are in fact a large number of measurement quantities which for international purposes use the International System of Units (SI) The SP-PV error is used to exert control on a process so that the value of PV equals the value of the SP. A classic use of this is in the PID controller A proportio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturation
Saturation, saturated, unsaturation or unsaturated may refer to: Chemistry * Saturation, a property of organic compounds referring to carbon-carbon bonds **Saturated and unsaturated compounds ** Degree of unsaturation **Saturated fat or fatty acid **Unsaturated fat or fatty acid * Non-susceptibility of an organometallic compound to oxidative addition * Saturation of protein binding sites * Saturation of enzymes with a substrate * Saturation of a solute in a solution, as related to the solute's maximum solubility at equilibrium ** Supersaturation, where the concentration of a solute exceeds its maximum solubility at equilibrium ** Undersaturation, where the concentration of a solute is less than its maximum solubility at equilibrium Biology * Oxygen saturation, a clinical measure of the amount of oxygen in a patient's blood * Saturation pollination, a pollination technique * Saturated mutagenesis, a form of site-directed mutagenesis * Saturation (genetic), the observed number o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Electronics
Analogue electronics ( en-US, analog electronics) are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal. The word analogue is derived from the el, word ανάλογος (analogos) meaning "proportional". Analogue signals An analogue signal uses some attribute of the medium to convey the signal's information. For example, an aneroid barometer uses the angular position of a needle as the signal to convey the information of changes in atmospheric pressure. Electrical signals may represent information by changing their voltage, current, frequency, or total charge. Information is converted from some other physical form (such as sound, light, temperature, pressure, position) to an electrical signal by a transducer which converts one type of energy into another (e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Control System
A distributed control system (DCS) is a computerised control system for a process or plant usually with many control loops, in which autonomous controllers are distributed throughout the system, but there is no central operator supervisory control. This is in contrast to systems that use centralized controllers; either discrete controllers located at a central control room or within a central computer. The DCS concept increases reliability and reduces installation costs by localising control functions near the process plant, with remote monitoring and supervision. Distributed control systems first emerged in large, high value, safety critical process industries, and were attractive because the DCS manufacturer would supply both the local control level and central supervisory equipment as an integrated package, thus reducing design integration risk. Today the functionality of Supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) and DCS systems are very similar, but DCS tends to be u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmable Logic Controller
A programmable logic controller (PLC) or programmable controller is an industrial computer that has been ruggedized and adapted for the control of manufacturing processes, such as assembly lines, machines, robotic devices, or any activity that requires high reliability, ease of programming, and process fault diagnosis. Dick Morley is considered as the father of PLC as he had invented the first PLC, the Modicon 084, for General Motors in 1968. PLCs can range from small modular devices with tens of inputs and outputs (I/O), in a housing integral with the processor, to large rack-mounted modular devices with thousands of I/O, and which are often networked to other PLC and SCADA systems. They can be designed for many arrangements of digital and analog I/O, extended temperature ranges, immunity to electrical noise, and resistance to vibration and impact. Programs to control machine operation are typically stored in battery-backed-up or non-volatile memory. PLCs were first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PID Controller
A proportional–integral–derivative controller (PID controller or three-term controller) is a control loop mechanism employing feedback that is widely used in industrial control systems and a variety of other applications requiring continuously modulated control. A PID controller continuously calculates an ''error value'' e(t) as the difference between a desired setpoint (SP) and a measured process variable (PV) and applies a correction based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms (denoted ''P'', ''I'', and ''D'' respectively), hence the name. In practical terms, PID automatically applies an accurate and responsive correction to a control function. An everyday example is the cruise control on a car, where ascending a hill would lower speed if constant engine power were applied. The controller's PID algorithm restores the measured speed to the desired speed with minimal delay and overshoot by increasing the power output of the engine in a controlled manner. The fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
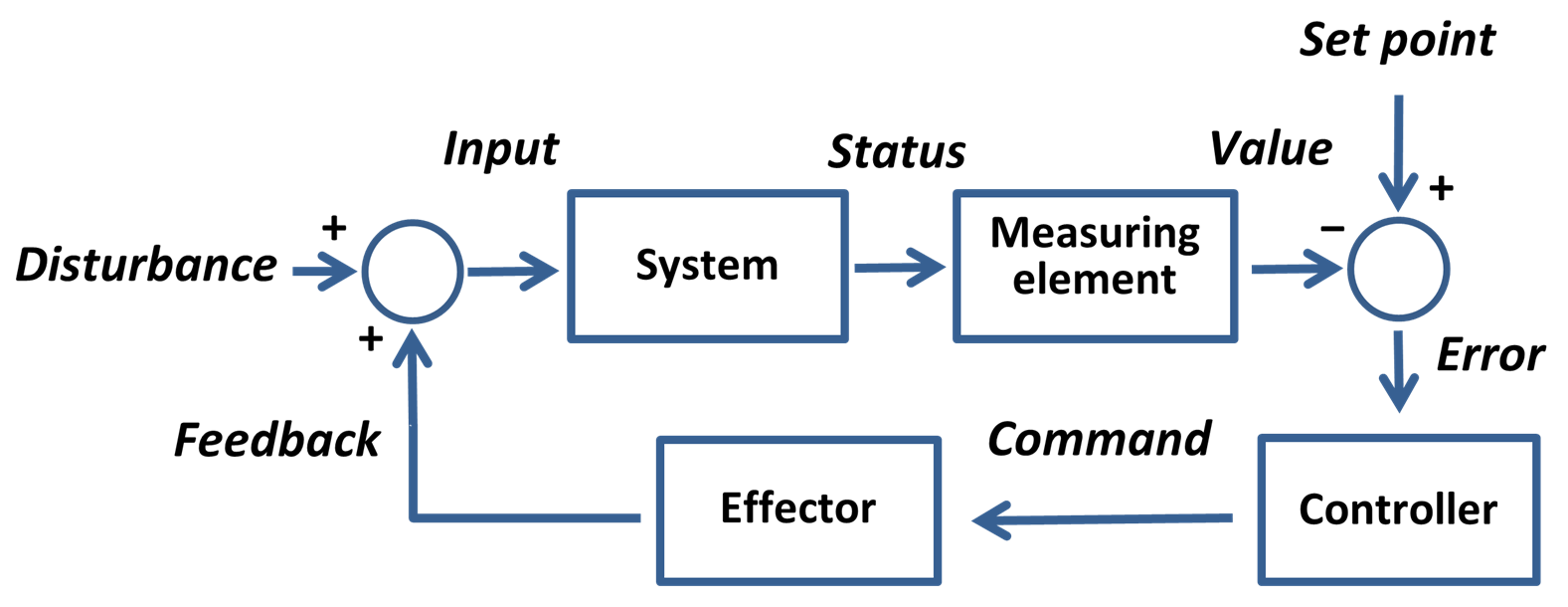
Control Engineering
Control engineering or control systems engineering is an engineering discipline that deals with control systems, applying control theory to design equipment and systems with desired behaviors in control environments. The discipline of controls overlaps and is usually taught along with electrical engineering and mechanical engineering at many institutions around the world. The practice uses sensors and detectors to measure the output performance of the process being controlled; these measurements are used to provide corrective feedback helping to achieve the desired performance. Systems designed to perform without requiring human input are called automatic control systems (such as cruise control for regulating the speed of a car). Multi-disciplinary in nature, control systems engineering activities focus on implementation of control systems mainly derived by mathematical modeling of a diverse range of systems. Overview Modern day control engineering is a relatively new field o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |