|
Indeo
Indeo Video (commonly known now simply as "Indeo") is a family of audio and video formats and codecs first released in 1992, and designed for real-time video playback on desktop CPUs. While its original version was related to Intel's DVI video stream format, a hardware-only codec for the compression of television-quality video onto compact discs, Indeo was distinguished by being one of the first codecs allowing full-speed video playback without using hardware acceleration. Also unlike Cinepak and TrueMotion S, the compression used the same Y'CbCr 4:2:0 colorspace as the ITU's H.261 and ISO's MPEG-1. Indeo use was free of charge to allow for broadest usage. History During the development of what became the P5 Pentium microprocessor, the Intel Architecture Labs implemented one of the first, and at the time highest-quality, software-only video codecs, which was marketed as "Indeo Video". It has been developed since the 1980s based on the hardware-only Digital Video Interactive (DV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Video Interactive
Digital Video Interactive (DVI) was the first multimedia desktop video standard for IBM-compatible personal computers. It enabled full-screen, full motion video, as well as stereo audio, still images, and graphics to be presented on a DOS-based desktop computer using a special compression chipset. The scope of Digital Video Interactive encompasses a file format, including a digital container format, a number of video and audio compression formats, as well as hardware associated with the file format. History Development of DVI was started around 1984 by Section 17 of The David Sarnoff Research Center Labs (DSRC) then responsible for the research and development activities of RCA. When General Electric purchased RCA in 1986, GE considered the DSRC redundant with its own labs, and sought a buyer. In 1988, GE sold the DSRC to SRI International, but sold the DVI technology separately to Intel corporation. DVI technology allowed full-screen, full motion digital video, as well as st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel Architecture Labs
__NOTOC__ Intel Architecture Labs (IAL) was the personal-computer system research-and-development arm of Intel during the 1990s. History and formation IAL was created by Intel Vice-president Ron Whittier together with Craig Kinnie and Steven McGeady to develop the hardware and software innovations considered to be lacking from PC OEMs and Microsoft in the late 1980s and 1990s. IAL pursued both hardware and software initiatives, both of which were important factors in the evolution of, and the control of, the PC industry. Rivalry with Microsoft Around the same time in the PC industry, Microsoft was emerging as the de facto industry standard in PC Operating Systems and software application for the PC. As IAL's software ambitions began to overlap with Microsoft's, a rivalry broke out between Intel and Microsoft as it related to the amount of influence, control, and the setting of standards in the rapidly growing PC industry. Over time, IAL's work in software projects was gradu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video For Windows
Video for Windows was a suite of video playing and editing software introduced by Microsoft in 1992. A runtime version for viewing videos only was made available as a free add-on to Windows 3.1, which then became an integral component of Windows 95. Video for Windows was mostly replaced by the July 1996 release of ActiveMovie, later known as DirectShow. Apple filed a lawsuit in 1994 alleging theft of several thousand lines of QuickTime source code to improve the software. The case was settled in 1997, when Apple agreed to make Internet Explorer the default browser over Netscape, and in exchange, Microsoft agreed to continue developing Microsoft Office and other software for Mac OS for the next 5 years, and purchase $150 million of non-voting Apple stock. Overview Video for Windows was first introduced in November 1992. It was developed as a reaction to Apple Computer's QuickTime technology, which added digital video to the Macintosh platform. Costing around $200, the product includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Quantization
