|
Injector
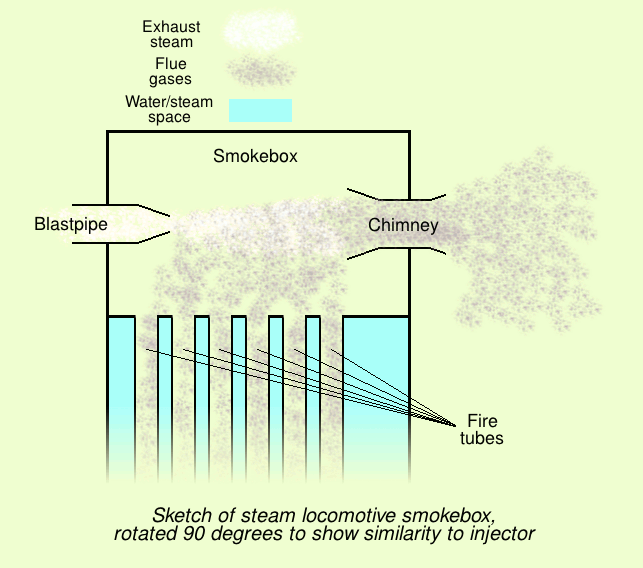
An injector is a system of ducting and nozzles used to direct the flow of a high-pressure fluid in such a way that a lower pressure fluid is entrained in the jet and carried through a duct to a region of higher pressure. It is a fluid-dynamic pump with no moving parts except a valve to control inlet flow. A steam injector is a typical application of the principle used to deliver cold water to a boiler against its own pressure, using its own live or exhaust steam, replacing any mechanical pump. When first developed, its operation was intriguing because it seemed paradoxical, almost like perpetual motion, but it was later explained using thermodynamics. Other types of injector may use other pressurised motive fluids such as air. Depending on the application, an injector can also take the form of an ''eductor-jet pump'', a '' water eductor'' or an ''aspirator''. An '' ejector'' operates on similar principles to create a vacuum feed connection for braking systems etc. History T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Injector Giffard-02
An injector is a system of ducting and nozzles used to direct the flow of a high-pressure fluid in such a way that a lower pressure fluid is entrained in the jet and carried through a duct to a region of higher pressure. It is a fluid-dynamic pump with no moving parts except a valve to control inlet flow. A steam injector is a typical application of the principle used to deliver cold water to a boiler against its own pressure, using its own live or exhaust steam, replacing any mechanical pump. When first developed, its operation was intriguing because it seemed paradoxical, almost like perpetual motion, but it was later explained using thermodynamics. Other types of injector may use other pressurised motive fluids such as air. Depending on the application, an injector can also take the form of an ''eductor-jet pump'', a ''water eductor'' or an ''aspirator''. An ''ejector'' operates on similar principles to create a vacuum feed connection for braking systems etc. History The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ejector Or Injector
An injector is a system of ducting and nozzles used to direct the flow of a high-pressure fluid in such a way that a lower pressure fluid is entrained in the jet and carried through a duct to a region of higher pressure. It is a fluid-dynamic pump with no moving parts except a valve to control inlet flow. A steam injector is a typical application of the principle used to deliver cold water to a boiler against its own pressure, using its own live or exhaust steam, replacing any mechanical pump. When first developed, its operation was intriguing because it seemed paradoxical, almost like perpetual motion, but it was later explained using thermodynamics. Other types of injector may use other pressurised motive fluids such as air. Depending on the application, an injector can also take the form of an ''eductor-jet pump'', a '' water eductor'' or an ''aspirator''. An ''ejector'' operates on similar principles to create a vacuum feed connection for braking systems etc. History The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Ejector
A vacuum ejector, or simply ejector is a type of vacuum pump, which produces vacuum by means of the Venturi effect. In an ejector, a working fluid (liquid or gaseous) flows through a jet nozzle into a tube that first narrows and then expands in cross-sectional area. The fluid leaving the jet is flowing at a high velocity which due to Bernoulli's principle results in it having low pressure, thus generating a vacuum. The outer tube then narrows into a mixing section where the high velocity working fluid mixes with the fluid that is drawn in by the vacuum, imparting enough velocity for it to be ejected, the tube then typically expands in order to decrease the velocity of the ejected stream, allowing the pressure to smoothly increase to the external pressure. The strength of the vacuum produced depends on the velocity and shape of the fluid jet and the shape of the constriction and mixing sections, but if a liquid is used as the working fluid the strength of the vacuum produced is l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
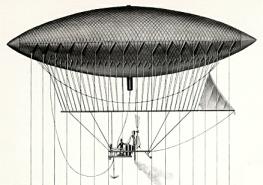
Henri Giffard
Baptiste Jules Henri Jacques Giffard (8 February 182514 April 1882) was a French engineer. In 1852 he invented the steam injector and the powered Giffard dirigible airship. Career Giffard was born in Paris in 1825. He invented the injector and the Giffard dirigible, an airship powered with a steam engine and weighing over 180 kg (400 lb). It was the world's first passenger-carrying airship (then known as a dirigible, from French). Both practical and steerable, the hydrogen-filled airship was equipped with a 3 hp steam engine that drove a propeller. The engine was fitted with a downward-pointing funnel. The exhaust steam was mixed in with the combustion gases and it was hoped by these means to stop sparks rising up to the gas bag; he also installed a vertical rudder. On 24 September 1852, Giffard made the first powered and controlled flight travelling 27 km from Paris to Élancourt. The wind was too strong to allow him to make way against it, so he was un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venturi Effect
The Venturi effect is the reduction in fluid pressure that results when a fluid flows through a constricted section (or choke) of a pipe. The Venturi effect is named after its discoverer, the 18th century Italian physicist, Giovanni Battista Venturi. Background In inviscid fluid dynamics, an incompressible fluid's velocity must ''increase'' as it passes through a constriction in accord with the principle of mass continuity, while its static pressure must ''decrease'' in accord with the principle of conservation of mechanical energy ( Bernoulli's principle). Thus, any gain in kinetic energy a fluid may attain by its increased velocity through a constriction is balanced by a drop in pressure. By measuring pressure, the flow rate can be determined, as in various flow measurement devices such as Venturi meters, Venturi nozzles and orifice plates. Referring to the adjacent diagram, using Bernoulli's equation in the special case of steady, incompressible, inviscid flows (suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1913 Ais Gill Rail Accident
The Ais Gill rail accident occurred on the Settle–Carlisle line in Northwest England on 2 September 1913. Two long trains were both ascending a steep gradient with some difficulty, because their engines generated barely enough power to carry the load. When the first train stopped to build-up steam pressure, the driver and fireman of the second train were distracted by maintenance routines, and failed to observe the warning signals. The collision wrecked several carriages, which were then engulfed by flammable gas, killing 16 people and injuring 38. Incident The two trains involved were both passenger trains, which had left Carlisle railway station in the early hours of 2 September, destined for St Pancras station. The Midland Railway, which owned and operated the Settle-Carlisle line, had a policy of using small engines, and the two locomotives had barely sufficient power to surmount the steep gradients on the line with the heavy trains they were assigned. In theory, the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Brake
A railway brake is a type of brake used on the cars of railway trains to enable deceleration, control acceleration (downhill) or to keep them immobile when parked. While the basic principle is similar to that on road vehicle usage, operational features are more complex because of the need to control multiple linked carriages and to be effective on vehicles left without a prime mover. Clasp brakes are one type of brakes historically used on trains. Early days In the earliest days of railways, braking technology was primitive. The first trains had brakes operative on the locomotive tender and on vehicles in the train, where "porters" or, in the United States brakemen, travelling for the purpose on those vehicles operated the brakes. Some railways fitted a special deep-noted brake whistle to locomotives to indicate to the porters the necessity to apply the brakes. All the brakes at this stage of development were applied by operation of a screw and linkage to brake blocks applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomotive's boiler to the point where it becomes gaseous and its volume increases 1,700 times. Functionally, it is a steam engine on wheels. In most locomotives, the steam is admitted alternately to each end of its cylinders, in which pistons are mechanically connected to the locomotive's main wheels. Fuel and water supplies are usually carried with the locomotive, either on the locomotive itself or in a tender coupled to it. Variations in this general design include electrically-powered boilers, turbines in place of pistons, and using steam generated externally. Steam locomotives were first developed in the United Kingdom during the early 19th century and used for railway transport until the middle of the 20th century. Richard Trevithi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Pacific 4294
Southern Pacific 4294 is a class " AC-12" 4-8-8-2 Cab forward type steam locomotive that was owned and operated by the Southern Pacific Railroad (SP). It was built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in March 1944 and was used hauling SP's trains over the Sierra Nevada, often working on Donner Pass in California. Today it is preserved at the California State Railroad Museum (CSRM) in Sacramento, California. History No. 4294 was the last of 20 Southern Pacific class AC-12 4-8-8-2 cab forward locomotives in a larger series of 256 Southern Pacific articulated cab forwards starting with class AC-1. Articulated locomotives are essentially two locomotives sharing fire box, boiler and crew. The front locomotive has its cranks quartered 90 degrees apart. The front and rear drive axles are free to roll out of phase with respect to each other. If unloaded, the locomotive has a vertical oscillation, near 50 mph, that can lift the tires above the rails. Its most distinguishing featur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulation Of Railways Act 1889
The Regulation of Railways Act 1889 (52 & 53 Vict c 57) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It is one of the Railway Regulation Acts 1840 to 1893.The Short Titles Act 1896 The Short Titles Act 1896 (59 & 60 Vict c 14) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It replaces the Short Titles Act 1892. This Act was retained for the Republic of Ireland by section 2(2)(a) of, and Part 4 of Schedule 1 to, the St ..., section 2(1) and Schedule 2 It was enacted following the Armagh rail disaster. Safety It empowered the Board of Trade to require any railway company to: * adopt the block system of signalling on any passenger railway; * provide for the interlocking of points and signals on such railways; * provide for and use on all passenger trains continuous brakes; the brakes must be instantaneous in action; self applying in the event of any failure in continuity; capable of being applied to every vehicle of the train; and in regular use in daily working. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crosshead
In mechanical engineering, a crosshead is a mechanical joint used as part of the slider-crank linkages of long reciprocating engines (either internal combustion or steam) and reciprocating compressors to eliminate sideways force on the piston. Also, the crosshead enables the connecting rod to freely move outside the cylinder. Because of the very small bore-to- stroke ratio on such engines, the connecting rod would hit the cylinder walls and block the engine from rotating if the piston was attached directly to the connecting rod like on trunk engines. Therefore, the longitudinal dimension of the crosshead must be matched to the stroke of the engine. Overview On smaller engines, the connecting rod links the piston and the crankshaft directly, but this transmits sideways forces to the piston, since the crankpin (and thus the direction the force is applied) moves from side to side with the rotary motion of the crank. These transverse forces are tolerable in a smaller engine. A l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |