|
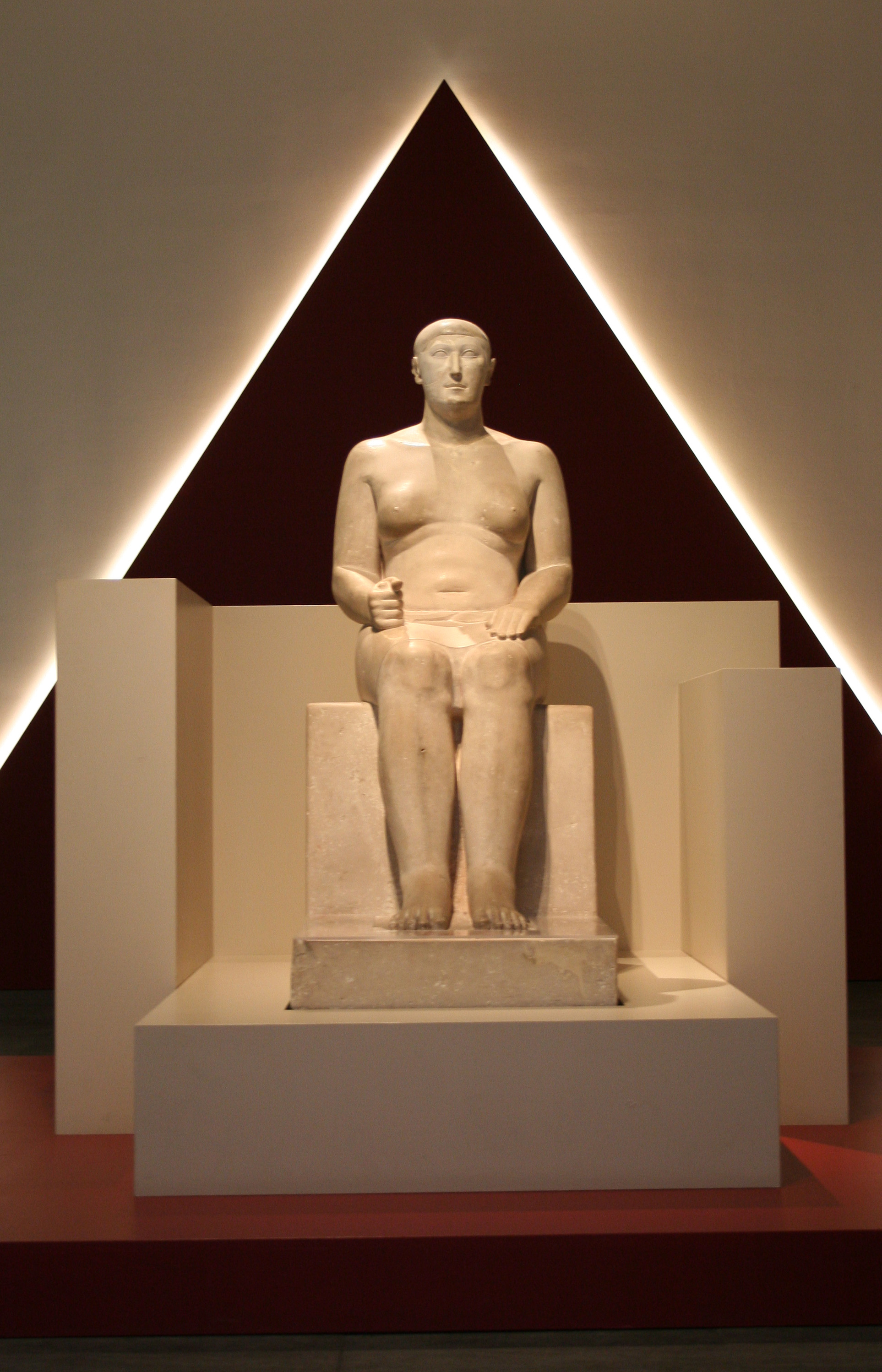
Intefiqer
The ancient Egyptian noble Intefiqer ''(ỉnỉ-ỉt.f ỉqr)'' was ''overseer of the city'' and Vizier under Amenemhet I and Senusret I during the early 12th Dynasty (1991–1802 BC). He is known from several rock inscriptions in Lower Nubia, showing that he was part of a military mission into this region. He appears in an inscription found at the Red Sea coast and in the so-called Reisner Papyrus. Two rock inscriptions in Lower Nubia mention him. They seem to indicate that he was involved in a military campaign into this region. The inscriptions are not dated, but other inscriptions in the region seem to indicate a military campaign in year 29 of Amenemhet I, which corresponds to the 9th year of Senusret I. Intefiqer is also known from a stela found at Wadi el-Hudi, dated to year 20. It reports the bringing of Amethyst. The tomb of his mother Senet in Thebes is in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna in the Theban Necropolis, opposite Luxor. Intefiqer was buried in a mastaba at Lisht Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TT60
The Theban Tomb TT60 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of a woman called Senet. She was related to the ancient Egyptian Vizier Intefiqer (mother or wife). It is one of the earliest burials in the area. Intefiqer was Governor of the city (i.e. Thebes) and Vizier of Senusret I in the 12th Dynasty. His tomb's entrance leads into a long corridor, which in turn leads into an inner chamber with a deep niche. From this room a shaft goes down to the actual burial chamber. In the innermost chapel, Senet is shown in front of an offering table. Other scenes show Intefiqer hunting and there is one (destroyed) scene showing the king Senusret I. The figure of Intefiqer is several times erased. See also * List of Theban tombs The Theban Necropolis is located on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Luxor, in Egypt. As well as the more famous royal tombs located in the Valley of the King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenemhet I
:''See Amenemhat, for other individuals with this name.'' Amenemhat I ( Ancient Egyptian: ''Ỉmn-m-hꜣt'' meaning 'Amun is at the forefront'), also known as Amenemhet I, was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the first king of the Twelfth Dynasty of the Middle Kingdom. Amenemhat I was probably the same as the vizier named Amenemhat who led an expedition to Wadi Hammamat under his predecessor Mentuhotep IV, and possibly overthrew him from power. Scholars differ as to whether Mentuhotep IV was killed by Amenemhat I, but there is no independent evidence to suggest this and there may even have been a period of co-regency between their reigns.E. Hornung, ''History of Ancient Egypt'', 1999 p.50 Amenemhat I was not of royal lineage, born to Senusret and Nefert who were possibly related to the nomarchial family of Elephantine. The composition of some literary works (the ''Prophecy of Neferti'', the ''Instructions of Amenemhat''M. Lichtheim, ''Ancient Egyptian Literature'', 1973 p.135 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vizier (Ancient Egypt)
The vizier () was the highest official in ancient Egypt to serve the pharaoh (king) during the Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms. Vizier is the generally accepted rendering of ancient Egyptian , etc., among Egyptologists. The ''Instruction of Rekhmire'' (''Installation of the Vizier''), a New Kingdom text, defines many of the duties of the , and lays down codes of behavior. The viziers were often appointed by the pharaoh. During the 4th Dynasty and early 5th Dynasty, viziers were exclusively drawn from the royal family; from the period around the reign of Neferirkare Kakai onwards, they were chosen according to loyalty and talent or inherited the position from their fathers. Responsibilities The viziers were appointed by the pharaohs and often belonged to a pharaoh's family. The vizier's paramount duty was to supervise the running of the country, much like a prime minister. At times this included small details such as sampling the city's water supply. All other lesser supervisors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senusret I
Senusret I (Middle Egyptian: z-n-wsrt; /suʀ nij ˈwas.ɾiʔ/) also anglicized as Sesostris I and Senwosret I, was the second pharaoh of the Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt. He ruled from 1971 BC to 1926 BC (1920 BC to 1875 BC), and was one of the most powerful kings of this Dynasty. He was the son of Amenemhat I. Senusret I was known by his prenomen, Kheperkare, which means "the Ka of Re is created." He expanded Egypt that allowed him to rule over an age of prosperity. He continued his father's aggressive expansionist policies against Nubia by initiating two expeditions into this region in his 10th and 18th years and established Egypt's formal southern border near the second cataract where he placed a garrison and a victory stele. He also organized an expedition to a Western Desert oasis. Senusret I established diplomatic relations with some rulers of towns in Syria and Canaan. He also tried to centralize the country's political structure by supporting nomarchs who were loyal t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lisht
Lisht or el-Lisht ( ar, اللشت, translit=Al-Lišt) is an Egyptian village located south of Cairo. It is the site of Middle Kingdom royal and elite burials, including two pyramids built by Amenemhat I and Senusret I. The two main pyramids were surrounded by smaller pyramids of members of the royal family, and many mastaba tombs of high officials and their family members. They were constructed throughout the Twelfth and Thirteenth Dynasties. The site is also known for the tomb of Senebtisi, found undisturbed and from which a set of jewelry has been recovered. The pyramid complex of Senusret I is the best preserved from this period. The coffins in the tomb of Sesenebnef present the earliest versions of the Book of the Dead. Overview The ancient Egyptian site of el-Lisht can be found on the west bank of the Nile River, around 65 km south of the city of Cairo. It is a Twelfth Dynasty necropolis, close to the city of Itj-Tawy from which the modern village assumably (given th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wadi El-Hudi
The Wadi el-Hudi is a wadi in Southern Egypt, in the Eastern Desert. Here were ancient quarries for amethyst. The Wadi el-Hudi is important in archaeology for its high number of rock inscriptions and stelae, mainly dating to the Middle Kingdom, as amethyst was especially popular in this period. The Wadi el-Hudi ends in the Nile valley a few kilometers north of Aswan and is coming there from the South-East. The ancient amethyst quarries are about 20 kilometres south-east from Aswan. Inscriptions The earliest datable inscriptions in the Wadi el-Hudi belong to king Mentuhotep IV who reigned around 2000 BC. in the 11th Dynasty. These are five texts dated to the first year of the king and clearly report the aim of the expedition as bringing amethyst. Further inscriptions date to the 12th Dynasty under king Senusret I. One of them mentions the vizier Intefiqer, another one the high steward Hor. The 12th Dynasty kings Amenemhat II, Senusret III and Amenemhat III are also attested with e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
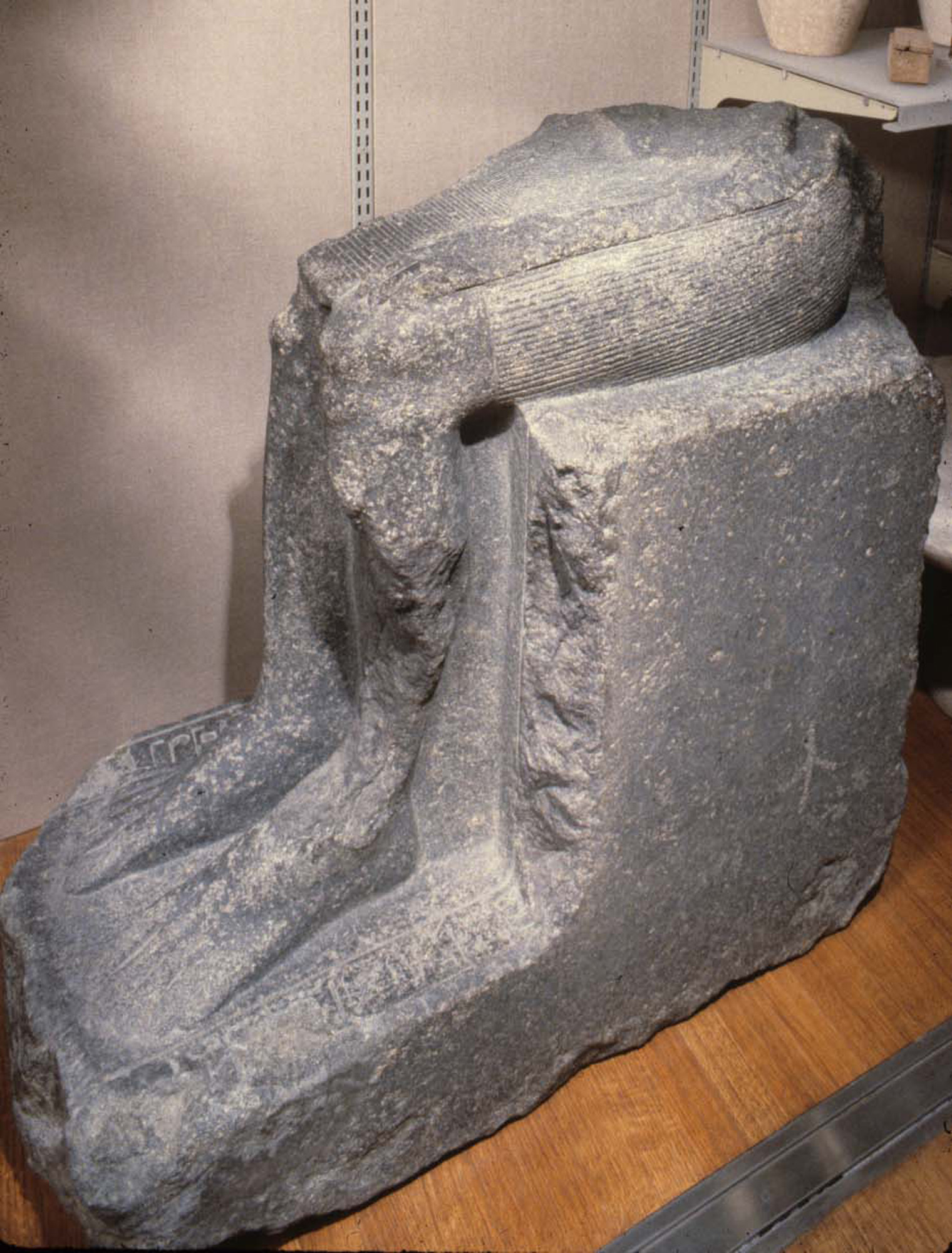
Lower Part Of A Statue Of The Vizier, Intefiqer MET 09
Lower may refer to: *Lower (surname) *Lower Township, New Jersey *Lower Receiver (firearms) *Lower Wick Lower Wick is a small hamlet located in the county of Gloucestershire, England. It is situated about five miles south west of Dursley, eighteen miles southwest of Gloucester and fifteen miles northeast of Bristol. Lower Wick is within the civil ... Gloucestershire, England See also * Nizhny {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luxor
Luxor ( ar, الأقصر, al-ʾuqṣur, lit=the palaces) is a modern city in Upper (southern) Egypt which includes the site of the Ancient Egyptian city of ''Thebes''. Luxor has frequently been characterized as the "world's greatest open-air museum", as the ruins of the Egyptian temple complexes at Karnak and Luxor stand within the modern city. Immediately opposite, across the River Nile, lie the monuments, temples and tombs of the west bank Theban Necropolis, which includes the Valley of the Kings and Valley of the Queens. Thousands of tourists from all around the world arrive annually to visit Luxor's monuments, contributing greatly to the economy of the modern city. The population of Luxor is 422,407 (2021), with an area of approximately . It is the capital of Luxor Governorate. It is among the oldest inhabited cities in the world. Etymology The name ''Luxor'' ( ar, الأقصر, al-ʾuqṣur, lit=the palace, pronounced , , Upper Egyptian: ) derives from the Ara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfram Grajetzki
Wolfram Grajetzki (born 1960, in Berlin) is a German Egyptologist. He studied at Free University of Berlin and made his Doctor of Philosophy at the Humboldt University of Berlin. He performed excavations in Egypt, but also in Pakistan. He published articles and several books on the Egyptian Middle Kingdom The Middle Kingdom of Egypt (also known as The Period of Reunification) is the period in the history of ancient Egypt following a period of political division known as the First Intermediate Period. The Middle Kingdom lasted from approximately ..., on administration, burial customs and queens. He is also a researcher at the Centre for Advanced Spatial Analysis, University College London, UK, working on the project 'Digital Egypt for Universities'. Works *''Two Treasurers of the Late Middle Kingdom'' (British Archaeological Report S1007) Oxford, 2001 ISSN 0143-3067 *''Burial Customs in Ancient Egypt: Life in Death for Rich and Poor'' Duckworth Egyptology, London 2003 *' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastaba
A mastaba (, or ), also mastabah, mastabat or pr- djt (meaning "house of stability", " house of eternity" or "eternal house" in Ancient Egyptian), is a type of ancient Egyptian tomb in the form of a flat-roofed, rectangular structure with inward sloping sides, constructed out of mudbricks. These edifices marked the burial sites of many eminent Egyptians during Egypt's Early Dynastic Period and Old Kingdom. In the Old Kingdom epoch, local kings began to be buried in Egyptian pyramids, pyramids instead of in mastabas, although non-royal use of mastabas continued for over a thousand years. Egyptologists call these tombs ''mastaba'', from the Arabic word (maṣṭaba) "stone bench". History The Ancient Egyptian afterlife beliefs, afterlife was important in the Ancient Egyptian religion, religion of ancient Egyptians. Ancient Egyptian architecture, Their architecture reflects this, most prominently by the enormous amounts of time and labour involved in building tombs. Ancient Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amethyst
Amethyst is a violet variety of quartz. The name comes from the Koine Greek αμέθυστος ''amethystos'' from α- ''a-'', "not" and μεθύσκω (Ancient Greek) / μεθώ (Modern Greek), "intoxicate", a reference to the belief that the stone protected its owner from drunkenness. Ancient Greeks wore amethyst and carved drinking vessels from it in the belief that it would prevent intoxication. Amethyst, a semiprecious stone, is often used in jewelry and is the traditional birthstone for February. Structure Amethyst is a purple variety of quartz (SiO2) and owes its violet color to irradiation, impurities of iron and in some cases other transition metals, and the presence of other trace elements, which result in complex crystal lattice substitutions.Michael O'Donoghue (2006), ''Gems'', Butterworth-Heinemann, 6th ed. The hardness of the mineral is the same as quartz, thus making it suitable for use in jewelry. Hue and tone Amethyst occurs in primary hues from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
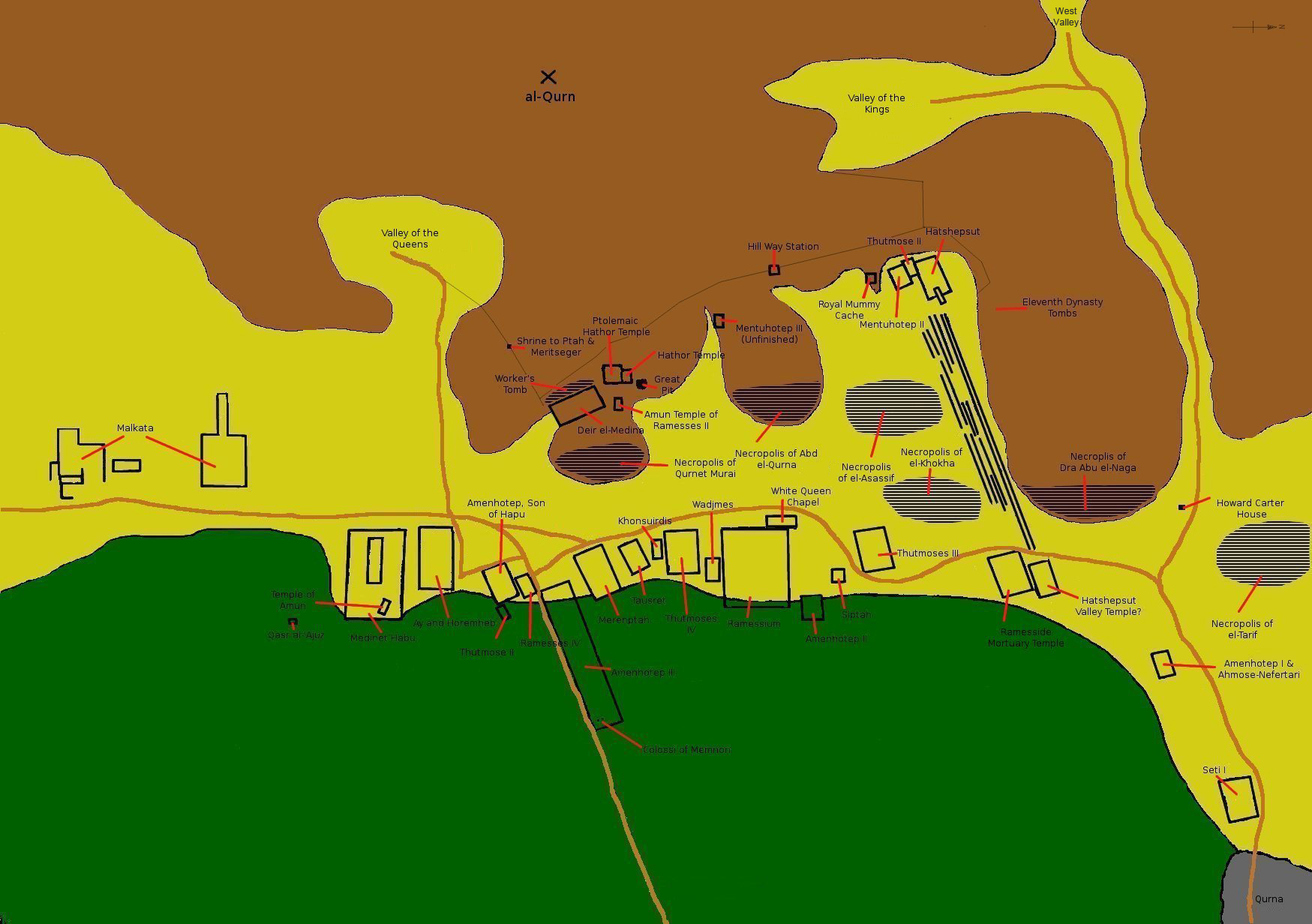
Theban Necropolis
The Theban Necropolis is a necropolis on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Thebes (Luxor) in Upper Egypt. It was used for ritual burials for much of the Pharaonic period, especially during the New Kingdom. Mortuary temples * Deir el-Bahri ** Mortuary temple of Hatshepsut ** Mortuary temple of Mentuhotep II ** Mortuary temple of Thutmose III * Medinet Habu ** Mortuary temple and palace of Ramesses III ** Mortuary Temple of Ay & Horemheb * Mortuary Temple of Amenhotep III ** Colossi of Memnon * Mortuary Temple of Merneptah * Mortuary Temple of Ramesses IV * Mortuary Temple of Thutmose IV * Mortuary Temple of Thutmose III * Mortuary Temple of Twosret * Temple of Nebwenenef * Qurna ** Mortuary Temple of Seti I * Mortuary Temple of Amenhotep II * Ramesseum (Mortuary Temple of Ramesses II) Royal Necropolis * Valley of the Kings (Modern: "''Wadi el-Muluk''") * Valley of the Queens (Modern: "''Biban el-Harim''") * Royal Cache * Bab el-Gasus Necropolis * Deir el-Medina ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_-_TIMEA.jpg)