Vector quantization (VQ) is a classical quantization technique from signal processing that allows the modeling of probability density functions by the distribution of prototype vectors. It was originally used for data compression. It works by dividing a large set of points (vectors) into groups having approximately the same number of points closest to them. Each group is represented by its centroid point, as in k-means and some other clustering algorithms. The density matching property of vector quantization is powerful, especially for identifying the density of large and high-dimensional data. Since data points are represented by the index of their closest centroid, commonly occurring data have low error, and rare data high error. This is why VQ is suitable for lossy data compression. It can also be used for lossy data correction and density estimation. Vector quantization is based on the competitive learning paradigm, so it is closely related to the self-organizing map model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audio Video Interleave
Audio Video Interleave (also Audio Video Interleaved and known by its initials and filename extension AVI, usually pronounced ), is a proprietary multimedia container format and Windows standard introduced by Microsoft in November 1992 as part of its Video for Windows software. AVI files can contain both audio and video data in a file container that allows synchronous audio-with-video playback. Like the DVD video format, AVI files support multiple streaming audio and video, although these features are seldom used. Many AVI files use the file format extensions developed by the Matrox OpenDML group in February 1996. These files are supported by Microsoft, and are unofficially called "AVI 2.0". In 2010 the US government's National Archives and Records Administration defined AVI as the official wrapper for preserving digital video. History Publishers faced a predicament regarding how they should distribute videos on CD-ROMs. Thirty seconds of video displayed in 24-bit color an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinepak
Cinepak is a lossy video codec developed by Peter Barrett at SuperMac Technologies, and released in 1991 with the Video Spigot, and then in 1992 as part of Apple Computer's QuickTime video suite. One of the first video compression tools to achieve full motion video on CD-ROM, it was designed to encode 320×240 resolution video at 1× (150 kbyte/s) CD-ROM transfer rates. The original name of this codec was Compact Video, which is why its FourCC identifier is CVID. The codec was ported to Microsoft Windows in 1993. It was also used on fourth- and fifth-generation game consoles, such as the Atari Jaguar CD, Sega CD, Sega Saturn, and 3DO. libavcodec includes a Cinepak decoder and an encoder, both licensed under the terms of the LGPL. History It was the primary video codec of early versions of QuickTime and Microsoft Video for Windows, but was later superseded by Sorenson Video, Intel Indeo, and most recently MPEG-4 Part 2 and H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. However, movies compressed with Ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TrueMotion S
On2 Technologies, formerly known as The Duck Corporation, was a small publicly traded company (on the American Stock Exchange), founded in New York City in 1992 and headquartered in Clifton Park, New York, that designed video codec technology. It created a series of video codecs called TrueMotion (including TrueMotion S, TrueMotion 2, TrueMotion RT 2.0, TrueMotion VP3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8). In February 2010, On2 Technologies was acquired by Google for an estimated $124.6 million. On2's VP8 technology became the core of Google's WebM video file format. History While known by the name ''The Duck Corporation'', they developed TrueMotion S, a codec that was used by some games for full motion video (FMV) sequences during the 1990s. The original office of the Duck Corporation was founded in New York City by Daniel B. Miller, Victor Yurkovsky, and Stan Marder. In 1994 Duck opened its first "satellite" engineering office in Colonie, NY under the management of Eric Ameres. Miller b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel I750
The Intel i750 is a two-chip graphics processing unit composed of the 82750PB pixel processor and 82750DB display processor. The i750 chip was used in video capture/compression cards such as the Intel Smart Video Recorder and Creative Labs Video Blaster RT300. These cards were needed to allow Video for Windows to record footage from a video camera. Although Intel had made earlier chips targeting graphics (e.g., 82786 graphics coprocessor), this was seen as Intel's first attempt to break into the video controller marketplace. The effort was a failure and led to Intel leaving the market for some time. The Indeo video compressor was originally built to work with the i750, but was later ported to other systems as well. Technical Details 82750PB The 82750PB pixel processor is packaged in a 132-pin PQFP running at 25 MHz. It contains 57 instruction set, eight entries 64 bit vector registers (same MM0~MM7 register naming as used on the x86, the only difference being that i750 h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 80386
The Intel 386, originally released as 80386 and later renamed i386, is a 32-bit microprocessor introduced in 1985. The first versions had 275,000 transistorsmit.edu—The Future of FPGAs (Cornell) October 11, 2012 and were the CPU of many s and high-end s of the time. As the original implementation of the |
Intel 80486
The Intel 486, officially named i486 and also known as 80486, is a microprocessor. It is a higher-performance follow-up to the Intel 386. The i486 was introduced in 1989. It represents the fourth generation of binary compatible CPUs following the 8086 of 1978, the Intel 80286 of 1982, and 1985's i386. It was the first tightly- pipelined x86 design as well as the first x86 chip to include more than one million transistors. It offered a large on-chip cache and an integrated floating-point unit. A typical 50 MHz i486 executes around 40 million instructions per second (MIPS), reaching 50 MIPS peak performance. It is approximately twice as fast as the i386 or i286 per clock cycle. The i486's improved performance is thanks to its five-stage pipeline with all stages bound to a single cycle. The enhanced FPU unit on the chip was significantly faster than the i387 FPU per cycle. The intel 80387 FPU ("i387") was a separate, optional math coprocessor that was installed in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
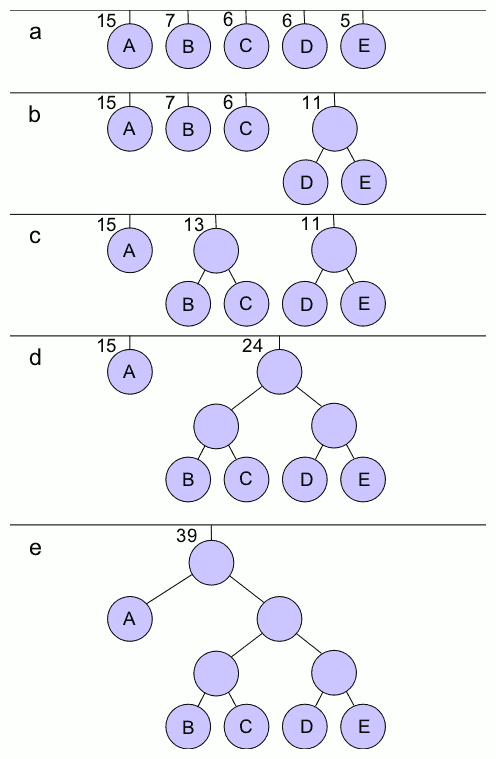
Huffman Coding
In computer science and information theory, a Huffman code is a particular type of optimal prefix code that is commonly used for lossless data compression. The process of finding or using such a code proceeds by means of Huffman coding, an algorithm developed by David A. Huffman while he was a Sc.D. student at MIT, and published in the 1952 paper "A Method for the Construction of Minimum-Redundancy Codes". The output from Huffman's algorithm can be viewed as a variable-length code table for encoding a source symbol (such as a character in a file). The algorithm derives this table from the estimated probability or frequency of occurrence (''weight'') for each possible value of the source symbol. As in other entropy encoding methods, more common symbols are generally represented using fewer bits than less common symbols. Huffman's method can be efficiently implemented, finding a code in time linear to the number of input weights if these weights are sorted. However, although opt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG-1
MPEG-1 is a standard for lossy compression of video and audio. It is designed to compress VHS-quality raw digital video and CD audio down to about 1.5 Mbit/s (26:1 and 6:1 compression ratios respectively) without excessive quality loss, making video CDs, digital cable/satellite TV and digital audio broadcasting (DAB) practical. Today, MPEG-1 has become the most widely compatible lossy audio/video format in the world, and is used in a large number of products and technologies. Perhaps the best-known part of the MPEG-1 standard is the first version of the MP3 audio format it introduced. The MPEG-1 standard is published as ISO/IEC 11172 – Information technology—Coding of moving pictures and associated audio for digital storage media at up to about 1.5 Mbit/s. The standard consists of the following five ''Parts'': #Systems (storage and synchronization of video, audio, and other data together) #Video (compressed video content) #Audio (compressed audio content) #Conformance tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |