|
Ilienses Proprii
The Ilienses (or ''Iolaes'', later known as ''Diagesbes''Strabo, Geographica V, 2,7.) were an ancient Nuragic people who lived during the Bronze and Iron Ages in central-southern Sardinia, as well as one of the three major groups among which the ancient Sardinians considered themselves divided (along with the Corsi and the Balares). After the Sicilian Wars began with the Punic invasion in the sixth century BC, part of them retreated to the mountainous interior of the island, from which they opposed for centuries the foreign rule. History Mythological origins According to the legend recorded by Greek historians, the etymology of their name (Iolaes) is to be traced back to Iolaus, the hero who led the ''Thespiades'', sons of Heracles and the daughters of Thespius (king of the Boeotian city-state of Thespiae) in Sardinia, where he founded a colony. Another myth tell that the old inhabitants of Ilium, better known as Troy, after the fall of the city established themselves in this part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see things at great distance as if they were nearby was also called "Strabo". (; el, Στράβων ''Strábōn''; 64 or 63 BC 24 AD) was a Greek geographer, philosopher, and historian who lived in Asia Minor during the transitional period of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. Life Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus (in present-day Turkey) in around 64BC. His family had been involved in politics since at least the reign of Mithridates V. Strabo was related to Dorylaeus on his mother's side. Several other family members, including his paternal grandfather had served Mithridates VI during the Mithridatic Wars. As the war drew to a close, Strabo's grandfather had turned several Pontic fortress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troy
Troy ( el, Τροία and Latin: Troia, Hittite language, Hittite: 𒋫𒊒𒄿𒊭 ''Truwiša'') or Ilion ( el, Ίλιον and Latin: Ilium, Hittite language, Hittite: 𒃾𒇻𒊭 ''Wiluša'') was an ancient city located at Hisarlik in present-day Turkey, south-west of Çanakkale and about miles east of the Aegean Sea. It is known as the setting for the Greek mythology, Greek myth of the Trojan War. In Ancient Greek literature, Troy is portrayed as a powerful kingdom of the Greek Heroic Age, Heroic Age, a mythic era when monsters roamed the earth and gods interacted directly with humans. The city was said to have ruled the Troad until the Trojan War led to its complete destruction at the hands of the Greeks. The story of its destruction was one of the cornerstones of Greek mythology and literature, featuring prominently in the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', and referenced in numerous other poems and plays. Its legacy played a large role in Greek society, with many prominent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barumini
Barumini ( sc, Barùmini) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of South Sardinia in the Italian region of Sardinia, located about north of Cagliari and about northeast of Sanluri. Barumini borders the following municipalities: Gergei, Gesturi, Las Plassas, Tuili, Villanovafranca. It is home to Su Nuraxi di Barumini, a Nuraghe complex listed in the UNESCO World Heritage Sites A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h .... Pictures File:ChiesaVergineImmacolataBarumini-pjt.jpg, Parochial church of the "Vergine Immacolata“ File:BaruminiPalazzoZapata-pjt2.jpg, Palazzo Zapata File:BaruminiPalazzoZapata-pjt1.jpg, Palazzo Zapata File:BaruminiSanGiovanniBatista-pjt.jpg, San Giovanni Batista References External links Official website Barumini Sistema Cultura Found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Su Nuraxi
Su Nuraxi is a nuraghe, nuragic archaeological site in Barumini, Sardinia, Italy. ''Su Nuraxi'' simply means "The Nuraghe" in Campidanese dialect, Campidanese, the southern variant of the Sardinian language. Su Nuraxi is a settlement consisting of a seventeenth century BC Nuraghe, a bastion of four corner towers plus a central one, and a village inhabited from the thirteenth to the sixth century BC, developed around the Nuraghe. They are considered by scholars the most impressive expression of the Nuragic civilization and were included in the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites in 1997 as ''Su Nuraxi di Barumini''. Nuraghe Structure The oldest part of the Nuraghe consists of a central tower with three superposed chambers (18.6m high). It was built in blocks of basalt between the seventeenth and thirteenth centuries BCE. Later, during the Late Bronze Age, four towers joined by a curtain wall with an upper balcony (no longer extant) were built around the central tower, all co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuraghi
The nuraghe (, ; plural: Logudorese dialect, Logudorese Sardinian , Campidanese dialect, Campidanese Sardinian , Italian language, Italian ), or also nurhag in English language, English, is the main type of ancient megalithic edifice found in Sardinia, developed during the History of Sardinia#Nuragic period, Nuragic Age between 1900 and 730 B.C. Today it has come to be the symbol of Sardinia and its distinctive culture known as the Nuragic civilization. More than 7,000 nuraghes have been found, though archeologists believe that originally there were more than 10,000. Etymology According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' the etymology is "uncertain and disputed": "The word is perhaps related to the Sardinian place names ''Nurra'', ''Nurri'', ''Nurru'', and to Sardinian ''nurra'' 'heap of stones, cavity in earth' (although these senses are difficult to reconcile). A connection with the Semitic base of Arabic ''nūr'' 'light, fire, etc.' is now generally rejected." The La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tirso River , the most important river of Sardinia
;Ships
*, a tugboat
{{disambig ...
Tirso is Spanish and Portuguese for Thyrsus, and usually refers to the saint of that name (Saint Thyrsus) (San Tirso, Santo Tirso). It can also refer to: People * Tirso Cruz III (born 1952), Filipino actor * Tirso de Molina (1579-1648), Spanish playwright, poet and friar Places *Ula Tirso, commune of Sardinia *Santo Tirso, city in Portugal *Santo Tirso parish, municipality in Portugal *San Tirso de Abres, municipality in Asturias Geography *Tirso (river) The Tirso ( sc, Tirsu, Latin ''Thyrsus'') is a river, the most important of the island of Sardinia (Italy). It rises from the plateau of Buddusò, on the slopes of the Punta Pianedda at an elevation of and crosses the island from east to west, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campidano
Campidano ( sc, Campidànu) is a plain located in South-Western Sardinia (Italy), covering approximately 100 kilometres between Cagliari and Oristano. Geography Geologically, it is a graben, a tectonic structure formed in the mid-Pliocene/early Pleistocene (4 to 2 million years ago). Later it was subject to large sedimentary deposition phenomena, creating an overall thickness of 600 m of sediments. The plain is crossed by the Tirso River, the longest in Sardinia. History Agriculture has been successful in Campidano since the Neolithic, continuing on through the Punic and the Romans, who cultivated here grains and grape. Dams of the large Sardinian rivers nourish the artichoke and wheat cultures, also typical products of this zone. Paddy fields are present near Oristano. The Sardinians from this area, and by extension all the people inhabiting the lowlands of Southern Sardinia, are called Campidanese ( sc, Campidanesus, it, Campidanesi). See also *Province of South Sard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iberian Language
The Iberian language was the language of an indigenous western European people identified by Greek and Roman sources who lived in the eastern and southeastern regions of the Iberian Peninsula in the pre-Migration Era (before about 375 AD). The ancient Iberians can be identified as a rather nebulous local culture between the 7th and 1st century BC. The Iberian language, like all the other Paleohispanic languages except Basque, became extinct by the 1st to 2nd centuries AD, after being gradually replaced by Latin due to the Roman conquest of the Iberian Peninsula. Iberian is unclassified: while the scripts used to write it have been deciphered to various extents, the language itself remains largely unknown. Links with other languages have been suggested, especially the Basque language, based largely on the observed similarities between the numerical systems of the two. In contrast, the Punic language of Carthaginian settlers was Semitic, while Indo-European languages of the pen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eduardo Blasco Ferrer
Eduardo Blasco Ferrer (Barcelona, 1956 – Bastia, 12 January 2017) was a Spanish-Italian linguist and a professor at the University of Cagliari, Sardinia Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label=Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after .... He is best known as the author of several studies about the Paleo-Sardinian and Sardinian language. Books *''Grammatica storica del catalano e dei suoi dialetti con speciale riguardo all'algherese.'' Tübingen: G. Narr, c1984. *''La lingua sarda contemporanea : grammatica del logudorese e del campidanese : norma e varietà dell'uso : sintesi storica''. Cagliari : Della Torre, c1986. *''Storia linguistica della Sardegna.'' Tübingen : Niemeyer, 1984. *''Le parlate dell'alta Ogliastra : analisi dialettologica : saggio di storia linguistica e culturale.'' Cagliari : Edizioni Del ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
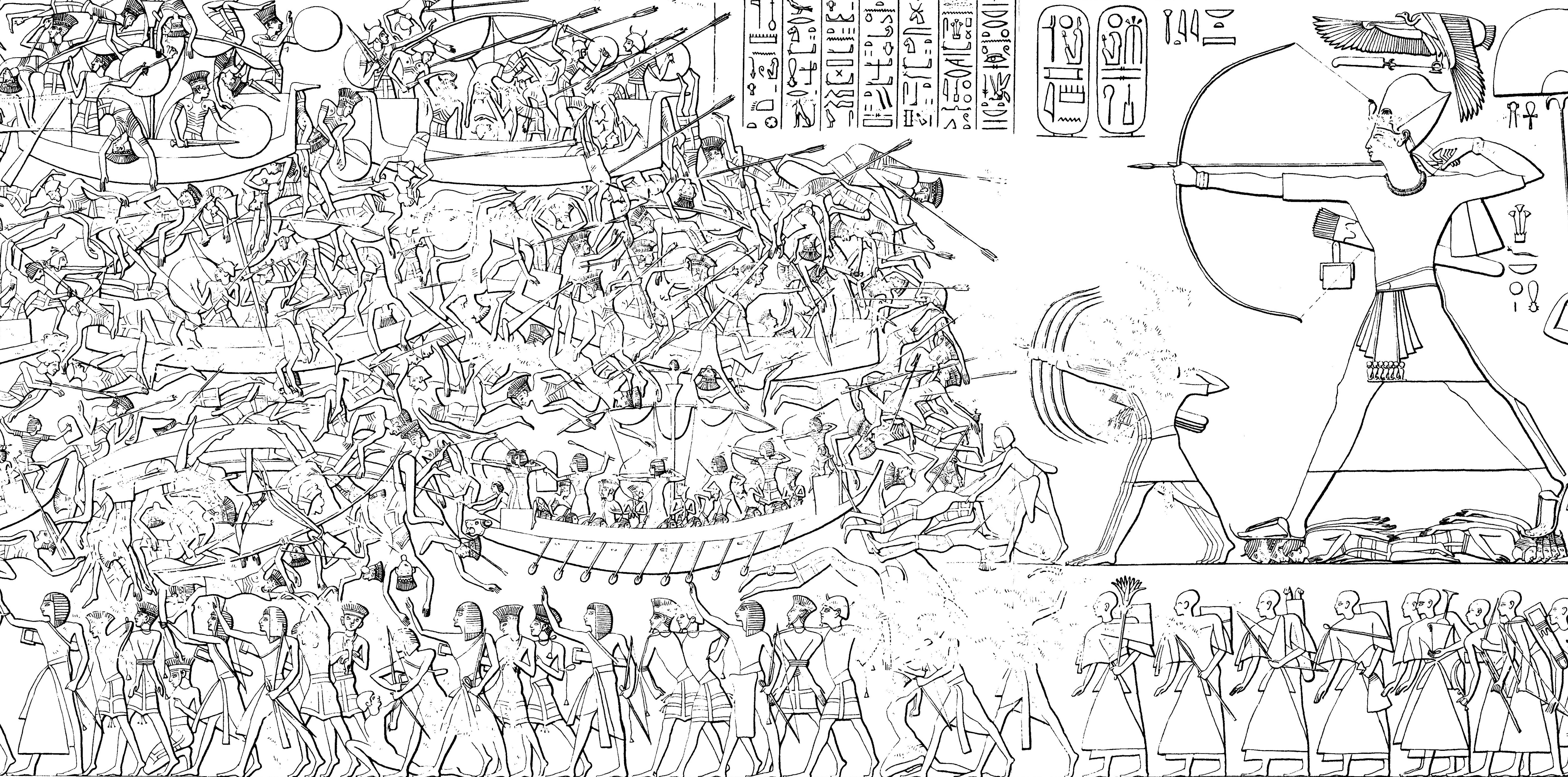
Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples are a hypothesized seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions in the East Mediterranean prior to and during the Late Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BCE).. Quote: "First coined in 1881 by the French Egyptologist G. Maspero (1896), the somewhat misleading term 'Sea Peoples' encompasses the ethnonyms Lukka, Sherden, Shekelesh, Teresh, Eqwesh, Denyen, Sikil / Tjekker, Weshesh, and Peleset (Philistines). [Footnote: The modern term 'Sea Peoples' refers to peoples that appear in several New Kingdom Egyptian texts as originating from 'islands' (tables 1–2; Adams and Cohen, this volume; see, e.g., Drews 1993, 57 for a summary). The use of quotation marks in association with the term 'Sea Peoples' in our title is intended to draw attention to the problematic nature of this commonly used term. It is noteworthy that the designation 'of the sea' appears only in relation to the Sherden, Shekelesh and Eqwesh. Subsequently, this term was applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sherden
The Sherden (Egyptian: ''šrdn'', ''šꜣrdꜣnꜣ'' or ''šꜣrdynꜣ'', Ugaritic: ''šrdnn(m)'' and ''trtn(m)'', possibly Akkadian: ''še-er-ta-an-nu''; also glossed “Shardana” or “Sherdanu”) are one of the several ethnic groups the Sea Peoples were said to be composed of, appearing in fragmentary historical and iconographic records ( ancient Egyptian and Ugaritic) from the Eastern Mediterranean in the late 2nd millennium BC. On reliefs, they are shown carrying round shields and spears, dirks or swords, perhaps of Naue II type. In some cases, they are shown wearing corslets and kilts, but their key distinguishing feature is a horned helmet, which, in all cases but three, features a circular accouterment at the crest. At Medinet Habu the corslet appears similar to that worn by the Philistines. The Sherden sword, it has been suggested by archaeologists since James Henry Breasted, may have developed from an enlargement of European daggers and been associated with the expl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |