|
Immigration To Japan
According to the Japanese Ministry of Justice, the number of foreign residents in Japan has steadily increased in the post Second World War period, and the number of foreign residents (excluding illegal immigrants and short-term foreign visitors and tourists staying more than 90 days in Japan) was more than 2.76 million at the end of 2021. With an estimated population of 125.57 million in 2020, the resident foreign population in Japan amounts to approximately 2.29% of the total population. History Due to geographic remoteness and periods of self-imposed isolation, the immigration, cultural assimilation and integration of foreign nationals into mainstream Japanese society has been comparatively limited. Historian Yukiko Koshiro has identified three historically significant waves of immigration prior to 1945; the 8th-century settlement of Korean artists and intellectuals; the asylum offered to a small number of Chinese families in the 1600s; and the forced immigration of up to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Japan
The Government of Japan consists of legislative, executive and judiciary branches and is based on popular sovereignty. The Government runs under the framework established by the Constitution of Japan, adopted in 1947. It is a unitary state, containing forty-seven administrative divisions, with the Emperor as its Head of State. His role is ceremonial and he has no powers related to Government. Instead, it is the Cabinet, comprising the Ministers of State and the Prime Minister, that directs and controls the Government and the civil service. The Cabinet has the executive power and is formed by the Prime Minister, who is the Head of Government. The Prime Minister is nominated by the National Diet and appointed to office by the Emperor. The National Diet is the legislature, the organ of the Legislative branch. It is bicameral, consisting of two houses with the House of Councilors being the upper house, and the House of Representatives being the lower house. Its members ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
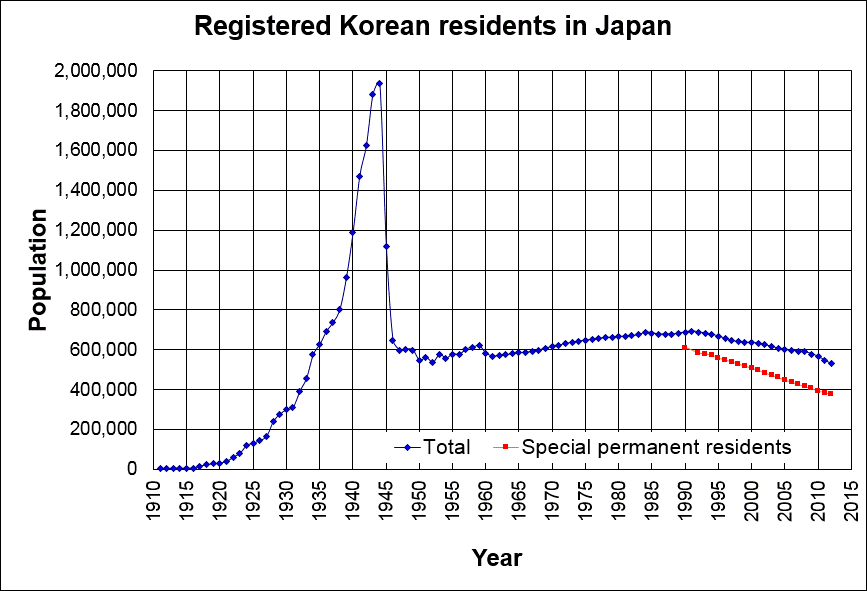
Zainichi
comprise ethnic Koreans who have permanent residency status in Japan or who have become Japanese citizens, and whose immigration to Japan originated before 1945, or who are descendants of those immigrants. They are a group distinct from South Korean nationals who have emigrated to Japan after the end of World War II and the division of Korea. They currently constitute the second largest ethnic minority group in Japan after Chinese immigrants, due to many Koreans assimilating into the general Japanese population. The majority of Koreans in Japan are , often known simply as , who are ethnic Korean permanent residents of Japan. The term Zainichi Korean refers only to long-term Korean residents of Japan who trace their roots to Korea under Japanese rule, distinguishing them from the later wave of Korean migrants who came mostly in the 1980s, and from pre-modern immigrants dating back to antiquity who may themselves be the ancestors of the Japanese people. The Japanese word "Zainic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Census In The United Kingdom
Coincident full censuses have taken place in the different jurisdictions of the United Kingdom every ten years since 1801, with the exceptions of 1941 (during the Second World War), Ireland in 1921/Northern Ireland in 1931,https://www.nisra.gov.uk/sites/nisra.gov.uk/files/publications/1926-census-preliminary-report.PDF and Scotland in 2021. In addition to providing detailed information about national demographics, the results of the census play an important part in the calculation of resource allocation to regional and local service providers by the UK government. The most recent UK census took place in England, Wales and Northern Ireland on 21 March 2021. Because of the COVID-19 pandemic, the census in Scotland was delayed to 20 March 2022. History Tax assessments (known in the later Empire as the indiction) were made in Britain in Roman times, but detailed records have not survived. In the 7th century AD, Dál Riata (parts of what is now Scotland and Northern Ireland) co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nationality
Nationality is a legal identification of a person in international law, establishing the person as a subject, a ''national'', of a sovereign state. It affords the state jurisdiction over the person and affords the person the protection of the state against other states. Article 15 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights states that "Everyone has the right to a nationality", and "No one shall be arbitrarily deprived of his nationality nor denied the right to change his nationality". By international custom and conventions, it is the right of each state to determine who its nationals are. Such determinations are part of nationality law. In some cases, determinations of nationality are also governed by public international law—for example, by treaties on statelessness and the European Convention on Nationality. The rights and duties of nationals vary from state to state,Weis, Paul''Nationality and Statelessness in International Law''. BRILL; 1979 ited 19 August 2012 . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnicity (other)
Ethnicity is the common characteristics of a group of people. Ethnicity may also refer to: * Ethnicity (United States Census), ethnicity as defined by the US census * Ethnicity (United Kingdom), ethnicity in the United Kingdom * Mono-ethnicity, singular ethnic identity * Metro-ethnicity, one of more recent concepts in ethnic studies * Symbolic ethnicity, symbolic attachment to a particular ethnicity * Supra-ethnicity, designation for several complex phenomena, "above" the level of basic ethnicity: ** Poly-ethnicity, pluralistic ethnic identity ** Pan-ethnicity, a particular concept in ethnic studies ** Meta-ethnicity, one of more recent concepts in ethnic studies * ''Ethnicities'' (journal), an academic journal * ''Ethnicity'' (album), an album by Yanni See also * Ethnicity theory * Ethnic studies Ethnic studies, in the United States, is the interdisciplinary study of difference—chiefly race, ethnicity, and nation, but also sexuality, gender, and other such marking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Race (human Categorization)
A race is a categorization of humans based on shared physical or social qualities into groups generally viewed as distinct within a given society. The term came into common usage during the 1500s, when it was used to refer to groups of various kinds, including those characterized by close kinship relations. By the 17th century, the term began to refer to physical ( phenotypical) traits, and then later to national affiliations. Modern science regards race as a social construct, an identity which is assigned based on rules made by society. While partly based on physical similarities within groups, race does not have an inherent physical or biological meaning. The concept of race is foundational to racism, the belief that humans can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. Social conceptions and groupings of races have varied over time, often involving folk taxonomies that define essential types of individuals based on perceived traits. Today, scientists co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Group
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, society, culture, nation, religion, or social treatment within their residing area. The term ethnicity is often times used interchangeably with the term nation, particularly in cases of ethnic nationalism, and is separate from the related concept of races. Ethnicity may be construed as an inherited or as a societally imposed construct. Ethnic membership tends to be defined by a shared cultural heritage, ancestry, origin myth, history, homeland, language, or dialect, symbolic systems such as religion, mythology and ritual, cuisine, dressing style, art, or physical appearance. Ethnic groups may share a narrow or broad spectrum of genetic ancestry, depending on group identification, with many groups having mixed genetic ancestry. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Permanent Resident (Japan)
A is a resident of Japan with ancestry usually related to its former colonies, Korea or Taiwan, specifically when those countries were under Japanese colonial rule. They had been subjects of the Empire of Japan, but had involuntarily lost that status after the war when the Treaty of San Francisco took effect in 1952 (i.e. former citizens of Japan and their descendants). Korean residents of Japan, known as Zainichi Koreans, were permitted to naturalise and become Japanese citizens, but many hesitated to do so given anti-Korean prejudice in Japan. In accordance with the law that took effect in Japan in November 1991, Zainichi Koreans gained Special Permanent Resident status. Although Special Permanent Residents are unable to vote in Japanese elections, they are usually afforded additional rights and privileges beyond those of normal Permanent Residents comparable to a citizen. For example, Special Permanent Residents are not subject to immigration control under Article 5 of thImmig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sadako Ogata
, was a Japanese academic, diplomat, author, administrator, and professor emerita at the Roman Catholic Sophia University. She was widely known as the head of the office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) from 1991 to 2000, as well as in her capacities as Chair of the UNICEF Executive Board from 1978 to 1979 and as President of the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) from 2003 to 2012. She also served as Advisor of the Executive Committee of the Japan Model United Nations (JMUN). Early and academic life She was born on 16 September 1927 to a career diplomat father Toyoichi Nakamura (who became in 1943 the Japanese ambassador to Finland) and her original name was Sadako Nakamura. Her mother was a daughter of Foreign Minister Kenkichi Yoshizawa and granddaughter of Prime Minister Inukai Tsuyoshi, who was assassinated when she was four years old, due to his opposition to Japanese militarism, whose assassination marked the end of civilian contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNHCR
The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) is a United Nations agency mandated to aid and protect refugees, forcibly displaced communities, and stateless people, and to assist in their voluntary repatriation, local integration or resettlement to a third country. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, with over 17,300 staff working in 135 countries. Background UNHCR was created in 1950 to address the refugee crisis that resulted from World War II. The 1951 Refugee Convention established the scope and legal framework of the agency's work, which initially focused on Europeans uprooted by the war. Beginning in the late 1950s, displacement caused by other conflicts, from the Hungarian Uprising to the decolonization of Africa and Asia, broadened the scope of UNHCR's operations. Commensurate with the 1967 Protocol to the Refugee Convention, which expanded the geographic and temporal scope of refugee assistance, UNHCR operated across the world, with the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refugee
A refugee, conventionally speaking, is a displaced person who has crossed national borders and who cannot or is unwilling to return home due to well-founded fear of persecution.FAQ: Who is a refugee? ''www.unhcr.org'', accessed 22 June 2021 Such a person may be called an asylum seeker until granted refugee status by the contracting state or the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protocol Relating To The Status Of Refugees
The Protocol Relating to the Status of Refugees is a key treaty in international refugee law. It entered into force on 4 October 1967, and 146 countries are parties. The 1951 United Nations Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees restricted refugee status to those whose circumstances had come about "as a result of events occurring before 1 January 1951", as well as giving states party to the convention the option of interpreting this as "events occurring in Europe" or "events occurring in Europe or elsewhere". The 1967 Protocol removed both the temporal and geographic restrictions. This was needed in the historical context of refugee flows resulting from decolonisation. Madagascar and Saint Kitts and Nevis are parties only to the convention, while Cape Verde, the United States of America and Venezuela are parties only to the protocol. The protocol gave those states which had previously ratified the 1951 Convention and chosen to use the definition restricted to Europe th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |