|
Imbert-Fick Law
Armand Imbert (1850-1922) and Adolf Fick (1829-1901) both demonstrated, independently of each other, that in ocular tonometry the tension of the wall can be neutralized when the application of the tonometer produces a flat surface instead of a convex one, and the reading of the tonometer (P) then equals (T) the IOP," whence all forces cancel each other. This principle was used by Hans Goldmann (1899–1991) who referred to it as the Imbert-Fick "law", thus giving his newly marketed tonometer (with the help of the Haag-Streit Company) a quasi-scientific basis; it is mentioned in the ophthalmic and optometric literature, but not in any books of physics. According to Goldmann, "The law states that the pressure in a sphere filled with liquid and surrounded by an infinitely thin membrane is measured by the counterpressure which just flattens the membrane." "The law presupposes that the membrane is without thickness and without rigidity...practically without any extensibility." A sphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Eugen Fick
Adolf Eugen Fick (3 September 1829 – 21 August 1901) was a German-born physician and physiologist. Early life and education Fick began his work in the formal study of mathematics and physics before realising an aptitude for medicine. He then earned his doctorate in medicine from the University of Marburg in 1851. As a fresh medical graduate, he began his work as a prosector.The Virtual Laboratory: Fick, Adolf Eugen accessed 5 February 2006 He died in at age 71. Career In 1855, he introduced |
Ocular Tonometry
Tonometry is the procedure eye care professionals perform to determine the intraocular pressure (IOP), the fluid pressure inside the eye. It is an important test in the evaluation of patients at risk from glaucoma. Most tonometers are calibrated to measure pressure in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg), with the normal eye pressure range between . Methods Applanation tonometry In applanation tonometry the intraocular pressure (IOP) is inferred from the force required to flatten (applanate) a constant area of the cornea, for the Imbert-Fick law. The Maklakoff tonometer was an early example of this method, while the Goldmann tonometer is the most widely used version in current practice. Because the probe makes contact with the cornea, a topical anesthetic, such as proxymetacaine, is introduced on to the surface of the eye in the form of an eye drop. Goldmann tonometry Goldmann tonometry is considered to be the gold standard IOP test and is the most widely accepted method. A spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency training specific to that field. This may include a one-year integrated internship that involves more general medical training in other fields such as internal medicine or general surgery. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care - medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training and many include research as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optometry
Optometry is a specialized health care profession that involves examining the eyes and related structures for defects or abnormalities. Optometrists are health care professionals who typically provide comprehensive primary eye care. In the United States and Canada, optometrists are those that hold a Doctor of Optometry degree. They are trained and licensed to practice medicine for eye related conditions, in addition to providing refractive (optical) eye care. In the United Kingdom, optometrists may also practice medicine (and provide refractive care) for eye related conditions. The Doctor of Optometry title can also be used in the UK for those that hold the postgraduate O.D. degree. Within their scope of practice, optometrists are considered physicians and bill medical insurance(s) (example: Medicare) accordingly. Moreover, many participate in academic research for eye related conditions and disease. Optometrists are the only health care professionals with a first professional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Membrane
A biological membrane, biomembrane or cell membrane is a selectively permeable membrane that separates the interior of a cell from the external environment or creates intracellular compartments by serving as a boundary between one part of the cell and another. Biological membranes, in the form of eukaryotic cell membranes, consist of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded, integral and peripheral proteins used in communication and transportation of chemicals and ions. The bulk of lipids in a cell membrane provides a fluid matrix for proteins to rotate and laterally diffuse for physiological functioning. Proteins are adapted to high membrane fluidity environment of the lipid bilayer with the presence of an annular lipid shell, consisting of lipid molecules bound tightly to the surface of integral membrane proteins. The cell membranes are different from the isolating tissues formed by layers of cells, such as mucous membranes, basement membranes, and serous membranes. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stiffness
Stiffness is the extent to which an object resists deformation in response to an applied force. The complementary concept is flexibility or pliability: the more flexible an object is, the less stiff it is. Calculations The stiffness, k, of a body is a measure of the resistance offered by an elastic body to deformation. For an elastic body with a single degree of freedom (DOF) (for example, stretching or compression of a rod), the stiffness is defined as k = \frac where, * F is the force on the body * \delta is the displacement produced by the force along the same degree of freedom (for instance, the change in length of a stretched spring) In the International System of Units, stiffness is typically measured in newtons per meter (N/m). In Imperial units, stiffness is typically measured in pounds (lbs) per inch. Generally speaking, deflections (or motions) of an infinitesimal element (which is viewed as a point) in an elastic body can occur along multiple DOF (maximum of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere
A sphere () is a Geometry, geometrical object that is a solid geometry, three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the Locus (mathematics), set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the centre (geometry), centre of the sphere, and is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the Greek mathematics, ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental object in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubble (physics), Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. spherical Earth, The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres rolling, roll smoothly in any direction, so mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incompressible
In fluid mechanics or more generally continuum mechanics, incompressible flow ( isochoric flow) refers to a flow in which the material density is constant within a fluid parcel—an infinitesimal volume that moves with the flow velocity. An equivalent statement that implies incompressibility is that the divergence of the flow velocity is zero (see the derivation below, which illustrates why these conditions are equivalent). Incompressible flow does not imply that the fluid itself is incompressible. It is shown in the derivation below that (under the right conditions) even compressible fluids can – to a good approximation – be modelled as an incompressible flow. Incompressible flow implies that the density remains constant within a parcel of fluid that moves with the flow velocity. Derivation The fundamental requirement for incompressible flow is that the density, \rho , is constant within a small element volume, ''dV'', which moves at the flow velocity u. Mathemat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
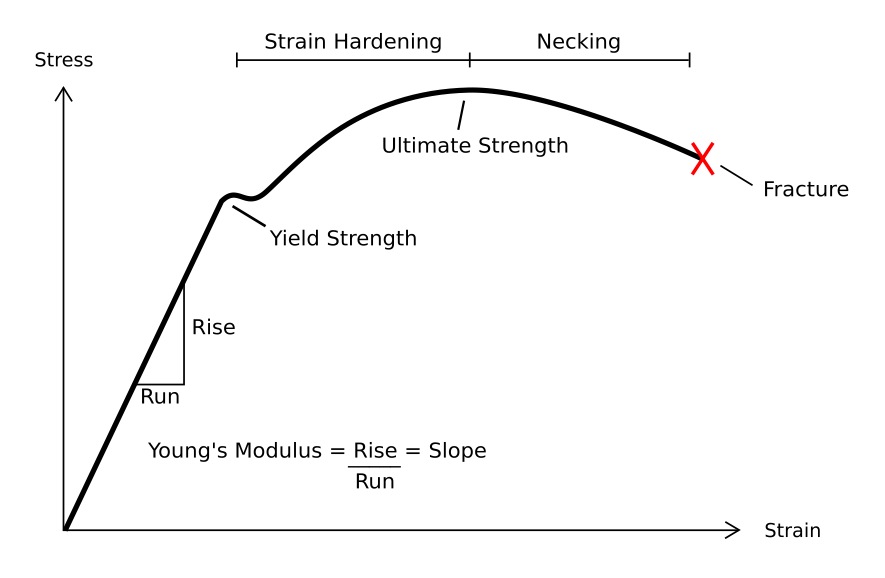
Deformation (engineering)
In engineering, deformation refers to the change in size or shape of an object. ''Displacements'' are the ''absolute'' change in position of a point on the object. Deflection is the relative change in external displacements on an object. Strain is the ''relative'' internal change in shape of an infinitesimally small cube of material and can be expressed as a non-dimensional change in length or angle of distortion of the cube. Strains are related to the forces acting on the cube, which are known as stress, by a stress-strain curve. The relationship between stress and strain is generally linear and reversible up until the yield point and the deformation is elastic. The linear relationship for a material is known as Young's modulus. Above the yield point, some degree of permanent distortion remains after unloading and is termed plastic deformation. The determination of the stress and strain throughout a solid object is given by the field of strength of materials and for a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Area
The surface area of a solid object is a measure of the total area that the surface of the object occupies. The mathematical definition of surface area in the presence of curved surfaces is considerably more involved than the definition of arc length of one-dimensional curves, or of the surface area for polyhedra (i.e., objects with flat polygonal faces), for which the surface area is the sum of the areas of its faces. Smooth surfaces, such as a sphere, are assigned surface area using their representation as parametric surfaces. This definition of surface area is based on methods of infinitesimal calculus and involves partial derivatives and double integration. A general definition of surface area was sought by Henri Lebesgue and Hermann Minkowski at the turn of the twentieth century. Their work led to the development of geometric measure theory, which studies various notions of surface area for irregular objects of any dimension. An important example is the Minkows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |